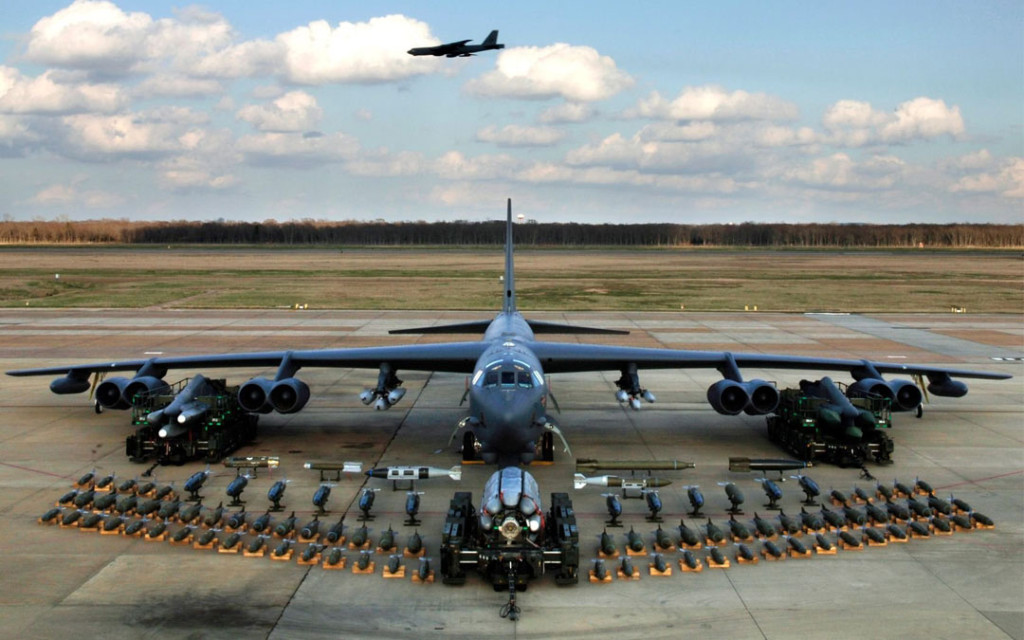
US Air Force B-52 bombers is undergoing modifications to increase the capacity of smart weapons carried by the aircraft by 50 percent. Under a US$24.6 million contract awarded to Boeing, the company will modify existing weapon launchers to fit into the bomb bay, allowing aircrews to use the B-52’s entire weapons capacity. The bomb bay upgrade will also enable the B-52 to carry weapons internally only, increasing fuel efficiency in flight. The modernization work will use parts from existing Air Force rotary launchers repurposed for conventional missions, as well as hardware and software already developed for the wing pylons. Under a separate program known as 1790 Internal Weapons Bay Upgrade (IWBU), the bombers’ rotary launcher is rewired to digitally connect to the aircraft weapon system. The rotary launcher was originally designed to support strategic nuclear tipped weapons such as air-launched cruise missiles (ALCM) and nuclear bombs. Under the IWBU upgrade, digital interfaces are added to the rotary launcher, to fit it to support conventional weapons. Resulting from these upgrades, Two B-52 bombers will be able to carry 40 weapons, compared to three B-52s carrying 36 weapons today – thus lowering the number of crews and amounts of fuel needed for typical mission.

Boeing will produce three prototype launchers for test and evaluation. Initial capability is expected in March 2016, and potential follow-on efforts could add additional weapons and allow a mixed load of different types of weapons. Following the upgrade’s first phase, the B-52s will be able to carry 24 500-pound Joint Direct Attack Munitions (GBU 30 JDAM) or 20 2,000-pound JDAMs (GBU-32). Later phases will add the Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (AGM-158A JASSM) and its extended range variant (JASSM-ER – AGM-158B), as well as the Miniature Air Launched Decoy (MALD) and its jammer variant (MALD/J – ADM-160C).

“When you combine that ability with the extremely long flying time of the B-52, you have an efficient and versatile weapon system that is very valuable to warfighters on the ground,” said Scot Oathout, Boeing’s B-52 program director. “This weapons capacity expansion joins the Combat Network Communications Technology (IWBU, CONECT) program, a $1.1 billion communication upgrade currently being installed on the aircraft, to give the warfighter even more flexibility.”
CONECT upgrades include software and hardware such as new servers, modems, radios, data-links, receivers, and digital workstations for the crew. One piece is the ARC-210 Warrior, a beyond-line-of-sight software programmable radio able to transmit voice, data and information in real time between B-52s and ground command and control centers, allowing for the transmission and receipt of data packets and files with updated intelligence, mapping or targeting information while the aircraft is in flight. Previously, an in-flight target change required copying down coordinates, while the ARC-120 allows machine to machine transfer of that data. This is useful on long-endurance missions where targets may have changed locations in the time it takes for the B-52 to travel to the combat zone. The aircraft will be able to receive information through Link-16. “We are bringing this amazing workhorse of a bomber into the digital age and giving our customer the infrastructure necessary for continued future improvements,” Oathout commented.


B-52s are periodically refurbished at USAF maintenance depots such as Tinker Air Force Base, Oklahoma. The Buff is expected to remain in service at least until 2045, nearly 90 years after the first B-52 entered service. The USAF continues to rely on the B-52 because it remains an effective and economical heavy bomber, particularly in the type of missions that have been conducted since the end of the Cold War against nations that have limited air defense capabilities. The B-52 has the capacity to loiter for extended periods over (or even well outside) the battlefield, and deliver precision standoff and direct fire munitions. It has been a valuable asset in supporting ground operations during all recent conflicts. Boeing is currently delivering eight kits in 2013. The first aircraft is currently undergoing the upgrading process, to be completed by April 2014. 10 additional kits will be delievered in 2014 and 2015.
Structurally, the airframes are still sturdy, but in terms of electronics capabilities, the bomber is a stone age relic. In July 2013, the air force began a fleet-wide upgrade of its B-52 bombers, introducing avionics, communications and cockpit upgrades under the Combat Network Communications Technology (CONECT). The new systems will enable aircrews to send and receive information via satellite links, which will enable them to change mission plans and retarget weapons while in flight. In addition, pilots will be able to interact better with other aircraft and with ground forces. Currently, mission information must be uploaded to a B-52 before a flight. Other improvements will include a state-of-the-art computing network with workstations at each crew position and an integrated digital interphone with increased capacity that will allow crew members to talk to each other on headsets equipped with noise-canceling technology. The $76 million CONECT upgrade will be performed by Boeing and covers low-rate initial production of the first CONECT kits, along with spare parts and maintenance and service at Tinker.