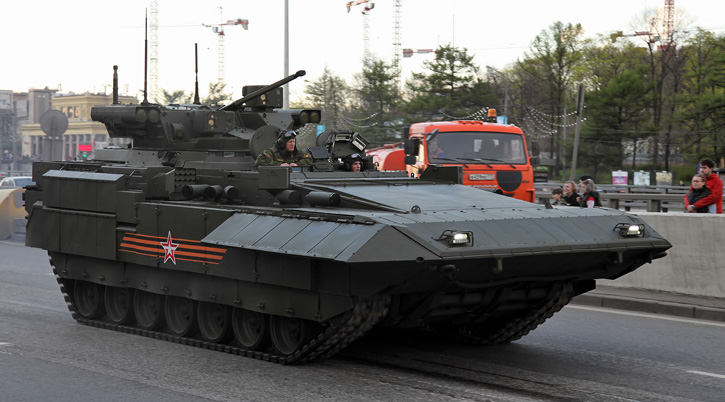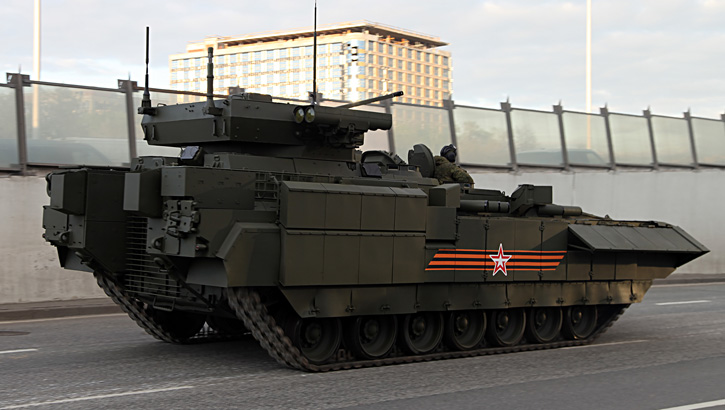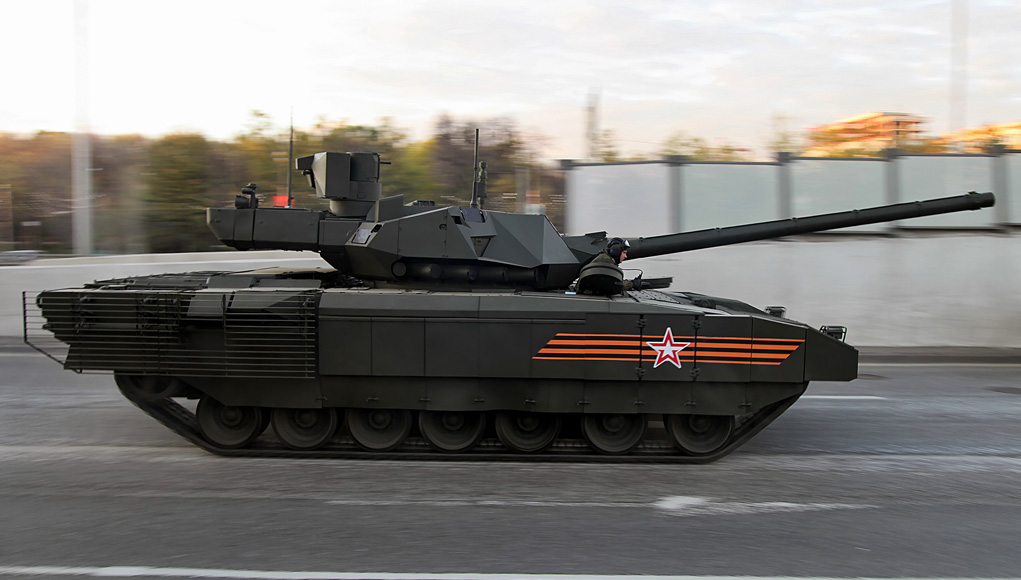
The Russian Ministry of defense is lifting the veil on a new family of combat vehicles that has been under development in the past years. The new family scheduled to enter service with the Russian ground forces in the next years will be unveiled in public for the first time May 9th, 2015 on the traditional ‘Victory Day Parade’, marking the 70th anniversary of the victory over Nazi Germany.The new family of vehicles consists of the Armata, a new tracked platform that will replace existing platforms that have been used in the T72 and T90 tanks since the mid-70s. The platform provides a common chassis for some 13 different combat vehicles weighing below 50 tons.
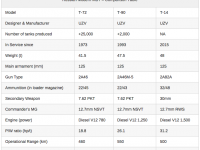
These include the new T-14 main battle tank that weighs 48 tons and T-15 infantry carrier; a new variant of the tank support vehicle (Terminator), an armored recovery vehicle (ARV), MT-A bridgelayer, Combat Engineering Vehicle (CEV), BMO-2 support vehicle carrying multiple launchers of thermobaric rockets, and USM-1 minelayer. Another variant that could be added in the future is a self propelled artillery system (SPG). However, the new Coalitziya SM SPG displayed on the May 9 parade is still based on the T-90 chassis.
An inspection of the T-14 tanks rehearsing for the May 9 parade shows a combination of layers of modular armor comprising active and hybrid protection. Adding protection beyond the frontal arc and sides is a common design feature today, adapting MBTs for combat in complex, urban terrain, where threats exist over 360 degrees.
Subscribe to read the full version of this article
Only $7.95 / month
Additional slat armor is used to protect the engine compartment and enable easy access to the sprocket. The forward section of the belly mounts an active counter-mine protection. Countermeasure dischargers firing instant smoke obscurants are employed, on both sides of the turret as part of the overall protection system.


The T-15 IVF (BMP) also shares the common Armata chassis. As a troop carrier, it will replace the current BMP-2 variants offering much improved mobility and protection although at a significant weight increase. The vehicle is operated by three crew members and accommodates eight troops. It is likely to be equipped with a new remotely operated weapon station designed by KBP. This turret mounts the 2A42 30mm cannon with 500 rounds, 7.62 coaxial machine gun and four Kornet-EM guided missiles (two on each side). The T-15 shares a protection system similar to that of Armata.






















