Merkava Mk4 represents the third evolutionary phase of the Merkava program. The Mk-4 is equipped with a 120 mm gun but the new gun is designed to sustain higher pressures, generating higher muzzle velocities which are an essential feature for advanced kinetic energy ammunition. The Merkava Mk4 can accomodate various 120mm ammunition types, including 120mm APFSDS-FS (kinetic) rounds, and their training derivatives, HEAT (hollow-charge) types and anti-personnel/anti-material ammunition which have already been used in combat operations with previous Merkava types. The tank will also be able to accommodate the Lahat missile as it becomes operational. The loader can load the gun from a fully automated, fire-proof magazine which accommodates up to 10 ready rounds and deliver up to four types of ammunition types to the loader.
Merkava Mk4 represents the third evolutionary phase of the Merkava program. The Mk-4 is equipped with a 120 mm gun but the new gun is designed to sustain higher pressures, generating higher muzzle velocities which are an essential feature for advanced kinetic energy ammunition. The Merkava Mk4 can accomodate various 120mm ammunition types, including 120mm APFSDS-FS (kinetic) rounds, and their training derivatives, HEAT (hollow-charge) types and anti-personnel/anti-material ammunition which have already been used in combat operations with previous Merkava types. The tank will also be able to accommodate the Lahat missile as it becomes operational. The loader can load the gun from a fully automated, fire-proof magazine which accommodates up to 10 ready rounds and deliver up to four types of ammunition types to the loader.
The tank is equipped with a modern fire control and sighting system which includes computerized ballistic calculations and compensations, a dual axes stabilized gunner sight and a dual axis stabilized commander panoramic sight, both equipped with an advanced FLIR and TV channels for day and night operation. The system is equipped with an improved tracking system which enables tracking of moving targets, such as tanks, helicopters, vehicles or soldiers. It also enables locking the sight and gun on targets when the tank is on the move, utilizing the ultra-fast gun stabilization and electrical turret drive system. Merkava Mk-4 is believed to be protected by a new type of hybrid armour, which can be conformed from modular elements, to match specific threats. The Mk-4 retains the hull design of the previous Merkava versions.
 The tank also utilize the Battle Management System (BMS) designed by Elbit Systems’ ElOp – the system is providing fast communication networking between the commander and subordinate units, and enables the crew to plan missions, navigate and continuously update their situation awareness. The system also enables recording and debriefing the operation, by utilizing the tank’s digital recorder. The Merkava Mk4 is equipped with the new VDS-60 digital data recorder produced by Vectop, it records and restores the sight images and observation data collected during the mission. The capture of such images can also be shared by other elements, which are networked with the Weapon Integrated BMS (WINBMS), to enable reporting of enemy targets.
The tank also utilize the Battle Management System (BMS) designed by Elbit Systems’ ElOp – the system is providing fast communication networking between the commander and subordinate units, and enables the crew to plan missions, navigate and continuously update their situation awareness. The system also enables recording and debriefing the operation, by utilizing the tank’s digital recorder. The Merkava Mk4 is equipped with the new VDS-60 digital data recorder produced by Vectop, it records and restores the sight images and observation data collected during the mission. The capture of such images can also be shared by other elements, which are networked with the Weapon Integrated BMS (WINBMS), to enable reporting of enemy targets.
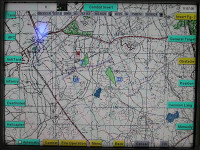
This concept is rapidly becoming an essential part of the “digitized land forces” integrated battlefield concept, combining tanks, anti-tank and combat helicopters in a combined task force at various levels. Each crew member has an individual flat-panel color displays showing the status of systems each member is responsible for. The gunner and commander can also see the sight images on their individual screens. The commander can use his display for map navigate, orientation and reporting. For example, the driver can see a rear and side view of the tank from the closed compartment. This capability is derived from a new, and unique system called Tank Sight System, developed by Vectop. The system provides video coverage the tank’s surroundings in day and night. It improves safety, especially when traveling backwards and in conditions where the driver’s visibility is impaired. Merkava Mk 4 uses four cameras installed in hardened cases embedded outside the tank. These cameras are providing full peripheral view displayed on high resolution monitors installed at the driver’s position and in the fighting compartment.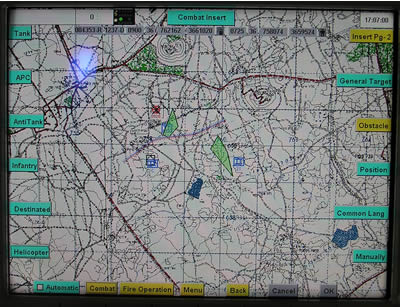 Another feature provided by the “computerization” of the Merkava Mk4 is the introduction of “integrated training capability”, providing the crew and unit a sophisticated training environment based on their tanks and readily available in the field. This capability will be integrated with the “virtual scenario” a set of virtual terrain features, friendly and enemy elements, and “intelligent” behaviors based on pre-set maneuvers, doctrinal concepts etc. All will be presented to the tank crew, and unit members, through their observation systems, sights and sensors, to support a comprehensive training scene in the field.
Another feature provided by the “computerization” of the Merkava Mk4 is the introduction of “integrated training capability”, providing the crew and unit a sophisticated training environment based on their tanks and readily available in the field. This capability will be integrated with the “virtual scenario” a set of virtual terrain features, friendly and enemy elements, and “intelligent” behaviors based on pre-set maneuvers, doctrinal concepts etc. All will be presented to the tank crew, and unit members, through their observation systems, sights and sensors, to support a comprehensive training scene in the field.
Unique among the main battle tanks of the world, the Merkava design features a front-mounted power pack, which presents a heavy mass in the forward area, which protects the crew from enemy attack. This configuration also cleared room at the rear section for a safe exit and enough space to carry a few fully armed infantrymen, in addition to the crew. The rear access hatch allows for the quick and safe exit of injured crewmen or pickup of wounded soldiers for evacuation.
The engine pack is easily replaced. The tank is powered by the new General Dynamics GD833 1,500-horsepower direct injection, liquid cooled diesel engine, (co-produced in the USA by General Dynamics and MTU). This type is also powering the French Leclerc MBT. This powerful weighs 1.9 tons net, and 4.9 tons with its entire power-pack. This powerful engine affords the tank greater mobility than the previous versions, which had the 900 and 1,200-horsepower engines. The tank utilizes an electric turret and gun control system, designed by Elbit Systems, which comprises two electrical brushless motors, produced by Bental Industries.
 Merkava 4 is expected to be equipped with an active full perimeter defense, which utilizes, among other capabilities, warning against laser-guided threats. Further improvements include the Trophy active protection system, which is currently under advanced engineering phase. The Mk-4 like its predecessors, is also equipped with a central filtering system designed by Kinetics, which maintains positive air pressure at the fighting compartment, for protection in a chemical biological and radiological (CBR) environment. The system also provides air conditioning for individual crew members (micro-cooling) and for the entire cabin, as well as auxiliary power when positioned at “silent watch” for battery recharging. Special modifications installed on Merkava Mk4 are preparing the tank to operate in urban environment of the Low Intensity Conflict. The merkava Mk 4 could soon mount a new Remotely controlled weapon station, mounting an 7.62mm machinegun, replacing the commander’s weapon station. Several designs have already been tested. An example of the ORCWS was shown by Elbit Systems. (below)
Merkava 4 is expected to be equipped with an active full perimeter defense, which utilizes, among other capabilities, warning against laser-guided threats. Further improvements include the Trophy active protection system, which is currently under advanced engineering phase. The Mk-4 like its predecessors, is also equipped with a central filtering system designed by Kinetics, which maintains positive air pressure at the fighting compartment, for protection in a chemical biological and radiological (CBR) environment. The system also provides air conditioning for individual crew members (micro-cooling) and for the entire cabin, as well as auxiliary power when positioned at “silent watch” for battery recharging. Special modifications installed on Merkava Mk4 are preparing the tank to operate in urban environment of the Low Intensity Conflict. The merkava Mk 4 could soon mount a new Remotely controlled weapon station, mounting an 7.62mm machinegun, replacing the commander’s weapon station. Several designs have already been tested. An example of the ORCWS was shown by Elbit Systems. (below)
Picture on this page: Top: AFP, Defense-update. Below: IDF Spokesman.
Defense-Update Merkava 4 Updated Gallery: