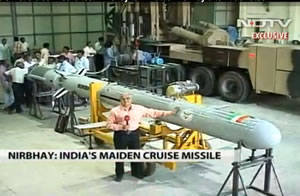
A test flight of India’s Nirbhay cruise missile failed today. “The missile blasted off from a mobile launcher positioned in the launch pad — 3 of the ITR missile test range at Chandipur, Odisha. at about 11:54 a.m.” DRDO announcement said. However, after a successful lift-off, about 17 minutes into the flight the missile had deviated from the planned flight path and the mission was terminated. Nevertheless, DRDO claims the missile “successfully” met the basic mission objectives and performed some of the manouveres satisfactorily before being terminated midway.
Under the planned test, Nirbhay (Fearless) will be required to complete a flight of 1,000 km, representing the weapon’s operational range. Originally, the test was scheduled for late 2012 but was delayed. Once development is completed Nirbhay will become part of India’s nuclear triad and an important complement in the country’s nuclear retaliatory capability, establishing viable ‘second strike’ through submarine-launched K-15 ballistic missiles and Nirbhay cruise missiles. A conventional armed variant will also improve the naval strike capability beyond the range of the current BrahMos.
A conventionally armed variant carrying a warhead of 450kg, will have a range of 750km. It will deploy with Jaguar strike fighters and Rafale MMRCA and used for land and naval surface attack applications. Using the same hybrid RLG/GPS navigation the missile will offer combined attack accuracy of about 20 meter CEP, which could be further improved using radar-based terminal-guidance. Most of the avionics used for the Nirbhay program are derivatives of avionic modules developed for the BrahMos missile.
Pakistan has already developed two versions of cruise missiles – the Raad and Babur, that has a range of 700 km. Pakistan developed its cruise missiles after recovering two US Tomahawk cruise missiles lost over its territory in the 1998.
















