 EADS is a global leader in aerospace, defence and related services. The Group – comprising Airbus, Astrium, Cassidian and Eurocopter is the largest European aerospace consortium. In 2009 the group employed a workforce of 119,000 personnel generating turnover of € 42.8 billion. Airbus, the manufacturer of the Airbus line of transport aircraft. Its defense oriented products include military derivatives of the Airbus A300 and A330, the A400 military transport and CN-212, 235 and 295 medium transport planes. Eurocopter is EADS’ helicopter manufacturing subsidiary, providing a wide range of military and civil helicopters. Among the military models are Fennec, EC-635, EC-645, Panther, Cougar, NH-90 and Tiger, Astrium is a wholly owned subsidiary of EADS dedicated to providing civil and defence space systems and services.
EADS is a global leader in aerospace, defence and related services. The Group – comprising Airbus, Astrium, Cassidian and Eurocopter is the largest European aerospace consortium. In 2009 the group employed a workforce of 119,000 personnel generating turnover of € 42.8 billion. Airbus, the manufacturer of the Airbus line of transport aircraft. Its defense oriented products include military derivatives of the Airbus A300 and A330, the A400 military transport and CN-212, 235 and 295 medium transport planes. Eurocopter is EADS’ helicopter manufacturing subsidiary, providing a wide range of military and civil helicopters. Among the military models are Fennec, EC-635, EC-645, Panther, Cougar, NH-90 and Tiger, Astrium is a wholly owned subsidiary of EADS dedicated to providing civil and defence space systems and services.
EADS
Cassidian (EADS)
![]() Cassidian, an EADS Company, is the defense and security division of the European aerospace consortium EADS. Cassidian provides lead system integration and value-added products and services to military and government customers worldwide. Its portfolio ranges from air systems including aircraft and unmanned aerial systems, land, naval and joint systems, through intelligence and surveillance to cyber security and secure communications as well as test systems, missiles, services and support solutions.
Cassidian, an EADS Company, is the defense and security division of the European aerospace consortium EADS. Cassidian provides lead system integration and value-added products and services to military and government customers worldwide. Its portfolio ranges from air systems including aircraft and unmanned aerial systems, land, naval and joint systems, through intelligence and surveillance to cyber security and secure communications as well as test systems, missiles, services and support solutions.
Diehl BGT Defence
 Diehl BGT Defence GmbH & Co. KG is the largest company within the Diehl Defence Corporate Division. Diehl Aerospace is one of the largest German corporations with international orientation. The company is structured into five divisions, including metal, controls, defense, aerosystems and metering.
Diehl BGT Defence GmbH & Co. KG is the largest company within the Diehl Defence Corporate Division. Diehl Aerospace is one of the largest German corporations with international orientation. The company is structured into five divisions, including metal, controls, defense, aerosystems and metering.
The company’s capabilities are associated with missile and precision engagement systems for land, air and naval weapons, reconnaissance, surveillance and warning systems, self-protection and training systems. Certain solutions offered by the company include air/air and surface/air missiles, guided projectiles for artillery and rockets.
New applications pursued by the company include unmanned systems (land, air and sea), intelligent sensors for reconnaissance and monitors and active protection systems.
Carl Zeiss Optronics
 Carl Zeiss Optronics GmbH the Defense & Security Division of Carl Zeiss AG. The division specializes in optronic equipment for land, sea, air and space applications. Among the systems provided by the company are laser rangefinders, cameras, thermal imagers and various image processing systems. Applications include aerial recce systems and cameras, stabilized EO payloads for helicopters and unmanned systems, head tracking systems. Naval systems from Zeiss include stabilized platforms, and optronic mast systems for submarines. For land applications Zeiss offers hand-held systems, driver vision systems, mobile or stationary, mast-mounted surveillance and observation systems, stabilized periscopes, binoculars and spotting scopes.
Carl Zeiss Optronics GmbH the Defense & Security Division of Carl Zeiss AG. The division specializes in optronic equipment for land, sea, air and space applications. Among the systems provided by the company are laser rangefinders, cameras, thermal imagers and various image processing systems. Applications include aerial recce systems and cameras, stabilized EO payloads for helicopters and unmanned systems, head tracking systems. Naval systems from Zeiss include stabilized platforms, and optronic mast systems for submarines. For land applications Zeiss offers hand-held systems, driver vision systems, mobile or stationary, mast-mounted surveillance and observation systems, stabilized periscopes, binoculars and spotting scopes.
The company is based in Germany and operates subsidiaries in the U.S, and South Africa.
Kongsberg Defense Systems
Middle East Defense Update
 Following are excerpts from recent news articles published in Defense-Update, covering the East Mediterranean, Middle-East & North African defense market. The countries included in this report are: Algeria | Bahrain | Cyprus | Egypt | Iran | Iraq | Israel | Jordan | Kuwait | Lebanon | Libya | Morocco | Oman | Qatar | Saudi-Arabia | Syria | Turkey | Tunisia | UAE | Yemen. For an insight into each of the countries, click on the country name for a detailed report listing the 10 recent news items for that specific country.
Following are excerpts from recent news articles published in Defense-Update, covering the East Mediterranean, Middle-East & North African defense market. The countries included in this report are: Algeria | Bahrain | Cyprus | Egypt | Iran | Iraq | Israel | Jordan | Kuwait | Lebanon | Libya | Morocco | Oman | Qatar | Saudi-Arabia | Syria | Turkey | Tunisia | UAE | Yemen. For an insight into each of the countries, click on the country name for a detailed report listing the 10 recent news items for that specific country.
European Defense Update
 Following are excerpts from recent news articles published ib Defense-Update, covering the European defense market. The countries included in this report are: Austria | Belgium | Bulgaria | Croatia |
Following are excerpts from recent news articles published ib Defense-Update, covering the European defense market. The countries included in this report are: Austria | Belgium | Bulgaria | Croatia |
Czech Republic | Denmark | Estonia | Finland | France | Germany | Greece | Hungary | Ireland | Italy | Latvia | Lithuania | Netherlands | NATO | Norway | Poland | Portugal | Romania | Serbia | Slovenia | Spain | Sweden | Switzerland. For an insight into each of the countries, click on the country name for a detailed report listing the 10 recent news items for that specific country.
Elbit Systems
 Elbit Systems Ltd. is an international defense electronics company engaged in a wide range of programs throughout the world. The Company, which includes Elbit Systems and its subsidiaries, operates in the areas of aerospace, land and naval systems, command, control, communications, computers, intelligence surveillance and reconnaissance (“C4ISR”), unmanned aircraft systems (“UAS”), advanced electro-optics, electro-optic space systems, EW suites, airborne warning systems, ELINT systems, data links and military communications systems and radios. The Company also focuses on the upgrading of existing military platforms, developing new technologies for defense, homeland security and commercial aviation applications and providing a range of support services.
Elbit Systems Ltd. is an international defense electronics company engaged in a wide range of programs throughout the world. The Company, which includes Elbit Systems and its subsidiaries, operates in the areas of aerospace, land and naval systems, command, control, communications, computers, intelligence surveillance and reconnaissance (“C4ISR”), unmanned aircraft systems (“UAS”), advanced electro-optics, electro-optic space systems, EW suites, airborne warning systems, ELINT systems, data links and military communications systems and radios. The Company also focuses on the upgrading of existing military platforms, developing new technologies for defense, homeland security and commercial aviation applications and providing a range of support services.
Yemen’s al Qaeda Power Base Alarms the World
The Al Qaeda wing in Yemen claimed responsibility for the attempted bombing last week of a Northwest Airlines flight. The group, known as Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) is the latest reincarnation of Islamist militant cells that have been active in Yemen for years. With an estimated 2,000 militants and sympathizers exploiting the country’s economic and political chaos AQAP has created a powerful training and operations base, for jihad activities at the edge of the Persian Gulf and the Horn of Africa.
The growth of Al Qaeda’s wing in Yemen and its selection of high-profile targets are partly the result of militants regrouping in the Arab world’s poorest country as the U.S. military has put pressure on Al Qaeda in Afghanistan and Iraq. Indeed, as the United States steps up the hunt for Al Qaeda in Afghanistan and Pakistan, some of the terrorist network’s veteran operatives are leaving the region and flocking to Yemen, where an escalating civil war is turning the nearly lawless Arab nation into an attractive alternative operational base.
Yemen’s unrest, including a secessionist movement in the south and a civil war in the north, has given Al Qaeda an ideal hub, especially in rugged rural and tribal regions where the government reach is limited. For five years, Shia fighters from the powerful Houthi clan have led an armed rebellion against the Sunni government in Sana’a. Dug into mountain bases, the rebels, estimated at between 5,000 to 10,000, have waged guerrilla insurgency in a conflict which has killed thousands and displaced more than 175,000. The so-called, Tehran sponsored ” Houtis war” has not only turned the already mostly lawless nation into an economic chaos, but also created an inter-religious clash between Iranian Shiites against Sunni Yemen, even drawing Saudi Arabia, the self-proclaimed “Guardian of Sunna” into the turmoil. Analysts warn that the Houti War in Yemen could become the prelude of Shia-Sunni conflict over Iraq, once President Obama’s strategy to withdraw US forces will leave that country in bloodshed.
But there is more at stake. Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula has already transformed itself from a regional threat into what western intelligence see as the network’s most active affiliate outside Pakistan and Afghanistan with global ambitions. The botched attack on the Detroit bound Northwest Airline, could signal the start of a new offensive by al Qaeda.
An imminent danger is building up at one of the most strategic waterways in the Middle East. Yemen, at the tip of the Arabian Peninsula, straddles a strategic maritime crossroads at the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden, the Bab el Mandeb strait – the access point to the Suez Canal. Across the gulf is lawless Somalia, an even more tumultuous nation where the United States has said al-Qaeda militants have been increasing their activity.
A rather strange development has actually helped to build al Qaeda’s power base in Yemen. Following President Obama’s orders to dismantle the Prison in Guantanamo Bay, Cuba some of the world’s most notorious terrorist leaders were set on free foot. Several of these did not waste time and flew to the new safe haven in Yemen, joining their comrades, having escaped the NATO hunters in Afghanistan and Pakistan.

 Several of the leading Al Qaeda figures now in Yemen were released from Guantanamo. An example is Ibrahaim Suleiman Al Rubaish (seen in the image on the left), one of the groups’ leading religious ideologues, who is affectionately known as the “poet of Guantanamo’. Rubaish was captured by the Pakistanis in 2001 and transferred to the Americans.
Several of the leading Al Qaeda figures now in Yemen were released from Guantanamo. An example is Ibrahaim Suleiman Al Rubaish (seen in the image on the left), one of the groups’ leading religious ideologues, who is affectionately known as the “poet of Guantanamo’. Rubaish was captured by the Pakistanis in 2001 and transferred to the Americans.
He was detained in Guantanamo for five years, until December 2006, when he was retured to Saudi Arabia for a ‘ rehabilitation for Jihadists’ program. As could be expected, Rubaish escaped and fled to Yemen where he is now operates. Another Guantanamo detainee, Said Ali al Shihri, is now the deputy of al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula. (Shihiri is seen in the photo below)
Yemen’s location next to oil-rich Saudi Arabia, where Al Qaeda has been trying to overthrow a government it sees as illegitimate protectors of Islam’s holiest sites, is also a central attraction for jihadists.
Since then, the organization has joined extremists situated in Yemen and Saudi Arabia under the leadership of Nassir Abdel-Karim Wahishi (photo on the left), a Yemeni with close ties to Osama bin Laden. Wahishi’s second in command is Saeed Ali Shehri, a Saudi national who, who upon his release from the U.S. military prison at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, in 2007, already went through a rehabilitation program in the kingdom.
 As for the Northwest Airlines flight incident. This foreshadowed the jetliner plot by revealing al Qaeda’s focus on using concealed explosives to circumvent security measures. In a little publicized incident, that happened last August, the group used an elaborate ruse, with an extremist cell plotting to assassinate Prince Muhammad bin Nayef, Saudi Arabia’s security chief.
As for the Northwest Airlines flight incident. This foreshadowed the jetliner plot by revealing al Qaeda’s focus on using concealed explosives to circumvent security measures. In a little publicized incident, that happened last August, the group used an elaborate ruse, with an extremist cell plotting to assassinate Prince Muhammad bin Nayef, Saudi Arabia’s security chief.
But then, the Pentagon should not have been surprised. Yemen’s Al Qaeda wing had already startled Washington back in 2000 when a motorboat packed with explosives slammed into the U.S. destroyer Cole in the port of Aden, killing 17 sailors. Al-Qaeda has attempted to use PTEN compounds to blow-up airplane for several years. This type of explosive material was used in 2001 by Al-Qaeda member Richard Ried, in an attempt to blow up American Airlines Flight 63 from Paris to Miami. Ried concealed the explosive device in his shoes. More recently this compound was integrated into a new device known as the ‘underwear bomb’, where explosives and primers are sewn into pockets concealled inside the bomber’s intimate areas. It was first used by a Saudi militant, who flew from Yemen to Jidda, Saudi Arabia, for a meeting with the prince. The assassin got through airport and palace security with the device undetected. Some reports claimed the explosive device was inserted into his body, similar to drugs being smuggled through airports. The explosive was triggered by a telephone call from Yemen as he was meeting his target, killing him but only wounding the prince. PTEN was also the material that Umar Farouk Abdulmutallab of Nigeria is accused of concealing in his underwear in the plot to destroy the Detroit-bound Northwest plane.
Yemen’s government, meanwhile, appears to be mounting a serious and aggressive campaign against al-Qaeda after years of treading carefully with the militants. Last week’s attack targeted a meeting of Yemeni and foreign al-Qaeda operatives believed to include the top leader of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, Naser Abdel-Karim al-Wahishi, and his deputy, Said al-Shihri. Although reports indicated that several top al Qaeda leaders were among the victims, among them al-Wahishi and al-Shihri, however, their demise has yet to be confirmed. While al-Qaeda’s planning and operations epicenter still remains the Afghanistan-Pakistan mountain borderlands. But the hard truth, that western counter-terrorist agencies will have to face, is that the fight against Islamic extremism will have to be waged on multiple fronts.
France Acquires Vikings to Equip its Rapid Intervention Forces

The French government has selected the latest version of the BAE Systems BvS10 MkII Viking all-terrain tracked vehicle to equip its rapid intervention combined-arms battle group. The BvS10 MkII is produced by the company’s Swedish based Hägglunds AB subsidiary. France is already operating a lighter version of the Small Unit Support Vehicle BvS 206S optimized for in mountainous areas, over snow, bog land and over wet terrain.

“The MkII version of the BvS10 completely fulfils the French Army’s requirements in terms of protection, mobility and payload while maintaining the flexibility to perform across the spectrum of military operations,” said Jan Söderström, managing director for BAE Systems’ Vehicles business. The vehicles will be protected against small arms, improvised explosive devices (IED), mines and Rocket Propelled Grenades (RPG).

The fully amphibious BvS10 is heavier, capable of carrying of up to five tons. It was developed for the British Royal Marines, and has been fielded by the Dutch Marines as well. Although the British forces have used the Viking extensively in Afghanistan, the British MoD has favored the heavier, more protected Singaporean Warthog all-terrain tracked vehicles to equip the Marines in Afghanistan. France has ordered 53 vehicles, part of a total of 129 worth over £220 million. The French have considered both the Singaporean and Swedish vehicles and selected the Swedish design. The vehicles will enhance the capabilities of French Army rapid intervention battlegroup, and be delivered in three versions – troop carrier, command and utility (logistics support) vehicle. Three prototypes will be delivered to France in 2010 for qualification and testing, followed by production deliveries from 2011 to 2014, equipping a rapid deployment battle group.
“The contract acknowledges the high performance and strong market position of our battle-proven BvS10 and secures the continued development of the vehicle” Söderström added.
Although the majority of the work will be done in Sweden, the British AeroSpace, Defence and Security trade organization A|D|S has expressed satisfaction from the French decision. “UK industry is pleased to see signs of greater Government openness and cooperation between the UK and France in the defence sector” said Ian Godden A|D|S Chairman. “The UK and France have very significant capabilities in technology but similar budget pressures, which makes further cooperation essential.” He added, noting that joint procurement by the two governments has waned over the last two decades. According to BAE Systems, the project will be run in close cooperation with French partners, such as Panhard and EADS.

Next-Generation FBCB2 JCR on the Test Bench
Northrop Grumman Corporation has delivered the next version of Force XXI Battle Command Brigade and Below (FBCB2) software to the U.S. Army to begin formal government testing. The new software, called Joint Capabilities Release (JCR), provides a common FBCB2 platform solution for both the Army and U.S. Marine Corps.
FBCB2 is the key situational awareness and command-and-control system used by U.S. and coalition forces in Iraq and Afghanistan. More than 85,000 FBCB2 systems have been deployed worldwide. The company was awarded the first FBCB2 development contract in January 1995 and introduced the system in the early 2000s. Offering comprehensive situational picture showing updated positions of friendly forces, FBCB2 was one of the main contributors to the U.S. victory in the land campaign of the second Iraq War in 2003. The system links communication devices, sensors, vehicles, rotary-wing aircraft and weapons platforms in a seamless digital network to provide a clear, continuous and common picture of the battlefield. Most FBCB2 systems communicate via a satellite-based network; about 30 percent use the Enhanced Position Location Reporting System, or EPLRS, tactical radio network.
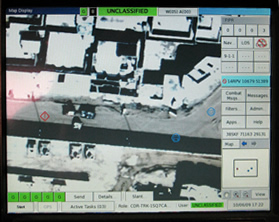
After 10 years in service FBCB2 is still useful but the current version of Blue Force Tracker (BFT), the core element of the system takes minutes to refresh friendly force position locations. JCR will solve that by fielding a new transceiver (BFT-2) and network upgrade, capable of updating friendly positions in seconds. Other new JCR features and functions include a commercial joint mapping tool kit; Type 1 encryption for relaying classified information; and an over-the-air “self descriptive situational awareness” (SDSA) capability. SDSA will eliminate inflexible fixed databases – one of the biggest complaints of the old system – and allow FBCB2-equipped units to change task organizations in the field to meet new mission requirements. The new FBCB2 also enables live streaming ‘picture in picture’ to be integrated on the display; it also provides for color marking of specific elements – a unit formation or vehicles in a convoy, obtaining better situational awareness in complex situations, where multiple friendly forces clutter the screen.
Future JCR releases will provide additional services including open office file transfers, image downloads, chat and instant messaging. Furthermore, the new system architecture is based on modular, reusable, upgradable and interoperable elements of the ‘Battle Command Product Line’ (BCPL) architecture developed by Northrop Grumman to extend the system through all users – combat command, aviation, dismounted soldiers, logistics and fires.
Weaponized RipSaw-MS2 UGV Evaluated for Convoy Security & Support
Most UGV programs are utilizing vehicles that move rather slowly and require relatively complex control, lacking effective 360 degrees situational awareness. Consequently, they can be easily outmaneuvered and disabled by an enemy that could get close or out run the robot. The U.S. Army is evaluating a much larger, powerful, agile and lethal robot developed by the Howe & Howe (H&H) company, known as ‘RipSaw Military Specification 2’, that offers many advantages that minimize such vulnerabilities. The RipSaw-MS2 is being tested as a convoy security and support vehicle.


The RipSaw Military Spec 1 (MS1) unmanned tracked vehicle provided a test platform for advanced off-road capabilities. Its capability to rapidly move off-road has triggered the Army to evaluate it as a convoy support ‘guardian angel’. The vehicle can rapidly move alongside the convoy, without obstructing the convoy movement, rapidly securing suspected IEDs sites or responding to enemy fire from ambushes, suppressing enemy fire sources or towing immobilized vehicles out of the line of fire. The RipSaw-MS1 has recently demonstrated such capabilities during the ‘Robotics Rodeo’ at Ft. Hood. Beyond the convoy support mission, RipSaw has other potential missions, including perimeter defense, surveillance, rescue, border patrol, crowd control and explosive ordnance disposal roles.

The RipSaw uses multiple cameras to gain continuous, 360 degrees coverage, providing the operator an ‘always on’ full situational awareness. Furthermore, the vehicle is large enough to support an effective perimeter defense system which can stop anyone from getting close. This active self-protection system utilizes multiple M5 Modular Crowd Control Munitions (MCCM) charges mounted on a belt around the vehicle. Relying on this deterrent weapon, RipSaw can break into crowds employing the MCCM’s flash-bang effect or use the non-lethal rubber bullets to repel hostiles from approaching the vehicle. Similar weapons can also be used as offensive weapons. Other payloads accommodated already been tested with the platform, include counter-IED devices and mines.

The Ripsaw MS2 is tele-operated from a nearby M113. However, as a semi-autonomous vehicle, many of the control functions are computer assisted via ‘drive by wire’ controls. It is designed as a highly adaptive platform that can be integrated with multiple weapon systems and different mission payloads.
The RipSaw MS2 is only 1.77 meter high, thus capable to effectively blend in the terrain, and mask itself from enemy observation. The low silhouette is also beneficial when moving forward as an advanced fire base; RipSaw-MS2 has already been tested with the 7.62mm and .50 Cal machine guns. The vehicle was also demonstrated carrying Javelin missiles, but none were fired sofar. The vehicle was weaponized by the Armys Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center (ARDEC) at Picatinny Arsenal, NJ. The kit included the installation of a remotely controlled M240 machine gun operated from a separate console installed in the control vehicle.
The RipSaw Origins

Originally the Ripsaw ‘unmanned tank’ was developed as a ‘one of a kind’ backyard garage project. The developer, Howe and Howe Technologies received the attention of the U.S. military as they submitted the vehicle for the first DARPA Challenge of 2005.
Two years later the small developing company received their first contract from the U.S. Army Research, development and Engineering Command (REDCOM) Tank and Automotive Division which modified the vehicle into an ‘unmanned ground vehicle capability demonstrators’.
The current version, called RipSaw MS2 was designed to be bigger, faster and more modular, than the MS1. The vehicle can take significant combat damage and still be rapidly repaired in the field, to be ready to fight another day. According to the manufacturer, unlike other vehicles that are usually damaged beyond repair by mine blast or IEDs, as damaged RipSaw could be ‘cannibalized’ in the field for its undamaged modules and assembled into a fully capable vehicle overnight.
Born to be Wild…


Weighing 4.5 ton (9,000 lbs) the RipSaw MS2 vehicle is sized like a HMMWV. It can carry about one ton (2,000 lbs) of payload and be controlled remotely or operated by a driver and a crewman. The vehicle uses a lightweight tubular chassis design, derived from NASCAR race cars, powered by a 6.6 liters duramax diesel engine, developing 600 hp and 1000 ft/lb of torque, providing exceptional power to weight ration for vehicles at this class. Fully weaponized and loaded, the RipSaw MS2 can accelerate from 0 to 50 mph in 5.5 seconds (!) reaching a top speed of about 60 mph. “Ripsaw is very quick and agile, it can easily outmaneuver a human” Michael Howe told Defense Update, indicating this is not trivial for a UGV.
The high power-to-weight ratio, efficient suspension and low ground pressure are providing RipSaw MS2 with exceptional maneuverability. Its center of gravity is located 70 cm (30″) above, contributing to the high stability in steep gradient (50degrees) and side slope (45 degrees). High ground clearance (60cm – 24″) and relatively low weight, wide tracks and the suspension’s long travel maintain low ground pressure of 2.8 lbs/square inch. This attribute enables the vehicle to traverse rugged terrain at high speed, negotiate vertical obstacles up to 1.5 meter (60″) high or rip through barriers like a heavy tank.
The innovative mechanical clutching system that controls the hydrostatic transmission with the power, speed and simplicity of a mechanical drive system is responsible for the vehicle’s rapid acceleration, maneuverability and control.
For a detailed review of the RipSaw MS1, check this 2008 Defense Review article by David Crane.

Prophet Enhanced – a New Tactical SIGINT for the U.S. Army
The industry team led by General Dynamics C4 Systems has been working since May 2009 integrating the Prophet Enhanced Signal Intelligence (SIGINT) into the new Panther Medium Mine Protected Vehicle, (MMPV). So far the GDC4 led team has been awarded $74 millions as part of the Prophet Enhanced six-year program which has a total value of $866 million. The production of the first MMPV based system was completed in December 2009.
Operating from MMPV and HMMWV vehicles, Prophet Enhanced enable tactical commanders to securely and accurately detect, identify, locate and deter a wide range of signal emissions on the battlefield. The new SIGINT system is empowered by advanced, software-defined systems offering rapid and flexibility and response to changing threats and battlefield requirements.
Prime contractor General Dynamics C4 Systems has teamed with L-3 Communications and Northrop Grumman Information Technology for this program. To meet the goal of reducing overall cost of future system upgrades and enhancements, the Prophet Enhanced design incorporates pre-planned upgrades and technology insertions and standardized training.
Helios 2 – the French Reconnaissance Satellite
Helios 2B is scheduled to replace the Helios 2A launched in 2004. These ‘second generation’ Helios satellites weigh 4.2 tons. It will orbit the earth at a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 700 km and is designed for useful mission life of five years.
The French military reconnaissance satellite was built by EADS Astrium, its high resolution imaging payload was developed by The Thales Alenia. The Helios satellites were developed in partnership with Belgium, Spain, Italy and Greece. Germany and Italy are also provided access to the Helios 2 system, under bilateral exchange agreements which also include e Cosmo-SkyMed SAR-Lupe radar imaging satellites.

December 10, 2009: Helios-2B was launched December 18, 2009 after a delay of several days. The satellite was launched on an Ariane 5 GS rocket oriuginally scheduled for launch on Flight 193 on December 9, 2009 from the French Guiana space centre at Kourou.

















