This hand held laser “flashlight” generates an extremely bright, variable width beam of red light. The beam is certified eye-safe at all ranges and under all tactical conditions. The laser beam sends a language-dependent warning and challenge that forces adversaries to signal their intent to retreat surrender or continue aggressive behavior. It dissuades and/or delays adversaries by producing an overpowering glare or flash blinding the individual. The laser illuminator is suitable for law enforcement missions where revealing a drawn weapon is not advisable. This device can be used as handheld augmentation to sidearms carried on law enforcement missions; use of sidearm enables quick conversion to lethal force.
Imaging (Visual / IIR) Precision Guidance System
Imaging sensors were used with precision guided weapons since the early 1970. Until recently, lack of processing power and datalink capacity have limited the use of such guidance techniques to relatively short range direct attack weapons (such as Maverick) and medium range strike missiles (such as Have Lite and SLAM). With the introduction of powerful thermal imaging sensors and signal processors, autonomous (fire and forget) missiles are now available for anti-tank uses. Similar capabilities are also provided to support standoff aerial weapons, both for autonomous and guided weapons. These weapons offer high precision, and inherent battle damage assessment capability which cannot be provided by GPS, SAL or radar directed weapons. Furthermore, EO sensors enable important functions which are becoming essential for modern warfare – such as positive, automatic or manual identification of targets, engagement of moving targets, and dynamic aimpoint selection even with autonomous weapons, with the use of target recognition and tracking (ATA/ATR). While “man in the loop” capability of EO guided weapons is extremely useful, deployment of many such weapons in simultaneous attack require significant investment in bandwidth and datalink coordination and support, which can complicate the execution.
IDF Vehicle Protection Program
In order to reduce the exposure of its troops to attack by small arms, demolition charges and anti-tank weapons, the IDF is currently operating several types of armored vehicles, protected at different levels, designed to meet the perceived threat at each region.
The heaviest armored elements deployed in the current LIC combat are the Merkava Mk 3 tanks, heavy armored troop carriers and heavy engineering vehicles. The Merkava Mk 3 LIC was slightly modified to reflect some of the recent lessons learned during the armored employment in LIC.
The Southern command, responsible for operations at the Gaza strip, where sophisticated explosive charges and determined attacks against armored vehicles are frequently encountered, is operating heavy APCs based on the Centurion hull, mounting an elevated infantry fighting compartment, which enables soldiers to observe and effectively engage targets in built up terrain. The heavy APC was fielded at the beginning of the current conflict in 2000. The IDF is planning to introduce a new and upgraded version by 2005.
The Northern command, responsible for the security of the Lebanon Border, fields a heavy APC called Nakpadon, which is equipped with special, much heavier armor protection systems designed to counter more sophisticated threats, including advanced anti-tank missiles and large standoff charges. The Nakpadon is also equipped with an electronic warfare broadband jamming system disrupting electronic remote control activation of roadside bombs.
The Golani Brigade is using a different vehicle, the Achzarit Infantry Armored Fighting Vehicle (AIFV) which is based on a modified T-55 chassis.
Further additions to the IDF order of battle are the introduction of armored wheeled vehicles, these will probably be the new 8×8 Stryker APC currently being procured for the US Army but the IDF decision has yet to be made.
A different approach was implemented with the preparation of the M-113 APC to continue its role in low intensity conflict. The current vehicle is fitted with surrounding mesh armor and an elevated fighting compartment, installed on the top of the existing fighting compartment. Beginning in 2005, the improved M-113 APC will be fitted with a new hybrid armor suite, new engine, improved steering mechanism and remotely controlled weapon system.
The protection of military forces is not limited to combat fighting vehicles, as troops operating in high risk areas must be protected continuously, including escort, transportation, logistics support and non combat activities. Current commander’s vehicles are based on the Soufa 4x 4 armored vehicles. By 2005 an improved commander’s vehicle, based on the Hummer, will be fielded, and augmented by improved Soufa. The IDF Hummer tactical vehicles are also fitted with enhanced protection, when compared to the standard set provided by the manufacturer. The IDF is currently buying protection suits from the USA, due to lack of local funding. These vehicles will be augmented in the near future by heavy armored cars, which are currently being evaluated Armored logistical vehicles, as well as protected patrol vehicles could also utilize the new Wolf platform, unveiled at LIC-2004 by RAFAEL. The IDF also evaluating a new high mobility vehicle – the Flyer Defense ITV-1 all terrain vehicle, which uses the same design as Light Strike vehicle used by the Army of Singapore.
FIREFLY – Miniature “Video Grenade”
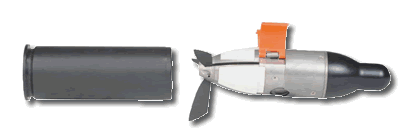
 FIREFLY, under development at RAFAEL is a miniature intelligence gathering projectile weighing 145g and launched from a standard M203 grenade launcher. The projectile is designed as a sub-caliber munition, 38mm in diameter and 155mm in length. When launched over a typical 600-m range, FIREFLY flies an 8-second flight, and transmits real-time photos of the area lying directly below. FIREFLY provide small infantry units with organic capability for tactical intelligence gathering. The system provides quick orientation awareness, including threat and armed/unarmed personnel identification. FIREFLY is suitable for operation in any terrain, including urban area.
FIREFLY, under development at RAFAEL is a miniature intelligence gathering projectile weighing 145g and launched from a standard M203 grenade launcher. The projectile is designed as a sub-caliber munition, 38mm in diameter and 155mm in length. When launched over a typical 600-m range, FIREFLY flies an 8-second flight, and transmits real-time photos of the area lying directly below. FIREFLY provide small infantry units with organic capability for tactical intelligence gathering. The system provides quick orientation awareness, including threat and armed/unarmed personnel identification. FIREFLY is suitable for operation in any terrain, including urban area.
The projectile is equipped with two CCD cameras. Throughout its flight, the video cameras record the ground scene lying directly under its trajectory. The video stream is transmitted in real-time to the operator in the field. Video can be viewed in real-time, recorded and analyzed on the PocketPC / PDA console or transmitted to other users, via wireless communications to other pocket PC.
The console is comprised of a standard pocket PC, coupled to a portable add-on receiver and antenna. The system is in an advanced stage of development and has passed firing tests which have proven concept worthiness.
M3 – Carl Gustaf Weapon System
The Garl Gustaf Weapon System is a multi-role man portable “artillery” providing infantry units the ability to engage any type of target, including armor, building, bunkers, personnel etc. The system enables deployment of smoke and illumination charges. The M3 system relies on a 84mm reloadable, recoilless launcher and a family of munitions including the HEAT 751 which uses a tandem warhead to defeat over 500mm of steel including reactive armor (ERA). The rocket is designed to pass through bushes or scrub without activating the precursor charge, thus enabling firing from ambush.
When ERA penetration is not required, the HEAT 551 variant can be used, offering extended range of up to 700 meters. For combat in urban terrain, M3 can be loaded with HEDP 502 dual purpose rocket which can defeat light armor, concrete, bunkers or brick walls. The HE 441 charge was designed specifically for engagement of soft targets. Unlike the other rockets, it is equipped with an impact or delay fuse, to enable air-burst effect. The warhead has 800 steel pellets enclosing the high explosive charge.
A different load – ADM 401 can be used for close-in protection of ambush teams armed with the M3. This rocket carries a payload of 1,100 flechettes and has an effective range of 100 meters.
The flechettes are released and accelerated by gas pressure in a cone, resulting in distribution of 5 – 10 flechettes per square meter at a distance of 100 meters. Smoke, illumination and training rounds complete this impressive weapon system.
EL/K-1891 Mobile SATCOM Terminal
The EL/K-1891 mobile / airborne SATCOM terminal is designed for X or Ku bands. The antennae uses 25×10 cm plannar array or 80cm dish. Mounted on dual stabilized pedestal. In the dismounted ground satellite communications station, the terminal use a commercial 9.3 meter dish. System is derived from an airborne platform developed for the IAF F-16I and AISIS SIGINT aircraft.

AT4 – Light Anti-Armor Weapon
The AT4 CS / CS HP was designed especially for urban combat – the anti-armor weapon (CS HP) uses an 84mm fin-stabilized rocket, armed with high penetration shaped charge which provides armor penetration capability exceeding 500mm of steel equipped with special internal ballistics allowing it to be fired from confined spaces such as tight jungle, in front of an obstacle or with own troops in close vicinity. The weapon has a high hit probability up to 300 meters. The weapon is carried in a dispensable canister/launcher weighing 7.8kg (the AT4 HEAT version which is not designed for use in a confined space weighs 6.7 kg and, has higher muzzle speed but lower armor penetration > 420mm).
AMX-10RC Upgrading
Under its upgrading program the wheeled recce Armored Car, operated by the French Armor Corps, will receive an information console (TIS) and new RP4G combat net radio. Improvements to the automotive system include softer transmission controls.
Other installations include add-on armor, KBCM defensive aids system including Gallix and LIRE IR active decoy, and provisions for thermal sight for the gunner and driver, improving operability under difficult weather conditions. Initial deliveries of the improved model are planned for late 2004.
Flexible Camouflage System
Fibrotex also developed special flexible tiles which have specific multi-spectral camouflage properties to provide concealment from Visual, Near IR, Thermal and radar. The camouflage is effective in all environments, both cold and hot climates, dry or wet conditions. Tiles are specifically designed for each section of the vehicle, and can be adapted to every size and shape of vehicle.
Precision Seekerless Guidance – PNAV
A new seekerless precision strike weapon system developed by Lockheed Martin, could revolutionize next-generation strike weapons. This all-weather, precision standoff seekerless 1,000 lb weapon uses an inexpensive wing set to provide maneuvering G’s and energy to interdict evasive targets. Target cuing is received via datalink from other sensors, resulting in a near-zero navigation Circular Error Probability (CEP). The weapon uses low-cost, two-way data link to receive continuous corrections to the current GPS system, providing a direct hit without the use of an end-game seeker. The datalink provides weapon tracking and status. PNAV is expected to be a key ingredient in future Small Diameter Bomb (SDB) applications, as it enables reduction of CEP well below the 4meter requirement without a costly seeker.
GlobaLight Satellite Communications terminal
Elbit Systems / Nice Systems
Elbit System’s GlobaLight SATCOM Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) can supports command post with two data (LAN) lines and two voice (phone) lines with total capacity of up to 2Mbps downlink and 500 kbps for the uplink – adequate for most multimedia, video rich applications.
Ghost Signature Reduction System
Natural body heat creates a distinctive signature inherent to human body, therefore, Infantrymen appear conspicuously hot on thermal image. Personal camouflage should significantly reduce heat signature reduction in addition to visual camouflage provided by the color scheme. The German company TEXPLORER has developed Ghost – a metallized fabric creating such an effect. The washable, reusable fabric can be adapted to all types of countryside and temperature ranges with various background printed patterns.
Active Radar / Milimeter Wave
Precision Targeting System
Radar (active) guidance technology prevailed in anti-ship and surface attack weapons during the 1980s. This guidance technique was recently adapted to land attack missiles. After the missile flies to a pre-designated location where line of sight to the target is expected, it activates its radar in a scan mode, and will home in on the signal expected to be the target. Such signal can be the strongest in the area, or one that emits a characteristic signature. Radar guided missiles are highly vulnerable to countermeasures and deception, which sometime necessitate human intervention for target verification and intervention at terminal phase. When used over land, radar seekers can be augmented by other elements (such as EO, GPS, LADAR etc).
Other applications of much smaller radar guidance use millimeter wave radars, to locate, classify, identify and engage armored vehicles and other priority targets. The use of millimeter wave seekers provides very high resolution, all weather capability and high immunity to current conventional countermeasure techniques employed by armored vehicles.