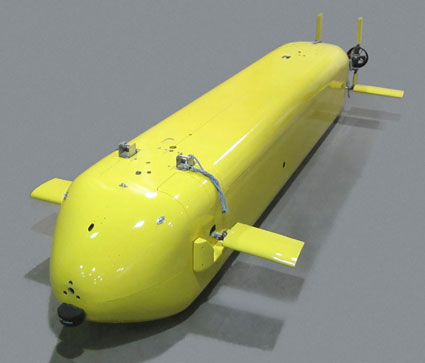
The US Navy is using General Motor’s (GM) hydrogen fuel cell technology to power its latest underwater vessel. Hydrogen fuel cells convert high-energy hydrogen efficiently into electricity, resulting in vehicles with greater range and endurance than those powered with batteries. Under the ONR’s Innovative Naval Prototype program for Large Displacement UUVs (LDUUV), energy is a core technology in the Navy’s goals for vehicles with more than 60 days endurance. Besides the GM fuel cell, the Navy has evaluated alternative power generation solutions from General Atomics, Lynntech and NexTech Materials.
The Naval Research Laboratory recently concluded an evaluation of a prototype UUV equipped with a GM fuel cell at the heart of the vehicle powertrain. The tests, a key step in the development of an at-sea prototype, were conducted in pools at the Naval Surface Warfare Center in Carderock, Md. The Navy plans to test the LDUUV in the open sea this year and could field a first squadron of the robotic submarines by 2020.
“Our in-water experiments with an integrated prototype show that fuel cells can be game changers for autonomous underwater systems,” said Frank Herr, ONR’s department head for Ocean Battlespace Sensing. “Reliability, high energy, and cost-effectiveness — all brought to us via GM’s partnering — are particularly important as Navy looks to use UUVs as force multipliers.”
Hydrogen fuel cell propulsion technology helps address two major automotive environmental challenges: petroleum use and carbon dioxide emissions. Fuel cell vehicles can operate on renewable hydrogen from sources like wind and biomass stored for later use. Once converted to electricity, water vapor is the only emission. Recharging takes only minutes.
GM’s fuel cells are compact and lightweight and have high reliability and performance. Lower cost is achievable through volume production supporting automotive applications. These attributes match the goals of the Navy to develop reliable, affordable systems.
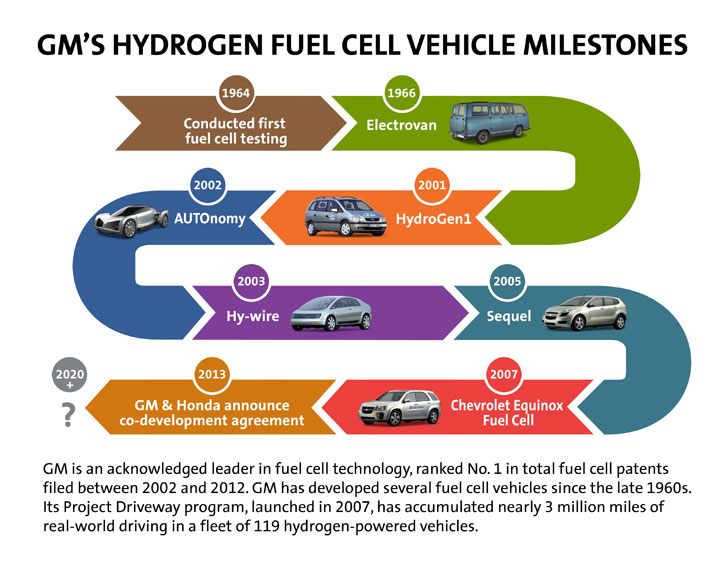
“The collaboration with the Navy leveraged what we learned in amassing more than 3 million miles of real-world experience with our Project Driveway fuel cell program,” said Charlie Freese, executive director of GM Global Fuel Cell Activities. “Our customers will benefit from additional lessons we learn about the performance of fuel cells in non-automotive applications that will be useful in GM’s drive to offer fuel cells across consumer markets.”