First unveiled by Israel Aerospace Industries’ (IAI) in April 2019, OPAL is designed to allow warfighters to respond effectively to combat threats characterized by Time Critical Targets (TCT), and forces that operate both in conjunction with other units and in remote areas, away from C2 coverage, according to Barak Israel, Product Line Manager.
According to Israel, military forces have been hampered by the combat platform’s inability to directly communicate with each other, this limitation is evident in the lack of connectivity that existed between fourth and fifth-generation fighter jets. “Modern warfare is very dynamic. If you don’t respond immediately, the threat won’t be there,” Israel stated.
Information Sharing
The need to share information among various forces and the critical requirement of militaries to see the same picture and speak the same language was the driving force behind OPAL’s development. “If you see something that I can’t see – I want to see what you’re seeing. Not through verbal descriptions, but through image and video sharing or data set transmissions. My physical location isn’t relevant for this to happen,” Israel stated.
Military forces have been struggling with the need to acquire sensor to shooter cycles that deliver sufficient information in time. Traditional solutions for combat needs moved slowly. OPAL introduced a focused and affordable solution to share actionable information in a very short timeframe. The end result, Israel said, is significantly enhanced lethality and survivability for customers, as well as savings on life cycle costs and time.
We took the Android concept and brought it to network-centric warfare
OPAL creates networking connectivity and enables data sharing among all members of a fighting force, irrespective of whether they are airborne, naval or land-based. It uses software-defined radios and any existing data links to share large amounts of real-time data, in line with operational needs, enabling end-users to take swift and relevant actions.
One of the unique capabilities in the OPAL networking layer is that it provides realtime communications. Unlike traditional datalinks that provide update rates of several seconds, OPAL operates in milliseconds, as it employs a real-time network that has been used to prevent mid-air collisions between fighter jets flying in close formations.
Developed over the past 15 years using open architecture, OPAL allows customers to program their own applications to match operational needs after the initial infrastructure is delivered by IAI.
Apps for the Strike Force
According to Eyal Yogev, Project Manager, Conversions and Upgrades Division at Aviation Group at IAI, the system is inspired by Android-like architecture, which all relies on common infrastructure, instead of the traditional military systems that rely on dedicated hardware running specific and unique software. “We took the Android concept and brought it to network-centric warfare (NCW). OPAL can be installed on any platform – aircraft, helicopters, UAVs, ground forces and ships. It supports any operational capability though this infrastructure, making it shareable by the network members, similar to how smartphone applications function,” he said.
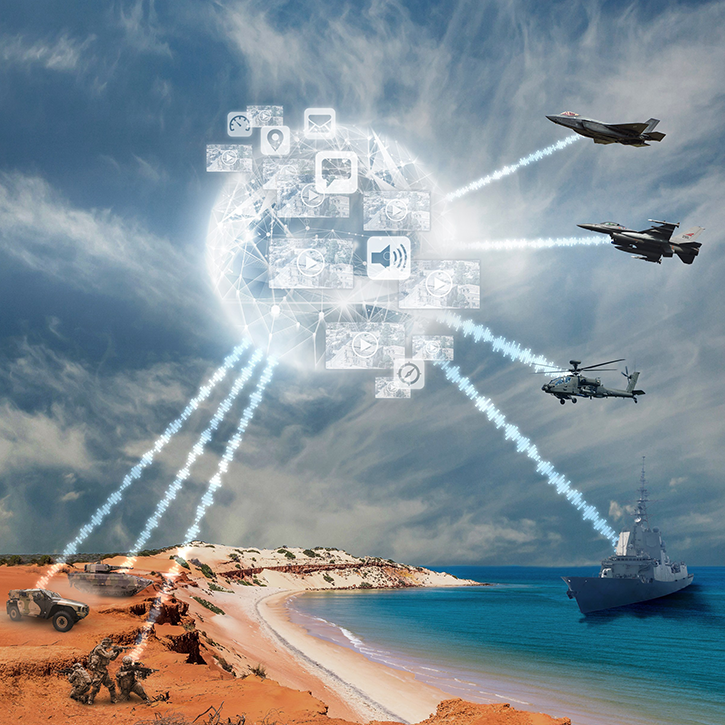 OPAL is comprised of a range of different hardware Line Replaceable Units (LRU) configures and optimized for each application, platform or end-user. This solution delivers an advanced application middleware with optimized applications and, where needed, advanced networking and connectivity services. OPAL features high processing and graphic capabilities, and deliver essential battlefield services to the participating members, enabling all users to share a common operating picture in real-time and to communicate in the same language.
OPAL is comprised of a range of different hardware Line Replaceable Units (LRU) configures and optimized for each application, platform or end-user. This solution delivers an advanced application middleware with optimized applications and, where needed, advanced networking and connectivity services. OPAL features high processing and graphic capabilities, and deliver essential battlefield services to the participating members, enabling all users to share a common operating picture in real-time and to communicate in the same language.
In terms of operational doctrine, an important advantage OPAL provides is introducing new capabilities in a very short time
The ability to share accurate real-time data among the different elements of the fighting forces significantly improves the efficiency and survivability of the different members, within the formation and among other forces, such as supporting elements, air and ground forces. “The implications for close air support, for example, are major,” Israel stated. “This represents a new and transformative capability for the military.”
OPAL shares local data over selected radio links with other users, ensuring that information is transported across network nodes in real-time, regardless of range, location, terrain obstacles, weather conditions, or the operational condition.
A Network Linking All Generations
OPAL provides customers with a high degree of operational independence. Customers have the option of ordering IAI’s radio systems and datalinks as a part of the OPAL battle management system or acquiring OPAL while utilizing existing communications and datalink networks. Moreover, customers can employ operational capabilities developed by the manufacturer, or develop their own applications, relying on OPAL’s inherent application infrastructure.
“In terms of operational doctrine, an important advantage OPAL provides is introducing new capabilities in a very short time,” said Israel “Once the system is installed, clients are independent. We transfer the relevant capabilities and tools so that users can develop their own capabilities.”
OPAL is proven and operational on jets, training aircraft, refuels, helicopters, mission aircraft, command and control centers, and ships as well as other platforms.
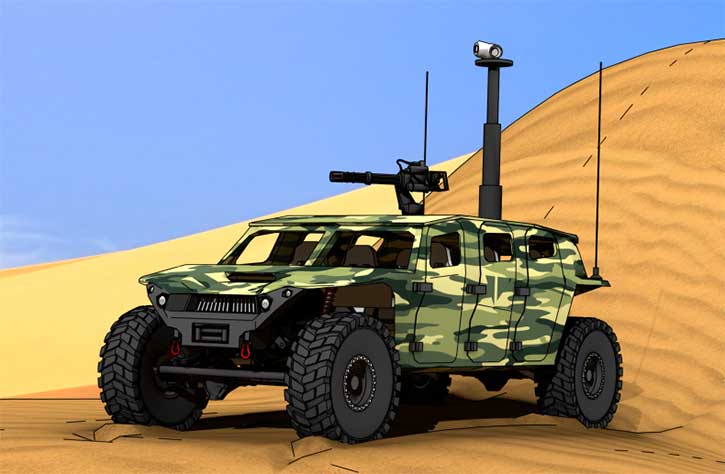
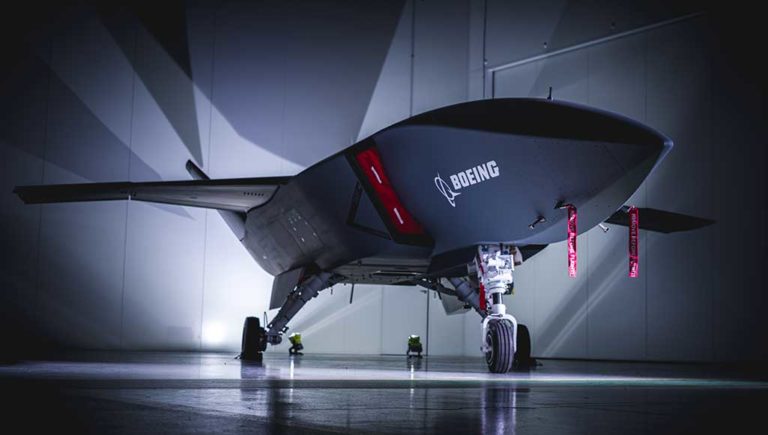
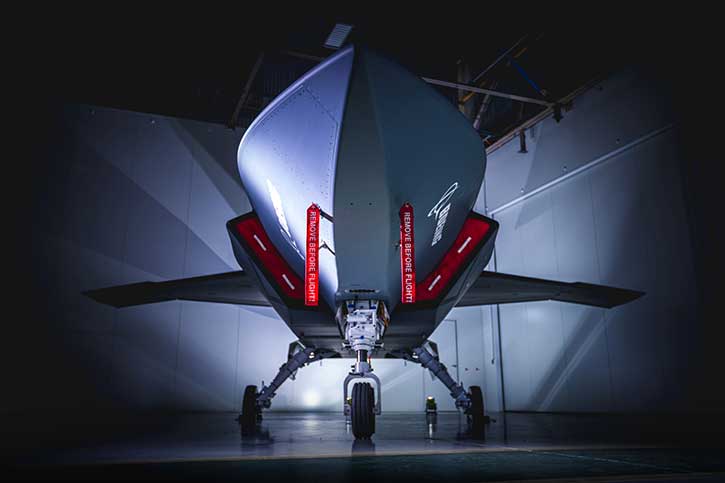
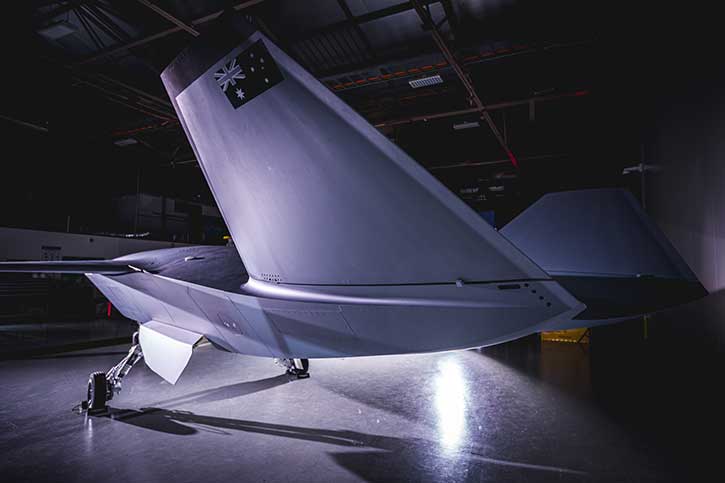
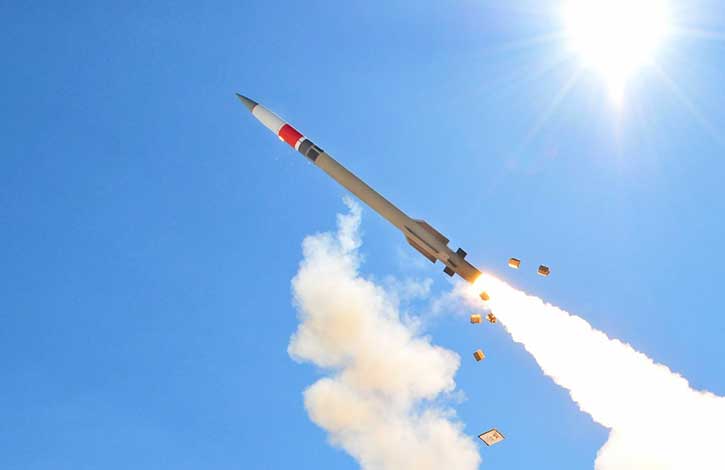
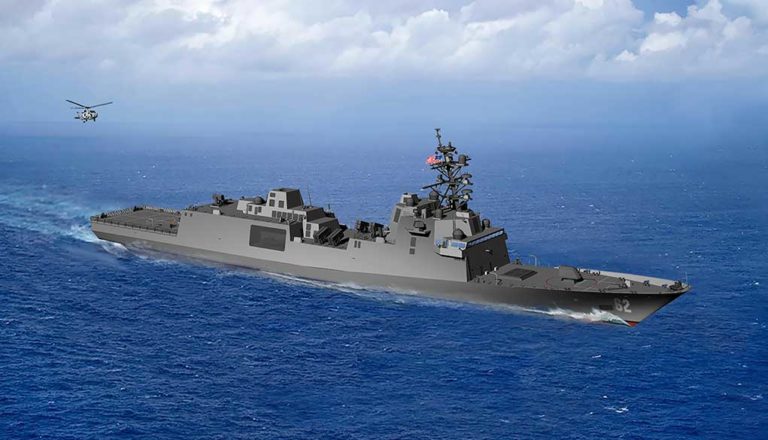
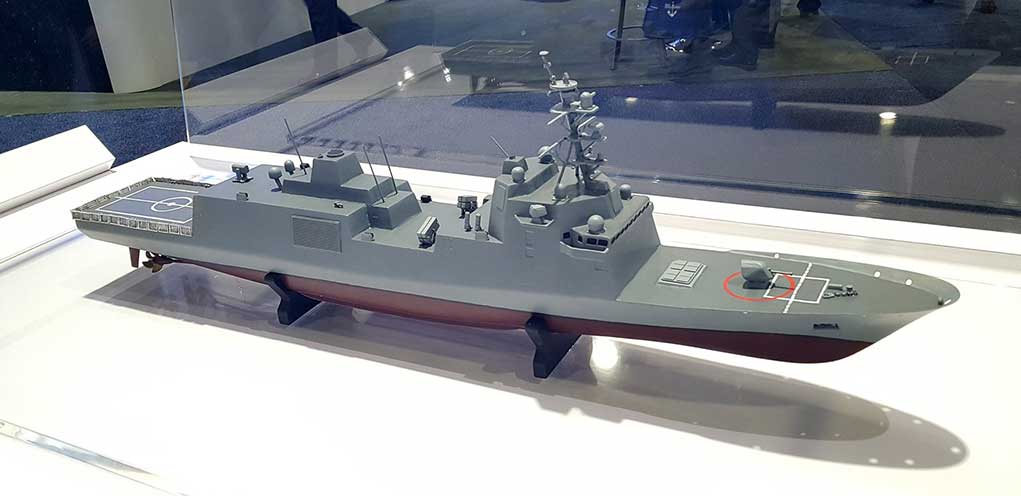
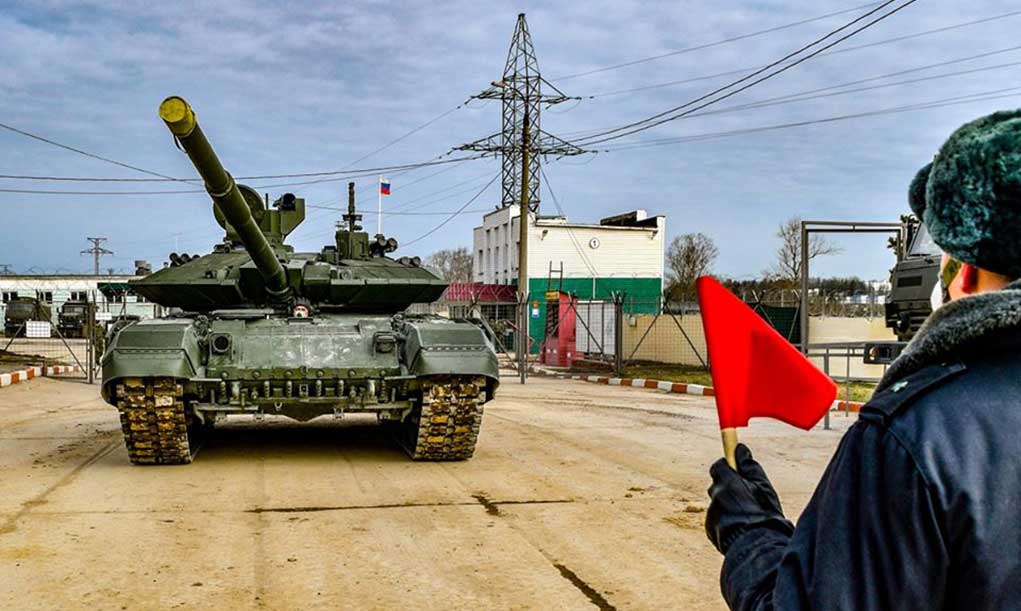
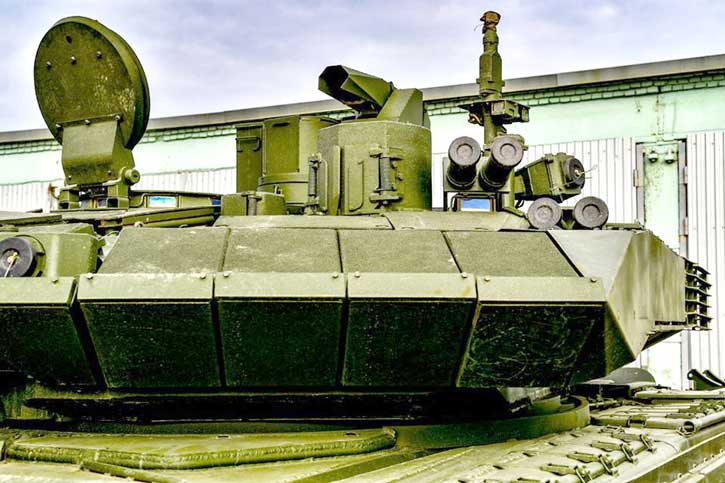
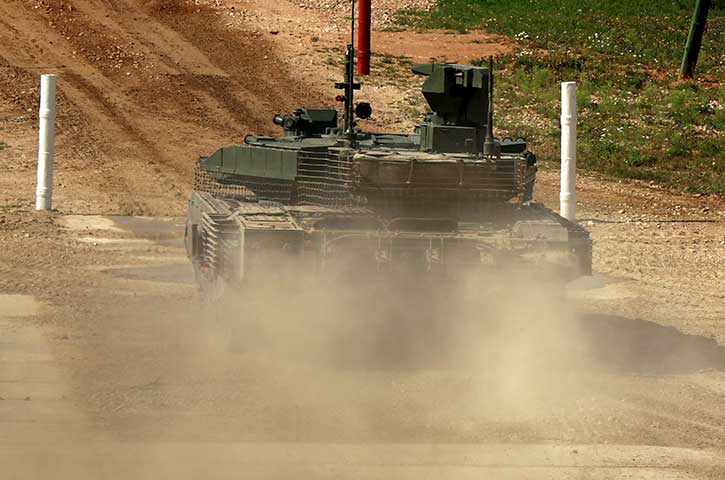
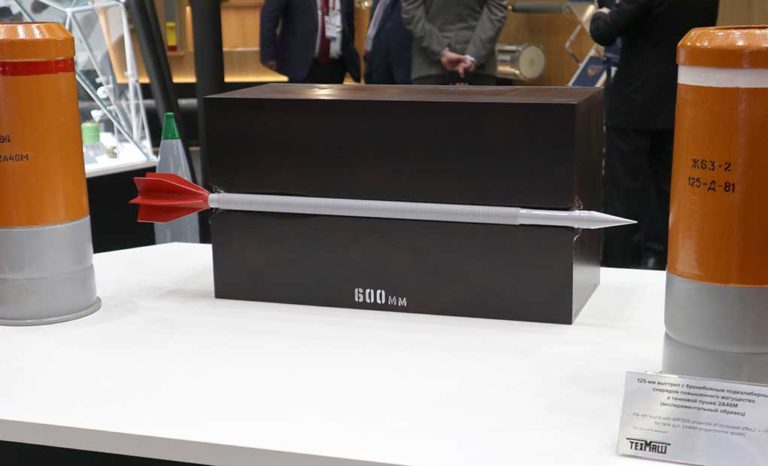
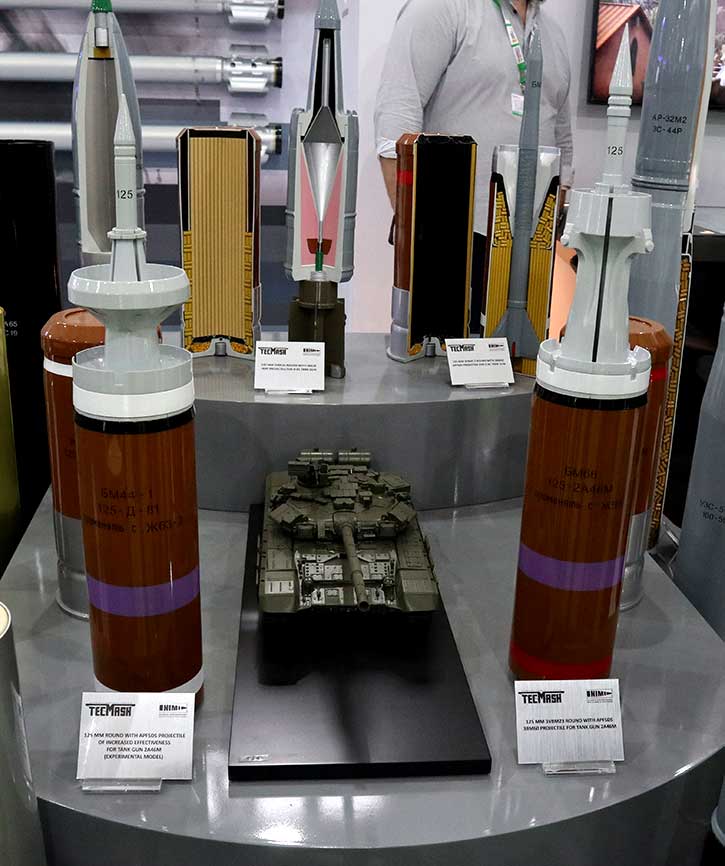
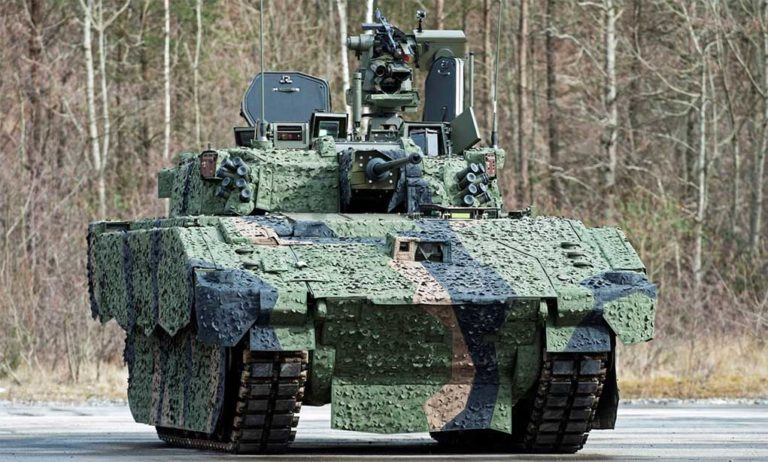





































 OPAL is comprised of a range of different hardware Line Replaceable Units (LRU) configures and optimized for each application, platform or end-user. This solution delivers an advanced application middleware with optimized applications and, where needed, advanced networking and connectivity services. OPAL features high processing and graphic capabilities, and deliver essential battlefield services to the participating members, enabling all users to share a common operating picture in real-time and to communicate in the same language.
OPAL is comprised of a range of different hardware Line Replaceable Units (LRU) configures and optimized for each application, platform or end-user. This solution delivers an advanced application middleware with optimized applications and, where needed, advanced networking and connectivity services. OPAL features high processing and graphic capabilities, and deliver essential battlefield services to the participating members, enabling all users to share a common operating picture in real-time and to communicate in the same language.




