An Autonomous Wide Area Search Munition (AWASM) is developed by Lockheed Martin for the USAF. The program is integrates a two-way data link in precision guided miniature loitering missile to enable wide area search and destroy. Under the proof-of-concept demonstration the company is integrating a data link into a wide area search munition, to transmit detected target information to a Command & Control (C2) authority and receive engagement authorization for one of the previously detected targets. AWASM will use a Laser Detection and Ranging (LADAR) seeker to automatically determine target aimpoints using demonstrated Automatic Target Acquisition algorithms. The munition will be compatible with F-16, F/A-22, Joint Strike Fighter, B-1 and B-2 aircraft. It will also be able to dispense from a Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) rocket or an Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missile.
Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS)
The Low Cost Precision Guided Rocket concept has evolved as a response to a US Army Low-Cost Precision Kill initiative, started in 1996. The idea was simple – strap a laser seeker on a 2.75″ Hydra 70 rocket. Originally, Hydra 70 was originally designed as a family of rockets, used for area suppression, but with additional sophistication, it is transformed into a high precision, low-cost weapon, which provides the precision of a hellfire missile with significantly less collateral damage. The rocket’s blast-fragmentation warhead is also more suitable for urban warfare and low-intensity conflict.
 General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products and BAE Systems designed the M151Guided Warhead Block I modification for the 70mm rocket. This warhead retains the same fuse and warhead section of the standard M151, adding a mid-section which includes four semi-active laser seekers are embedded in the wing roots of forward canards, which are used for flight control. The Distributed Aperture Semi-Active Laser Seeker (DASALS) technology utilizes an array of four fixed detectors, which provide the same accuracy at a lower cost, compared to a gimbaled seeker. The complete assembly is emplaced between the warhead and rocket motor assemblies. The modified warhead length is extended from 4.2 cm to 90.9 and increase in weight from 4.2kg to 8.9kg. M151 Block I is currently under development and is scheduled to enter low rate initial production by 2006. Subsequent improvements of other Hydra 70 warheads and elements are planned for future production blocks.
General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products and BAE Systems designed the M151Guided Warhead Block I modification for the 70mm rocket. This warhead retains the same fuse and warhead section of the standard M151, adding a mid-section which includes four semi-active laser seekers are embedded in the wing roots of forward canards, which are used for flight control. The Distributed Aperture Semi-Active Laser Seeker (DASALS) technology utilizes an array of four fixed detectors, which provide the same accuracy at a lower cost, compared to a gimbaled seeker. The complete assembly is emplaced between the warhead and rocket motor assemblies. The modified warhead length is extended from 4.2 cm to 90.9 and increase in weight from 4.2kg to 8.9kg. M151 Block I is currently under development and is scheduled to enter low rate initial production by 2006. Subsequent improvements of other Hydra 70 warheads and elements are planned for future production blocks.
The Guided APKWS technology demonstration program was launched in 2002 and until September 2004 completed five flight tests, hitting targets at ranges of 1,500 to 5,500 meters.
AMAP Protection System
IBD unveiled its new Advanced Modular Armor Protection (AMAP) composite armor concept, follow-on to their combat proven Modular Expandable Armor System (MEXAS) protection, which has provided basic protection suite for over 12,500 combat vehicles worldwide, AMAP, utilizes ultra-fine powders made from nano-particle ceramics to create thinner, lighter but tougher ceramic modules. AMAP is already utilized for a number of new applications including the protection kits for the Italian army’s MLV, the Norwegian CV-9030 and Swedish CV-9040 armored vehicles. New add-on armor suits are on development for Patria’s 8×8 AMV IFV and command vehicles, scheduled for deliveries to the Finnish and Polish armies.
Command Post Of the Future (CPOF)
The latest trend in C2 tech is Command Post Of the Future (COPF), a system currently deployed at division level, enabling division and brigade commanders to discuss and collaborate when processing information, share ideas, and attend virtual meetings without assembling at one place. As of October 2006, over 500 units are operational with US forces in Iraq.
CPOF runs on a commercial off-the-shelf computer workstation with three screens that provide a shared environment that distributes, manipulates and displays, current operational information about the locations of all friendly units, known enemy forces, and relevant operational plans. Information, including images and data, is seen in two and three dimensions across the distributed workspace. Commanders can be better informed and thus make better decisions, by sharing situational awareness and collaborating with headquarters.
Commanders attending the virtual meeting do not have to attend in the same location, or even the same country, to discuss and draw on the same map. CPOF was developed as a technology demonstration by DARPA. The prototype was deployed with the 1st Cavalry division and is currently operating in Baghdad, connecting the division HQ and five brigades. DARPA is expanding the system with the introduction of advanced visualization tools such as multi-screen video wall, video and audio conferencing and online collaboration tools, allowing brigade commanders to communicate, collaborate and share information. The first unit receiving the enhanced CPOF was the 3rd US Infantry Division. The program transitioned from DARPA to the Army in February 2006. CPOF is now managed by PM Battle Command at Ft. Monmouth, NJ, which directs the program’s deployment, sustainment and feature development for the Army. In May 2006, the U.S. Marine Corps launched an engineering design to determine how CPOF could be integrated into its Combat Operations Centers. CPOF was also used in the U.S. Air Force’s Joint Expeditionary Force Experiment 06 (JFEX 06) at Langley AFB, Va., and the U.S. Joint Forces Command Urban Resolve 2015 series of experiments in October 2006.
CPOF enables forward command elements to reduced staff to operate C2 systems. In the distant future, advanced CPOF systems will eliminate parts of the brigade’s Tactical Operations Centers (TOC) primarily the forward and assault TOC which could be transformed into virtual TOCs. COPF relies on wideband data-communications links currently available to the Army, via military and commercial satellite communications services. The commander’s battleboard is interfaced to the system supporting all communication, collaboration, and information feeds he needs.
The system is maintained as “liquid information” in database format, which separate the data from the viewing space. This method enables faster visualization and optimal maintenance of large volumes of constantly changing information. The system gathers real-time and near-real-time feeds from multiple C2 applications. Constant monitoring of the battlefield is provided, by tracking the combat elements on maps or satellite photos and video feeds from battlefield sensors, following enemy forces through intelligence reports, ground observations, forward units or UAVs. Commanders no longer have to call on the radio to check the status of each unit. CPOF support commercial presentation style briefings, including map, photos and video. The participants can respond, sketching out their comments on the shared “Battleboard” presented in each location and at the central CP’s video wall. The Agile Commander program provided a scalable, reconfigurable operator environment which enabled commanders to access all command post information and functions anywhere, anytime, utilizing advanced MOSAIC and Global Mobile networking.
October 6, 2011: As part of the planned enhancements under a $78 million two year contract awarded to the manufacturer, General Dynamics C4, CPOF’s collaboration capabilities will be expanded, with users able to see and share information from multiple control systems, including ground, aviation, logistics, fires and airspace control systems. The system will also integrate the ‘next-generation command and control architecture’, increasing the number of concurrent users sharing the same information from hundreds to thousands. This will allow users who are purposely or inadvertently disconnected from the network to continue their collaborative efforts without interruption to operations or loss of data. The work done to enhance the collaborative command and control capabilities for the CPOF system directly supports the Army’s Mission Command Collapse initiative in which several mission command and control systems are collapsed into a consolidated product line.
Aladin Mini UAV
 Designed as a Miniature Aerial Vehicle (MAV), Aladin is currently operational with recce units of the German Army. The MAV is powered by an electrical motor. It has a takeoff weight of 3 kg. Typical missions of 45 minutes are flown over 5 km range, at an altitude of 30 – 200 meter above ground. Aladin is designed for autonomous missions. It carries an integral EO payload which can be replaced by other mission specific payloads. The control station comprises a 2D or 3D for navigation and mission planning, which also includes obstacle avoidance, based on a 3d terrain model, monitoring displays, video displays and digital recording modules.
Designed as a Miniature Aerial Vehicle (MAV), Aladin is currently operational with recce units of the German Army. The MAV is powered by an electrical motor. It has a takeoff weight of 3 kg. Typical missions of 45 minutes are flown over 5 km range, at an altitude of 30 – 200 meter above ground. Aladin is designed for autonomous missions. It carries an integral EO payload which can be replaced by other mission specific payloads. The control station comprises a 2D or 3D for navigation and mission planning, which also includes obstacle avoidance, based on a 3d terrain model, monitoring displays, video displays and digital recording modules.
Active Defense System (ADS)

IBD developed an active protection concept utilizing a kill mechanism based on blast effect. The system is already implemented in two programs, AAC developed by Akers for the Swedish MOD and Shark, developed in cooperation with Thales, for the French Army.
blast The system uses laser warning sensors to spot threats at very close range (five meters). The threat warning is handed over to the countermeasures array, located in strategically located multiple modules, which create a hemispherical coverage of the protected platform. Based on the threat parameters, the best location is selected for activation, launching an explosive charge which creates a strong blast effect but without fragments, which counteracts with the incoming projectile (IBD claims the blast countermeasures are effective against both CE and KE threats).
The intercept is performed at a very close range (up to two meters). The choice of such a close range is derived from the requirement to minimize collateral damage or threat to nearby troops. (This is also evident in another German development – the CLARA reactive armor by Dynamit Nobel). The operating parameters of the ADS require substantial base armor to protect the vehicle from fragments resulting from the intercept, which maintain substantial residual kinetic energy to create some damage to soft skinned vehicles. The system is undergoing testing and was already proposed for two ADS programs currently considered by European armies.
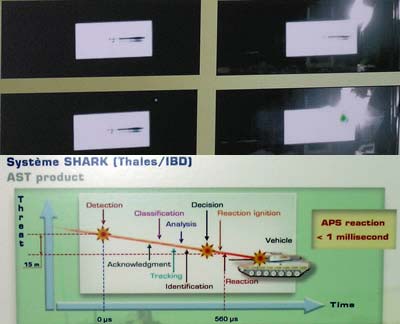
SHARK Active Protection System
The SHARK active protection system is developed under cooperation between Thales and IBD. It is designed to protect armored fighting vehicles from shaped charge (RPGs and anti-tank missiles) and IED while degrading the potential threat of KE threats. The system utilizes the distributed architecture developed by IBD, which provides full 360 degrees hemispherical coverage, with distributed, overlapping sensor-countermeasures modules located all around the vehicle. Each module covers a specific sector, detecting any threat fired toward the vehicle and engaging it by blast effect at close-in range, specifically designed to comply with operational restrictions of urban environment. SHARK requires about 560 microseconds to detect, analyze, and launch a countermeasure. At this time, an incoming missile or RPG will travel some 15 meters – which is the minimum safety zone which should be protected by the system. The French developers claim that by using distributed modules and close-in intercept, their system achieves much faster reaction time, about 40% less of competing systems, while operating at much shorter range.
The system is designed to protect from multiple attacks. Maintaining reaction time of less than one milisecond (from threat detection to kill), engaging targets at at close range (about 15 meters) and in different directions. SHARK is designed to operate under all weather conditions and is agnostic to the vehicle’s or turret attitude.
IQBOT
The IQbot was designed to provide surveillance and first response capability in area contaminated by chemical, biological or radiological / Nuclear (CBRN) agents. The platform uses proven systems adapted from Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) robotic platforms providing high mobility in urban and rural terrain, including stair climbing and obstacle crossing. At a total weight of 400kg, (150kg payload) IQbot reaches a maximum road speed of 25 km/h and up to 10 km/h in rough terrain and operate for over 5 hours.
The platform mounts video cameras and proximity sensors, sending up to four video streams, back to the control unit. Payloads include Thermal / IR camera, electronic countermeasures and a range of sensors, including chemical, biological and radiological sensors and probes. For the CBRN surveillance mission it is equipped with the HAPSITE chemical detection and identification system, providing rapidly deployable remote sensing capability. Alternative payloads can accommodate biological sensors, radiological sensors, thermal / IR cameras and electronic countermeasures. The robot is remotely controlled from a hand held unit which can also be linked back to a network for net-centric connectivity. The complete set can be transported in an EOD vehicle.
Close-Range Active Defense (CARD)
Close-Range Active Defense (CARD) munitions are proposed by RUAG as means for active protection of armored fighting vehicles, threatened by infantry and anti-tank weapons at close or medium range. When deployed in urban combat, such vehicles are often engaging targets at very close ranges, where employment of the main gun or automatic cannons is not effective. For these situations, CARD offers an effective means to deliver fragments at close range, even behind protection.
CARD uses controlled fragmentation technology which is already implemented in the 81 and 60mm MAPAM (Mortar Anti-Personnel Anti-Material bombs) which guarantees that all fragments are of the same size and energy, contributing to increased lethality and well defined safety zones (for accompanying troops). Each CARD is lauched from standard smoke launchers to a range of 35m’ and is programmed to burst at a height of 2-7 meters above surface, generating over 1,000 0.3 gram fragments. CARD can be launched from standard smoke launchers which can be turned into an active defense system. RUAG plans to have CARD in low rate production for testing by late 2004 and will be able to deliver the system by mid 2005.
Unmanned Systems in BOA Program
The French BOA program will include several unmanned vehicles for airborne and ground applications. Among the systems considered are Autonomous Ground Vehicles (UGV) which will be used to carry sensors and various loads in assistance to dismounted infantry equipped with FELIN suits. Systems under considerations are small robots, (EOD vehicle size) used for short range sensor deployment, surveillance of urban environments, and larger weapons carriers, used either in tele-operated or autonomous operating modes. The program evaluates various concepts including human-robot interactions.
One such concept is focused on the use of a wearable display computer, which is also considered for FELIN. With operator assistance, the robot will optimize the negotiation of obstacles, focusing on the main points of interest, while scouting an objective. The computer will be able to display images captured by the sensors, generate maps of the interior in buildings using of distance measuring devices or detect moving objects.
The organization of autonomous control architecture will be examined, with evaluation of navigation and orientation (concepts including inertial measurements, vision and telemetry, odometry and GPS). Aspects unique to the cooperation among groups of robots will be studied. mobility means to be examined, will include combinations of wheeled, tracked and legged mobility systems. Under a different program the French OPART system was developed as a video sensor dedicated for robotic applications. The sensor utilizes two video images taken through a split lens which provides both wide field of view and aimable narrow field of view imaging. The system is considered for applications such as unstructured road boundaries tracking and target acquisition.
CyberEye Mini UAV
This mini UAV was developed by Cyberflight as a lightweight remotely piloted or autonomous platform, launched from a 40 meter runway, at a weight of 25 kg on missions up to 100km. The UAV is operated by an autonomous control system supporting up to six hours mission patrolling predefined GPS waypoints. The CyberEye has an on-board digital recorder which enables “silent” operations (without electronic emission). CyberEye can patrol or loiter over a designated target at low speed (20-25 mph) at altitude of up to 10,000 feet. Another UAV developed by the company is Cyber-1. Utilizing an advanced bi-plane design, Cyber-1 is smaller and more efficient than CyberEye. The aircraft weighs 8.27kg (including 12 pound payload), and can operate from a 15 m’ strip, to a range of 50km. Cyber-1 also uses an autonomous GPS based mission control system, and digital recording for silent missions. Maximum speed is 100 km/h and operational height is 1,000 feet above ground.
LIQUIDMETAL Amorphous Alloys
The modification of the physical properties of armor of steel made, or titanium based alloys, is achieved through a new fabrication technique called Liquidmetal. This process produces advanced alloys at lower temperature, offering twice the strengths characteristics of titanium at a processing efficiency of plastics.
Liquidmetal was one of the possible approaches which can be used to compose the basic structural assembly of FCS. Such structure could use integral, composite laminate armor elements and modular add-on composite armor suites, which could be upgraded or modified to counter specific threats. In September 2006 Liquidmetal Technologies received a US$2 million US Navy contract to fund a 24 months development program of Titanium based composite alloys. The new alloy will have very high strength, corrosion resistance and net-shape forming capabilities based on proprietary Liquidmetal alloy technology. Such alloys could have various applications ranging from fasteners to lightweight structures used by both defense and commercial industries. Lockheed Martin – Missile and Fire Control Systems is sub-contractor on this project.
Since those days Liquidmetal Technologies has partnered with other DOD agencies and contractors to enhance defense and tactical product performance. Alloys have now demonstrated 2-3 times the strength of both stainless steel and titanium, yet can be molded like plastic into complex shapes and parts.
Liquidmetal alloys and composites material properties are highly beneficial for numerous Space, Air, Land and Sea applications. The Liquidmetal optimized process, chemistry and atomic structure enables near net-shape processing characteristics making the fabrication of highly sophisticated and complex structures possible while eliminating most secondary machining and processing.
Liquidmetal also have done work with the US Army developing penetrators and armor piercing shells. The Kinetic Energy Penetrator (KEP) rod designed to replace Depleted Uranium (DU) penetrators currently used in armor piercing ammunition, due to its high density and self-sharpening behavior. Ballistic tests conducted by the Army have proven that the Liquidmetal composites exhibit self-sharpening similar to the DU KEP, but environmentally benign KEP rods. The high strength and lightweight attributes of Liquidmetal alloys will enable the development of lighter, smaller and more cost effective ammunition.
The properties of amorphous alloys as developed by Liquidmetal Technologies, Inc. make these matrerials suitable for many defense applications. Properties such high yield strength, high Hardness and high strength to weight ratio and superior elastic limit, compared to metallic structures. As a non magnetic material, with high resistance to corrosion and wear and unique acoustical properties, it also has specific applications in naval and underwater applications. Low melting temperature enables net-shape casting and fabrication process similar to plastics.
Liquidmetal Technologies’ amorphous alloys were initially developed from research jointly funded by NASA, the California Institute of Technology and the U.S. Department of Energy. The alloy presented a new class of material that is sparking an industrial revolution much in the same way as the invention of steel or plastics.
AGILITY – Mobile SATCOM Terminal
The AGILe Information Transfer abilitY – AGILITY on-the-move satellite terminal was developed by BAE Systems, in partnership with Roke Manor Research and QinetiQ. Utilizing electronically beam-steered antenna packed into a 40 cm sphere, the static antenna offers full hemispheric coverage and high bandwidth. The system offers secure and assured satellite communications (satcom) to-and-from land vehicles, aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles and naval vessels. The system has near instant deployment and satellite acquisition times. It automatically tracks the satellite, by implementing platform motion compensation.
The antenna structure is based upon a modified dodecahedron comprising 40 identical triangular tiles, each of which contains six cross-dipole elements. This design approach provides a high proportion of active elements for any steer direction. The modular tile concept enables reconfiguration to meet semi-conformal applications for aircraft or unmanned aerial vehicles. Beamforming and steering are performed at element level using custom MMIC (Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuit) devices specifically designed for AGILITY. These act as digitally controlled phase shifters, as well as providing an LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) on receive and PA (Power Amplifier) on transmit.
For communications on the move, an on-board inertial navigation sensor provides real-time measurements of the vehicle attitude and heading. These are used to calculate a beam pointing angle that compensates for the vehicle orientation. From this, the phase data is calculated and distributed to the MMICs on each tile. This operation is conducted over 20 times per second to providing agile beam steering. The system is expected to be ready for fielding by 2004.
Hornet Real-Time Targeting (HART)
The US Navy and Boeing are developing the Hornet Autonomous Real-time Targeting (HART) system, based on the Hornet’s on-board radar imaging capability. The system will enable aircrews to designate targets and deploy JDAM independent of pre-planned mission requirements. The Navy plans to deploy HART on aboard the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet. The HART precision guided kit includes an infrared sensor, a processor, and image-matching software. Using the Active Electronically Scanned Array radar system built into the Super Hornet, the pilot will be able to acquire and designate a target and transfer a reference image of the target to the weapon. After release, the weapon compares the reference image to that in its sensor’s field of view, guiding it to the point designated in the target scene. Boeing plans to begin low rate initial production of the HART in late 2006, with initial operational capability expected in December 2007. Boeing expects to produce about 6,600 HART units through 2011.
Hammer – Armament Air-Sol Modulaire (AASM)

An advanced precision guided air/ground weapon – Armament Air-Sol Modulaire, is developed by Sagem for the French Air force. The weapon dubbed ‘Hammer’, is designed in both glide and powered configurations, offering standoff capability exceeding 50 km when released from high altitude and 15km, in low altitude flight profile. AASM is designed to replace AS-30L laser guided missiles, and complement the Scalp EG, as a low cost weapon. The basic configuration uses a GPS/INS navigation kit, strapped to a standard 500 pound warhead (such as Mk 82 bomb). The initial configuration which will be fielded by early 2005, will offer JDAM-class precision, and all-weather capability, while follow on versions that are scheduled for fielding by 2007 will also include passive IR guidance which will offer an accuracy compatible with laser guided weapons. A laser-guided version of the AASM is also in development, enabling attack of targets of opportunity, including mobile targets.
In a first operational test conducted December 1, 2006 GPS/INS guided AASM was dropped from a Mirage 2000 N at the Biscarosse Launch Missile Test Center in the southwest region of France. The weapon was dropped at low altitude, high speed and under strong load factor, thus validating the AASM’s GPS/INS guided version’s performance in difficult, tight maneuvers.
In May 2008 MBDA France and Sagem Défense Sécurité signed a cooperation agreement shifting the sales and marketing of Sagem’s modular air-to-ground weapon (AASM) to MBDA. and infrared guidance for tactical missiles. Under the terms of the agreement, MBDA France will be responsible for all sales and marketing of the AASM family developed by Sagem Défense Sécurité. The two companies will also combine their respective areas of expertise to form a close partnership for the joint development of future versions of the AASM family.
Sagem has been awarded a contract to supply 3,400 AASM Air-to-Ground Weapons to equip the French Air Force Rafale aircraft. The order also covers the initial order of 680 weapons. This latest order follows the initial contract won by Sagem for 750 AASMs to be delivered to the French air force. The AASM has been deployed on Rafale fighters in Afghanistan for the last two years.
The basic version will integrate an upgraded, GPS module and be prepared to receive an Inertial/GPS and laser terminal guidance systems. The new multi-sensor guided version expands the AASM family, which already includes two versions qualified on the Rafale multirole combat aircraft, with inertial/GPS or inertial/GPS/infrared guidance. In particular, the new version enables precision strikes against moving targets. The AASM weapon family comprises kits and augmentation kits fitting 1,000, 500, 250, and 125 kg bombs.
Launched from standoff distance, day or night and in all weather conditions, the AASM offers a range exceeding 50 kilometers. The AASM can be released at low altitude, and can also be fired off-axis, in relation to the aircraft’s flight path. It offers very high precision and strikes its target vertically, a feature suited to asymmetrical conflicts. This makes it the perfect weapon for combat in difficult terrain or urban environments, for both planned missions and opportunity fire.















