Produced by Thales, The TRC 5010P is a Personal Role Radio (PRR) designed for inter-squad communications and urban warfare. The lightweight (150 gr) radio set is operating in the 420-450 MHz UHF frequency band offering short range communications – 150 m in urban areas and up to 800 m in open terrain. The system has 20 pre-selected channels and has special features to enable intra-squad communications, including a squad leader pre-emption capability. The unit is operated by a remote finger PTT or by pushbuttons placed on the radio itself. A specially designed lightweight headset are provided for the system, for added Autonomy. The radio can operate for 16 hours with NiMH rechargeable battery or for more than 24 hours, with standard high power AAA alkaline cells. Low cost system
Commander’s Digital Translator
Phraselator is a truly mobile PDA based translator which can be used by foot patrols and combat teams, developed by VoxTech. The system uses a Intel XScale 400 PXA255 processor running Windows CE powered pocket PC, loaded with 1,000 spoken English phrases and their local language equivalents. US troops in Afghanistan and Iraq have used this device for humanitarian assistance, in medical, security, travel, and law enforcement assignments.
Another translation application adapted to combat use is the Forward Area Language Converter (FALCon), an Optical Character Recognition and machine translation system integrated on a portable computer (laptop PC) for translation foreign languages documents. the system was designed and developed by the Army Research Laboratory, based on National Security Agency (NSA) know-how. It provides the Military Intelligence Community a quick and reliable way to translate and analyze captured documents. FALCon can translate up to 47 languages including Arabic and Asian languages and is being used in both Iraq and South West Asia.
SYRANO – UGV
BOA will also employ a range of military robots, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) and autonomous ground vehicles (UGV). Developments in this field were pursued by GIAT, with the implementation of the EBC mine breaching system, installed on the AMX-30B2DT tank.  Current operation is enabled at a range of 300 meters which will be extended soon to 2,000 m’. Another autonomous robot called Syrano is designed to collect battlefield information, primarily in urban scenario. It will have an operating range of 10km and enable target acquisition and designation of targets which are obscured or hidden from to the firing units, or beyond line of sight. Syrano in development by GIAT, Sagem and CAP Gemini.
Current operation is enabled at a range of 300 meters which will be extended soon to 2,000 m’. Another autonomous robot called Syrano is designed to collect battlefield information, primarily in urban scenario. It will have an operating range of 10km and enable target acquisition and designation of targets which are obscured or hidden from to the firing units, or beyond line of sight. Syrano in development by GIAT, Sagem and CAP Gemini.
SAFT To Supply Power Sources For Land Warrior Suites
Saft has already supplied power sources for the Land warrior program. The company based its design on the high performance, compact format MP series prismatic Li-ion cells, which are already in use with many existing military radio communications customers. A key advantage of the MP cell is its unique rectangular shape which gives it an extremely high capacity, compared to conventional cylindrical cells – a single prismatic cell has some 20 per cent higher volumetric energy density than an equivalent pack of cylindrical cells. The battery performs in an operating temperatures range from -30°C to +60°C (in discharge), and will retain 95 per cent of its charge after one month’s storage. These batteries are supplied in a ruggedized, water resistant metal housing, complete with protection circuitry, state of charge indicator and a commercial off the shelf connector.
Intelligent Penetration Vehicle
Developed in France, Vipere is an autonomous, intelligent “snake robot” optimized for counter-terrorist warfare as well as covert, observation, offensive or neutralization missions. The unique caterpillar like propulsion system uses multiple legs which provides continuous and stable movement over rough terrain and through dense vegetation and sand climbing stairs or crawling through narrow pipes or caves.
The back-packable Vipere measures only few in diameter. Vipere is battery powered to endure missions of 1 – 2 hours. Each Vipere carries a payload of several kilograms, including video cameras, communications equipment as well as mission dependent payloads such as incapacitating agents, explosives etc.
Strix Precision Guided 120mm Mortar Launched Weapon
Projectile guidance technology has already been used since 1994 in 120 mm mortars, with the IR homing Bofors/Saab Strix. This weapon can engage targets at a range of 7 km, operates in an autonomous heat-seeking mode which can intelligibly recognize targets and discriminate targets among decoys and burning targets. Strix has been in service with the Swedish Army since 1994 and also has been ordered by the Swiss Army. It is optimized as an anti-armor weapon, defeating targets with top-attack.
Software Defined Radios
The next generation Software Defined Radio (SDR) will provide the answer to the demand for flexible and versatile systems, and efficient joint operations communications as this new generation of military radios will swiftly adapt to different protocols or “waveforms”. SDR will use a common core programmable radio, which will be able to communicate with existing generation wireless systems, as well as new and enhanced systems. One of the main advantages of these new systems is their ability to be programmed to link with other communications systems, such as commercial radios, cellular systems (wireless phones) and standard telephones. The most advanced SDR currently in development is the Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS), under development for the US armed forces. These systems will augment, and later replace all existing wireless communications systems currently in service.
SCARAB
Designed for armored scout and liaison missions, SCARAB armored vehicle is equipped with a powerful automotive system to provide speed and agility. The vehicle uses a 6,370cc OM906LA 240hp Mercedes Benz 6 cylinder diesel engine and an Allison MD 3560 six speed automatic transmission. At a maximum battle weight of 11.1 tons and a payload capacity of 2.5 tons, Scarab offers high protection level. The basic protection offers all-round 7.62 AP protection and mine protection, including AT mines, including self-forging fragments mines such as the TMRP-6. Additional appliqué armor can enhance the protection level to withstand medium cannon rounds. The vehicle can be configured to meet changing requirements, such as airborne operations, border patrols, and reconnaissance and armored command vehicles.
Tomahawk Block IV Tactical Cruise Missile (TLAM)
The latest version of the 32 year old Tactical Tomahawk is the Tomahawk Block IV cruise missile, currently in full rate production at Raytheon. Like its predecessors, the missile is equipped with a conventional warhead and offers flexible targeting and loitering capabilities. The new missile is supported by an improved mission planning and platform weapons control capabilities.
 Deployed with surface ships and submarines, TLAM is equipped with a two-way satellite data link that enables the missile to respond to changing battlefield conditions. The strike controller can “flex” the missile in flight to alternate targets preprogrammed before launch, or redirect it to a new target. This targeting flexibility includes the capability to loiter over the battlefield, awaiting a more critical target. The missile can also transmit battle damage indication imagery and missile health and status messages via the satellite data link. And, for the first time, firing platforms have the capability to plan and execute GPS-only missions.
Deployed with surface ships and submarines, TLAM is equipped with a two-way satellite data link that enables the missile to respond to changing battlefield conditions. The strike controller can “flex” the missile in flight to alternate targets preprogrammed before launch, or redirect it to a new target. This targeting flexibility includes the capability to loiter over the battlefield, awaiting a more critical target. The missile can also transmit battle damage indication imagery and missile health and status messages via the satellite data link. And, for the first time, firing platforms have the capability to plan and execute GPS-only missions.
Block IV will also introduce an anti-jam GPS receiver for improved mission performance. The Block IV costs less half the price of a newly built Block III missile. Another variant of the Tomahawk is the Penetrator under development as part of a US Navy Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration (ACTD). This missile variant is equipped with a penetrating warhead and a new Hard Target Smart Fuze, also sponsored by DTRA. Further enhancements could also see the use of Morphing Wings, which would enable efficient flight at multiple speeds and altitudes without sacrificing performance as is currently the case when operating off the optimized cruise point.
OneWay Transparent Armor / Labock Industries
 This transparent armor enables the occupants inside the vehicle to shoot out freely, while stopping
This transparent armor enables the occupants inside the vehicle to shoot out freely, while stopping
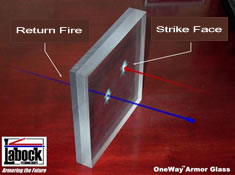 projectiles coming from outside, from penetrating the shield. OneWay armor glass can be designed to provide Level II and III protection. This material weighs less than comparable armor glass, and offers additional advantages, such as blast protection and high transparency (90%). Another advantage of the OneWay glass is the fact that the impact affects only a small area of the window, while the entire area remains functional and transparent.
projectiles coming from outside, from penetrating the shield. OneWay armor glass can be designed to provide Level II and III protection. This material weighs less than comparable armor glass, and offers additional advantages, such as blast protection and high transparency (90%). Another advantage of the OneWay glass is the fact that the impact affects only a small area of the window, while the entire area remains functional and transparent.
SAG Weapon Station Shield
S.A.G (Save A Gunner) weapon station bullet proof shield is designed for installation on the roof of the vehicle, providing protection for the gunner. The completeturret assembly weighs only 200 pounds and is designed to interface precisely with standard Humvee rotating turret rings. It can be installed by two people in less than one hour. The turret is produced from G-LAM nano-fiber material and offers protection from multi hits of up to 12.7mm AP ammunition.
OFRO – Outdoor Security Robot
OFRO is designed to carry out outdoor surveillance of protected sites, such as airports, correctional facilities, power stations and nuclear plants and military and government installations. The robot is dispatched to respond to alarms, and should be able to determine the actual cause of an alarm and take proper countermeasures. The robot is equipped with several sensors, including thermal camera, ultrasonic distance measurement systems, and GSM (wireless phone) communications. The tracked robot weighs 50 kg and uses electrical propulsion.
Storm Shadow / SCALP EG Cruise Missile
Storm Shadow / SCALP EG is an advanced, conventionally armed cruise missiles currently operational with the RAF and French Air Force. It is optimized for pre-planned attacks on static targets, whose positions are accurately known before the mission. (bridges, airbases, radar installations, communications hubs, port facilities, bunkers etc.) With long-range and efficient stealth design, Storm Shadow can eliminate strategic components of enemy defensive systems, without risking manned aircraft. The missile weighs 1,300 kg and is powered by a turbojet engine, offering mission range in excess of 250km The missile is equipped with the BROACH (Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge) unitary warhead for maximum effect against hard targets.
Since the missile flies at subsonic, and at very low altitudes, the selection of ingress rotes is extremely important, to avoid most of the enemy threats. The missile can be launched from low or medium altitude, and descend to its optimum low-level cruising altitude to avoid radar detection. Navigation is fully autonomous, incorporating digital TERPROM (TERrain PROfile Matching) aided by GPS and inertial sensors.
Terminal guidance uses the passive imaging infra-red (IIR) sensor with Autonomous Target Recognition (ATR) system. On its terminal phase, as it approaches the target, the missile is positioned where it will be able to positively locate the target and identify the specific points where it should strike. At the terminal phase of its flight the missile climbs to a medium altitude, jettison its nose cap to enable the IIR seeker to view the target. As the seeker acquires the target and compare it with files stored in its memory, the aim point is identified and tracked and is used as the reference for the missile terminal guidance.
The target acquisition process is constantly repeated with a higher resolution data set to refine the aim point, as the missile closes in on the target. Tracking will continue against this refined aim point until the precise target location is identified. On impact, the missile should be positioned at the optimum dive angle selected during mission planning. The Broach warhead activated with a precursor charge perforating the target structure, and any soil covering, and the follow through penetrator warhead continue to penetrate inside the target and detonated after a pre-selectable delay.
The missile is also equipped with an “abort” mechanism, which is initiated if conditions for potential high collateral damage are expected. In such situation, the mission will be aborted if the target identification and acquisition process is unsuccessful. In this case the missile will fly to a predetermined crash site.
To support Storm Shadow / SCALP EG missions, complex and pre-determined missions require such information to be prepared well in advance at the Command Headquarters. Following an Air Tasking Order, the operating squadron prepares the mission data file with the pre-planned data, together with the latest operational intelligence. The flight path of the missile is planned before the mission on a dedicated system which supports up to 16 missiles. This capability enables the pilot to launch the missile from a relatively wide “window”, which does not expose him to risk of detection and engagement with enemy air defenses. The missile is launched as a “fire and forget” weapon, representing minimum additional workload for the air crew of two-seater and single-seat aircraft.
Storm Shadow is currently operational with RAF Tornado GR4 aircraft and French Mirage 2000D aircraft. It is cleared for the Eurofighter Typhoon and Dassault Rafale as well as Mirage 2000-B2 Mk2 aircraft and designed to be compatible with the F-35 JSF. Around 30 missiles were deployed by 617 “Dambusters” squadron in Operation Iraqi Freedom in 2003 against high-value, heavily fortified targets such as communications bunkers, with great success. Further deployment of the missile is planned with the Typhoon (Eurofighter). The Scalp EG version is operational with French Air Force Mirage 2000D and Rafaele aircraft and is planned for deployment with the Naval version of the Rafale, deployed on the Charles de Gaulle aircraft carrier. Italy and Greece ordered the Scalp EG for Italian Tornados and Greek Mirage 2000-5 Mk2. The UAE ordered the missile variant designated Black Shaheen.
Recent enhancements of the Storm Shadow / SCALP EG include the capability to relay target information just before impact, utilization of one-way (link-back) datalink, to relay battle damage assessment information back to the host aircraft. This upgrade is already under development under a French DGA contract. Another feature planned for insertion into the weapon is in-flight retargeting capability, utilizing a two-way datalink. Future derivatives of the missile are the naval surface and submarine launched versions. These vertically launched land attack missiles will have high commonality with the air launched version, and equip the future FREMM frigates and fleet of Barracuda class submarines of the French Navy. The Naval derivative of the Storm Shadow / SCALP EG is scheduled to enter production in 2006.
Saudi Arabia will equip its Eurofighter Typhoon aircraft with standoff, MBDA Storm Shadow precision attack weapons. The weapons package ordered for the RSAF will also include the Brimstone anti-armor missile. For the air-to-air role the Saudis opted for the IRIS-T short range AAM, from Diehl BGT Defence, this missile is also being used by the German Air Force. According to news sources, the weapons package for the Typhoons could be worth over $1.8 billion.
ODIN Mini UAV
 ODIN is a miniature ducted-fan powered, vertical takeoff and landing miniature autonomous vehicle (Mini-UAV) designed for day/night observation in an urban environment. With a range of few kilometers and endurance of over 60 minutes Odin can hover over a target or fly at low speed following advancing troops, to provide valuable, real time images from the target. The drone is highly automated and has an auto-pilot function, making it easy to operate. The ODIN will be carried in a backpack and operated from a miniature PDA sized ground control station which controls the flight path, receives real-time video feed and distribute it to other users in the FELIN equipped unit.
ODIN is a miniature ducted-fan powered, vertical takeoff and landing miniature autonomous vehicle (Mini-UAV) designed for day/night observation in an urban environment. With a range of few kilometers and endurance of over 60 minutes Odin can hover over a target or fly at low speed following advancing troops, to provide valuable, real time images from the target. The drone is highly automated and has an auto-pilot function, making it easy to operate. The ODIN will be carried in a backpack and operated from a miniature PDA sized ground control station which controls the flight path, receives real-time video feed and distribute it to other users in the FELIN equipped unit.




















