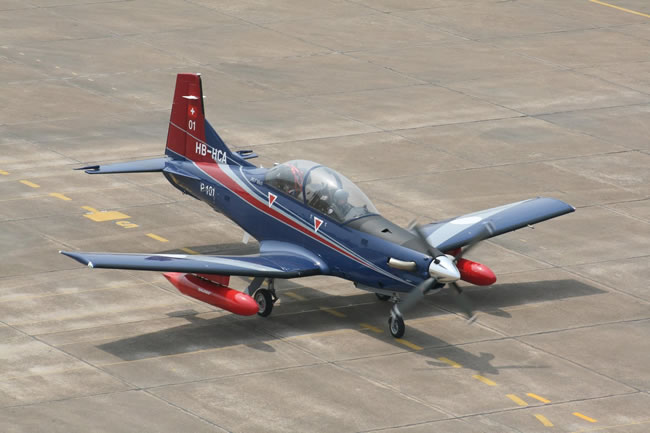
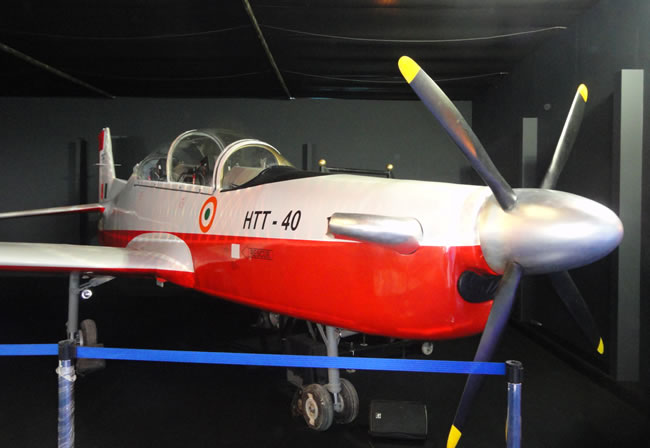
The Indian Air Force’s first Pilatus PC-7 Mk II trainer flew into India on the eve of Aero India 2013. This aircraft (tail number P101), which has, somewhat unusually, retained Pilatus company house colours, was flown to AFS Yelahanka on the morning of 5 February. In the cockpit were Pilatus test pilot Stefan Greub, along with Sqn Ldr S Mitra of the IAF. Delivery of the last batch of 75 PC-7s on order will be completed by end-2015. Reacting to reports that this batch will be followed either by orders for additional aircraft directly from Pilatus or that HAL will undertake licence production of the type in India, an IAF officer has said that there was no provision in the existing contract for the latter option. This hints at a face off between the IAF whose requirement for basic training aircraft totals 181 units, and HAL which is currently engaged in designing its HTT- 40 turboprop basic trainer against the Air Staff Requirement issued to it by the IAF. Chairman HAL has stated that design and development of the HTT-40 is proceeding and Vayu learns that metal cutting is to begin “shortly.”

Design engineers at HAL’s ARDC are confident that the HTT-40 will not only meet the IAF’s requirements fully, but also that the type would have considerable advantages over the Pilatus aircraft. Scoffing at “rumours” that the HTT-40 is more expensive than the PC-7 Mk II, a HAL executive said that while the Pilatus costs Rs 37 crore per unit, the HTT-40 would be for Rs 34.5 crore per unit, of which only the powerplant and ejection seats are imported at an FE of Rs 6 crore. Most importantly, while the Swiss government forbids employment of any armament on its aircraft, the indigenous equivalent will have six weapon stations underwing and a centreline station for a targeting/reconnaissance pod. The IAF could certainly employ the indigenous trainer for light attack and COIN tasks as a secondary role. The Air Chief, however, has been vocal in his rejection of the HTT-40, saying that there was “no need for it.” Further, he said “we have the Pilatus PC-7. It’s a proven aircraft. The project HAL plans is from scratch. Our indications are that the costs will be too high. There is no need for all this.” Chairman HAL stated in his interview with Vayu, “most of the preliminary design, including configuration studies and sizing, cockpit layout and wind tunnel model testing have been completed… any cost comparison with other basic trainers should be on the basis of life cycle costs, ensuring maintenance support for the next 30 years, in which HAL will be competitive.”
For a different view, check Shiv Aroor’s recent post at Livefist