Viper Strike is a gliding munition capable of stand-off precision attack using GPS-aided navigation and a semi-active laser seeker. It is intended for operations that require a flexible angle of inclination (steep or shallow), particularly in mountainous terrain or built-up areas where strict rules of engagement are in force. Its small size and precision provide for low collateral damage in cluttered urban environments.
The weapon was developed as a derivative of the autonomous Brilliant Attack Munitions (BAT) Submunitions during a quick reaction, nine-week program at Northrop Grumman’s Land Combat Systems facility at Redstone Arsenal, Huntsville, Ala.The weapon is suitable for operations that require top-down attack, particularly in built-up areas where strict rules of engagement are in force. It requires a “man in the loop” to lase the target, either from the ground in sight of the target or from directly by the UAV, controlled from the ground station, a process which ensures the greatest possible accuracy and minimizes the chances of collateral damage.
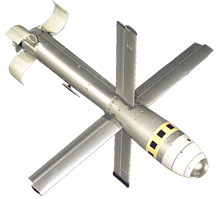 The Viper Strike’s warhead is smaller than the hellfire’s, which is used with the US Air Force armed Predator UAVs, containing only four pounds of Anti-Tank High Explosive (HEAT) charge, for reduced collateral damage in an urban built-up area. It also has a self-destruct mechanism, to eliminate post-strike hazards. The final version of Viper Strike could be equipped with fragmentation belt as well as an optional blast fragmentation and thermobaric warhead.
The Viper Strike’s warhead is smaller than the hellfire’s, which is used with the US Air Force armed Predator UAVs, containing only four pounds of Anti-Tank High Explosive (HEAT) charge, for reduced collateral damage in an urban built-up area. It also has a self-destruct mechanism, to eliminate post-strike hazards. The final version of Viper Strike could be equipped with fragmentation belt as well as an optional blast fragmentation and thermobaric warhead.
By late 2004 the US Army deployed to Iraq some Viper Strike munitions with MQ-5 Hunter unit. There were no details about combat engagements of these weapons. In 2005 Northrop Grumman continued development of the weapon, and is preparing to test it with MQ-1 armed Predator and AC-130 gunships, which will use the weapon as a stand-off precision guided munition (SOPGM). Ac-130 integration with Viper Strike is currently developed under a Special Operations Command (SOCOM) for an advanced technology demonstration (ACTD). The first phase of the program is scheduled for completion by December 2006. The weapon is being updated with additional GPS guidance system and fragmentation belt, placed around the shaped charge warhead.
















