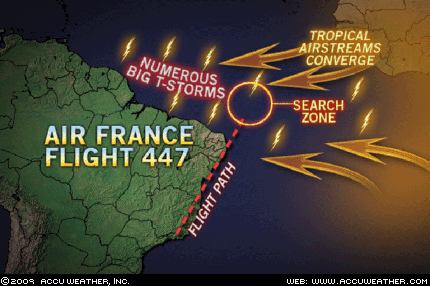
AccuWeather.com reports after extensive research into the weather that may have affected the Air France Airbus A330 on Sunday evening, it is believed that the plane flew into thunderstorms, and the updrafts or turbulence associated with those storms in addition to lightning may have played a role.
The projected flight path of flight 447 took the aircraft near Sao Luis, Brazil, where it may have first encountered a thunderstorm. Later in the flight, the plane appears to have flown into or near a large cluster thunderstorms that were in the development stages northeast of Fernando De Noronha, which is located off Brazil’s northern coast, and along the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), the belt of low pressure that surrounds the Earth at the equator.
Based on weather information from Fernando De Noronha, the updrafts associated with the thunderstorms may have reached up to 100 mph. Such an updraft would lead to severe turbulence for any aircraft. In addition, the storms were towering up to 50,000 feet and would have been producing lightning. TheAir France plane would have encountered these stormy conditions, which could have resulted in either some structural failure or electrical failure as noted in the communications between the Airplane and Air France headquarters.
Based on satellite information, the Air France flight had little chance of going around the storms given that they stretched for over 400 miles and were developing along the flight path. The airplane was flying at cruising altitude of 35,000 feet. With the updrafts pushing the storms up to 50,000 feet, the plane had to fly through the storms and not over them.
Despite the presence of the storms Sunday evening, the only lightning detected along the flight path was near Sao Luis, Brazil. Lightning strikes were not being detected with the storms northeast of Fernando De Noronha and along the ITCZ at the time.
According to Brazilian aviation officials, wreckage that has been found in theAtlantic Ocean about 400 miles off the northern coast of Brazil could be from the Air France aircraft. The debris sighted includes metallic objects and plane seats. This wreckage still hasn’t been confirmed as being part of the Air France jet.
Tropical thunderstorms and the lightning patterns generated by them are different from storms that typically occur over the United States. Studies have shown that the top region of tropical thunderstorms is highly charged and more conducive to lightning, which indicates that an airplane flying near the top of a tropical thunderstorm could be more susceptible to a lightning strike. Tropical thunderstorms are also notorious for producing frequent cloud-to-cloud, as well as cloud-to-air lightning.
Story by AccuWeather.com Meteorologists Heather Buchman, Kristina Pydynowski and Henry Margusity, and AccuWeather.com News Correspondent Gina Cherundolo