RAFALE Missile Division

LITENING incorporates in a single pod all the targeting features required by a modern strike fighter. The LITENING program, launched by Israel’s Research and Development authority RAFAEL in 1992, combines multiple sensors for maximum flexibility in a single pod at low cost. The original pod included a 1st Generation FLIR, a TV camera, a flash-lamp powered laser designator, laser spot tracker for tracking target designated by other aircraft or from the ground, and an electro-optical point and inertial tracker, which enabled continuous engagement of the target even when the target is partly obscured by clouds or countermeasures.
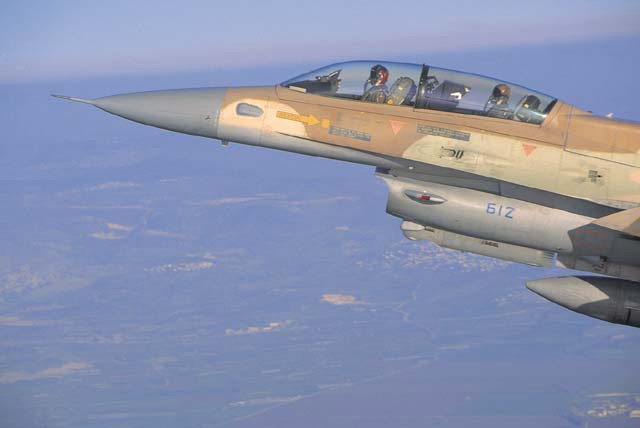
Above: An Israel Air Force/Lockheed Martin F-16D equipped with a Rafael Litening I targeting pod. The IAF plans to procure the more advanced version of Litening III for its F-16C/D/I and F-15Is, in addition to the versions currently deployed. Below: Litening II breakdown view.
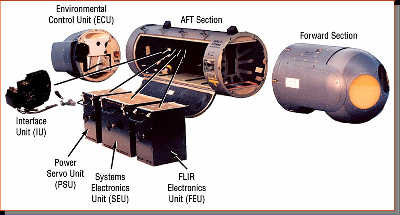
This integrated array enabled the pilot to effectively detect, recognize, identify, track and engage ground targets in day, night and under adverse weather conditions. With the pod’s systems they can designate such targets by laser, for attack by other aircraft or by precision guided weapons carried on board. The pod integrates the necessary laser rangefinder and designator, required for the delivery of Laser Guided Bombs, cluster and general purpose bombs. Laser spot detection is utilized in cooperative missions, for rapid orientation, detection and recognition of targets, marked by other forces. Identification of aerial targets from BVR ranges is also provided with the INS assisted gimbaled sensors, as the sensors can continuously point to the target’s direction, irrelevant to the aircraft position, or interference of clouds or obscurants. This combination also enables employment of the sensors in “point of interest” mode, where LITENING enables free maneuvering during and after the attack path, while maintaining the target clearly visible and marked for precision attack. The same sensors can provide imagery for night navigation as well as hit verification and battle damage assessment after the attack.
Below: Litening II+ pod fitted to an Air National Guard F-16 aircraft.

The evolution of the Litening pod continued with the Litening III version, which utilized a more capable Gen III (3-5micron) FLIR, with a 640×480 digital detectors array. This system is also equipped with a target marker, which improves the coordination of ground and air forces, by designation of targets by day or night. Litening III system is also equipped with a dual-wavelength diode-pumped laser, which is compatible with training (eyesafe) and wartime operational modes. The system also employs electronic image stabilization, to provide cleaner images of targets, acquired at long standoff range.
Logistically, the integration of the pod is easy and straightforward; it can fit the centerline or E/O pod mounts available with most modern aircraft and require no structural changes in the aircraft. Pods can also be installed on different aircraft, in support of specific missions. For example, the US Reserves currently field eight pods per wing. The pod requires minimal maintenance and technical support on the flight line. It is self boresighting in flight, therefore requires no alignment prior to the mission and improved accuracy during operations.
The Israeli targeting pod was procured by14 air forces, including the US Air Force Reserve’s and Air National Guards for their F-16 Block 25/30/32 Fighting Falcon. Other air forces operating the system include the US Marine Corps (AV-8B), Israeli air Force (F-16), Spanish and Italian Navy (AV-8B) and Spanish air force (F/A-18), German Air Force (Tornado IDS), and the Venezuela (F-16A/B). The pods were also selected for South Africa’s Grippens, India’s Mirage 2000, MiG-27 and Jaguar. The most recent inquiry for the pods came in March, for a planned procurement of F-16s by Austria. The pod is also fully integrated in the Eurofighter, F-5E, MiG-21 and other types. Testing are underway to integrate the pod with Boeing F-15I operated by the Israel Air Force.
|
Litening III Specifications:
|
| Length: |
220 cm |
| Diameter: |
406 mm |
| Total weight: |
440 lb |
| Operational altitude: |
+40,000 |
| IR Sensor: |
640×480 FPA Mid-IR wavelength |
| Daylight sensor: |
CCDTV |
| Wide FOV: |
18.4 x 24.1 |
| medium FOV: |
3.5×3.5 |
| Narrow field of view: |
1×1 |
| Field of regard: |
+45 / -150 |
| Roll: |
+/- 400 |
| Laser: |
Diode pumped laser designator, dual wavelength |
| Laser spot tracker |
|
| IR target marker |
|









 OFEQ-5, built by IAI/MBT, belongs to the class of small and lightweight satellites. Its launch weight is about 300 kg, it has a height of 2.3 meters and 1.2 meter diameter. It is a three-axes stabilized, lightweight satellite platform, adapted for high-resolution observation, scientific, or, technological payloads. Its design is based on the proven technologies employed in the Ofeq series.
OFEQ-5, built by IAI/MBT, belongs to the class of small and lightweight satellites. Its launch weight is about 300 kg, it has a height of 2.3 meters and 1.2 meter diameter. It is a three-axes stabilized, lightweight satellite platform, adapted for high-resolution observation, scientific, or, technological payloads. Its design is based on the proven technologies employed in the Ofeq series.







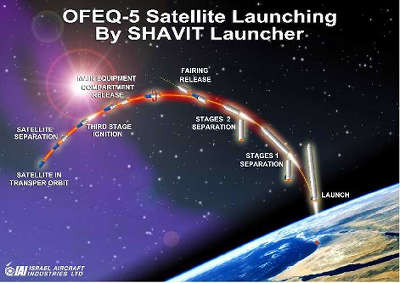
 SHAVIT is a three-stage satellite launcher, powered by three solid fuel rocket motors. The first two stages lift the launcher to an altitude of approximately 110 km. From this point, the launcher continues to gain height while coasting up to approximately 250 km, where the launcher positions itself and ejects the satellite shroud. After the separation of the main instrumentation compartment and while the launcher is spinning, the third stage motor is ignited. Thus, the satellite is inserted accurately into its transfer orbit at an altitude of approximately 260 km.
SHAVIT is a three-stage satellite launcher, powered by three solid fuel rocket motors. The first two stages lift the launcher to an altitude of approximately 110 km. From this point, the launcher continues to gain height while coasting up to approximately 250 km, where the launcher positions itself and ejects the satellite shroud. After the separation of the main instrumentation compartment and while the launcher is spinning, the third stage motor is ignited. Thus, the satellite is inserted accurately into its transfer orbit at an altitude of approximately 260 km.




