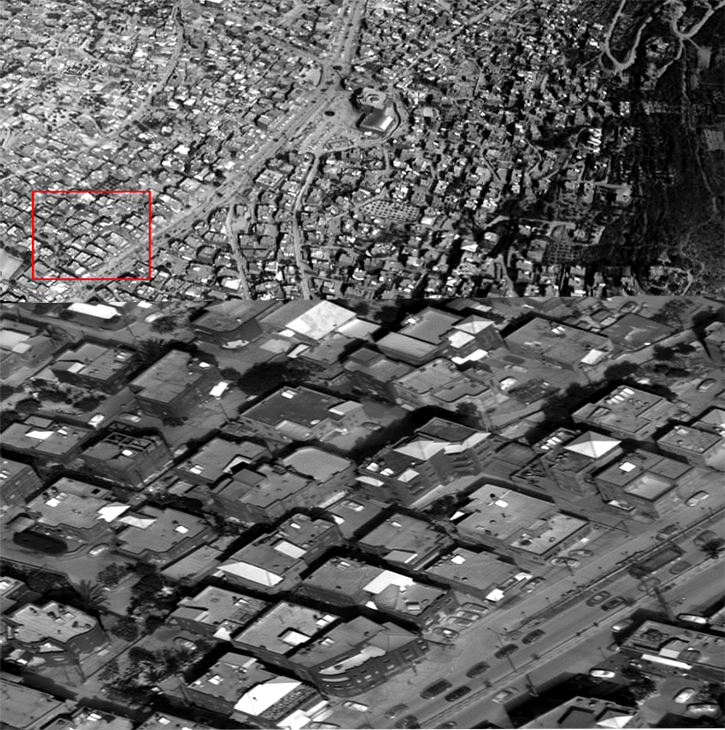
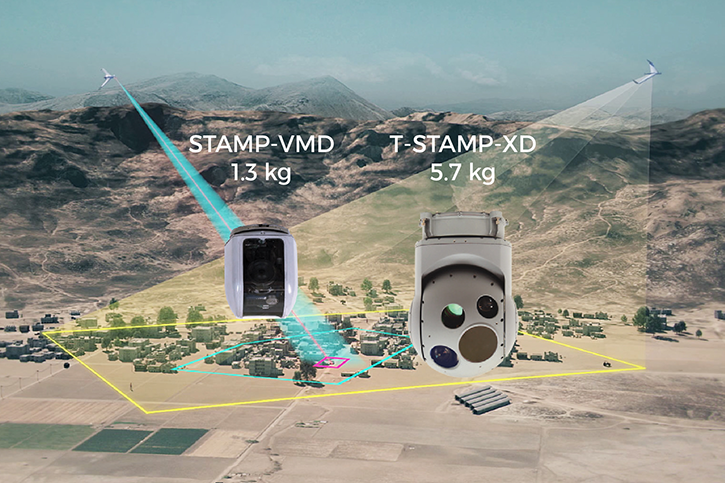
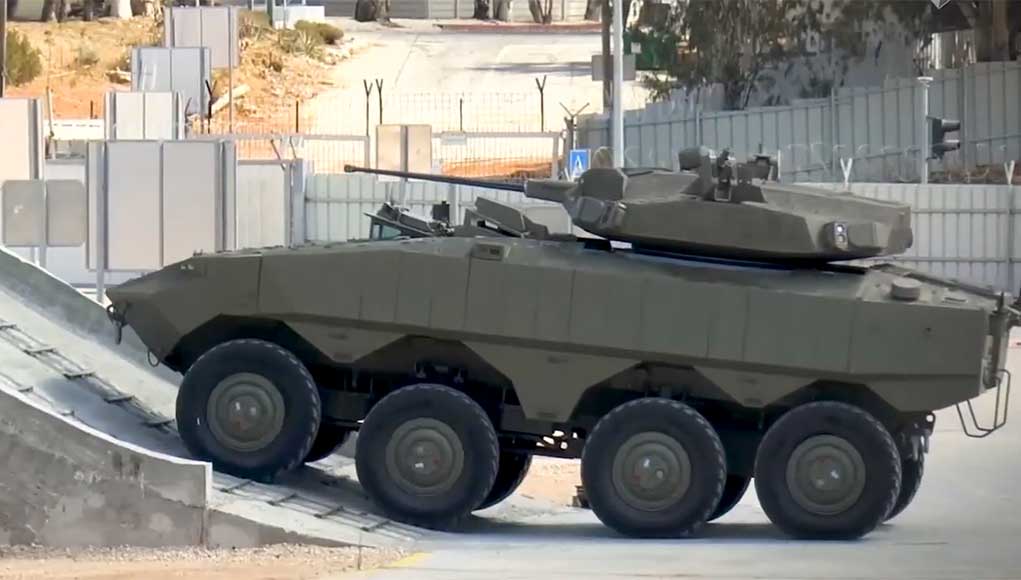
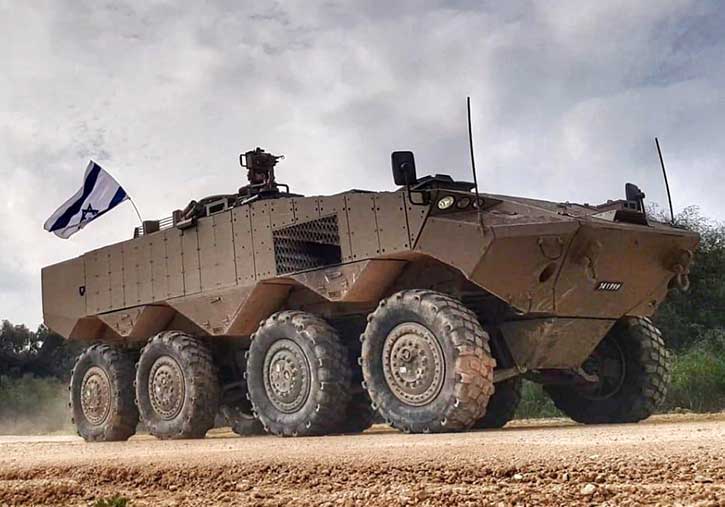
WASHINGTON: The US Navy awarded Marinette Marine Corporation (MMC) a contract to design and produce the next generation small surface combatant, the Guided Missile Frigate (FFG(X)). MMC is part of the Fincantieri Marine Group (FMG), a subsidiary of the Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri. The contract covers the production of up to 10 Guided Missile Frigates.
The current award at the amount covers the detail design and construction (DD&C) of the base ship. If all options are exercised under this contract, nine more ships will be built at a total value of $5.58 billion. The total cost of the lead ship will be $1.281 billion, with $795 million of that covering the shipbuilder’s detail design and construction costs and the rest covering systems delivered by the US Government. The lead ship of this (yet unnamed) class will be delivered in 2026 and is expected to reach initial operational capability by 2030. Nine additional ships will be ordered until 2024. By 2025 the Navy will decide how and who will produce the remaining ten ships of this class.
The FFG(X) will be based on the successful ‘European multi-purpose frigate’ designed by Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri and the French Naval Group. Ships of this design are already operated by the French, Italian, Egyptian and Moroccan and will also be supplied to Brazil. FREMM is a versatile ship built with the multi-mission capability to conduct air warfare, anti-submarine warfare, surface warfare, electronic warfare, and information operations.
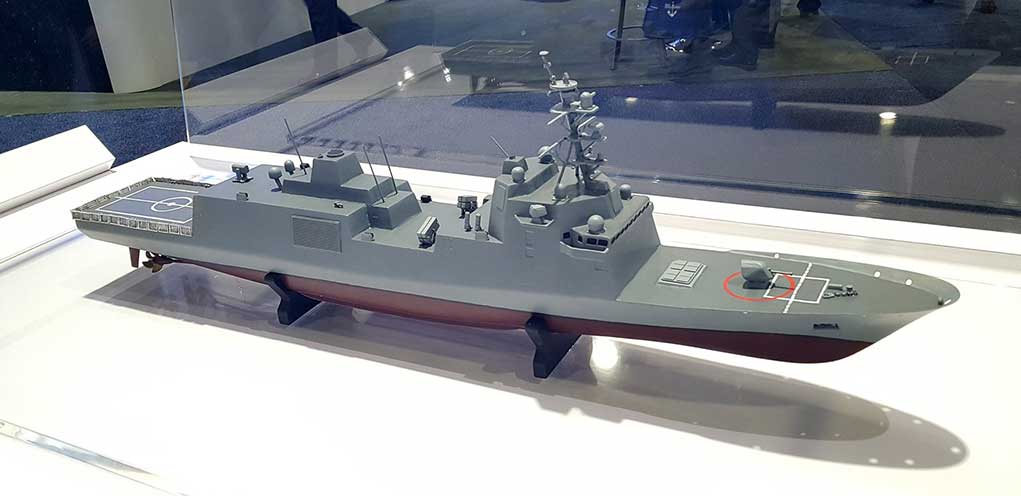

The vessel will be 151 meters long, with 21 m’ overall beam. It will be powered by a Combined diesel-electric and gas (CODLAG) system offering a sustained maximum speed above 26 knots, or economic (electrical powered) cruising at 16 kt. The ship will accommodate up to 200 sailors and equipped to operate at a range of more than 6000 nm.
Unlike the European vessels of this class, the FFG(X) will be equipped with US-made systems derived from existing destroyers, specifically the Enterprise Air Surveillance Radar (EASR based on Raytheon’s SPY-6 Air and Missile Defense Radar), Baseline Ten (BL10) AEGIS Combat System from Lockheed Martin, which will also produce the Mk 41 Vertical Launch System (VLS). Other government-furnished equipment includes communications systems, BAE Systems’ MK 57 Gun Weapon System (GWS), countermeasures, EW/IO area, and design flexibility for future growth.


The ship is designed with space and power for future enhancements, including the addition of laser weapons, to enhance point defense, and to free up VLS tubes for offensive weaponry. Each ship will also accommodate one manned helicopter and one unmanned air vehicle and will have storage and deck space to support all manned and unmanned vertical-lift aviation operated by the US Navy.
The acquisition process for FFG(X) began in 2017. Since then the Navy has worked closely with Industry to balance cost and capability. The accelerated selection process took less than a year, as the Navy released the FFG(X) DD&C Request for Proposals to industry on June 20, 2019. “Throughout this process, the government team and our industry partners have all executed with a sense of urgency and discipline, delivering this contract award three months ahead of schedule.” James Geurts, assistant secretary of the Navy for research, development, and acquisition said. Marinette Marine was in competition with four other shipyards for the contract: Austal USA of Alabama; Bath Iron Works in Maine; Huntington Ingalls of Mississippi: and Lockheed Martin in Maryland. Following the selection, the Wisconsin yard plans to invest up to $100 million to maintain a production rate of two FFG(X) frigates per year.
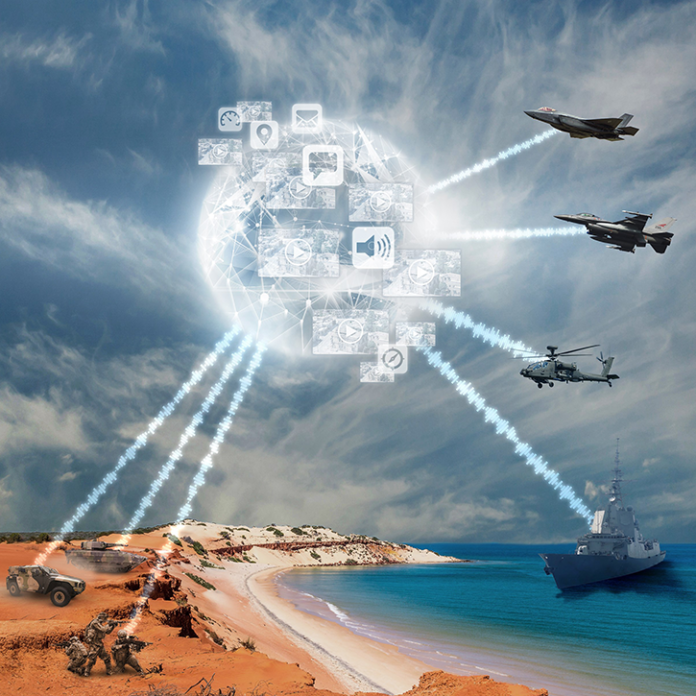

















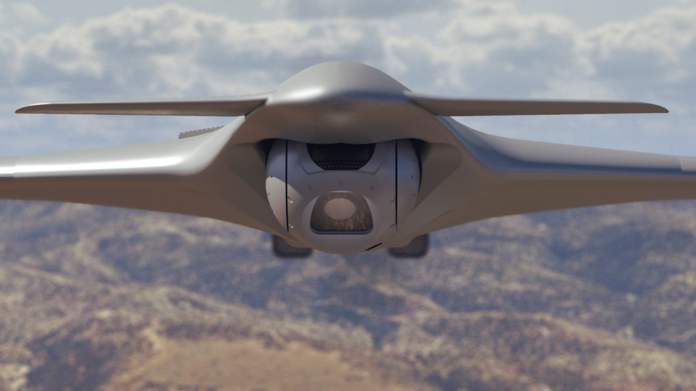
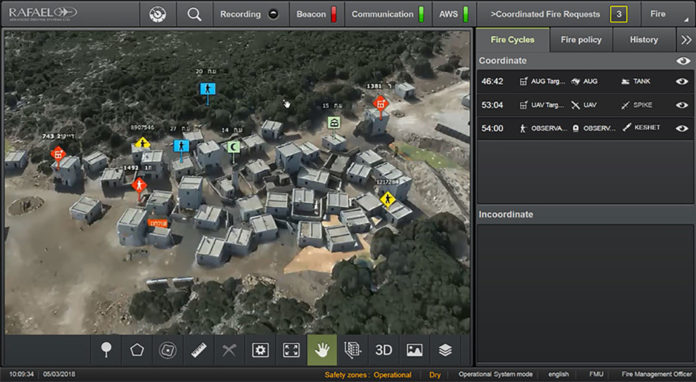
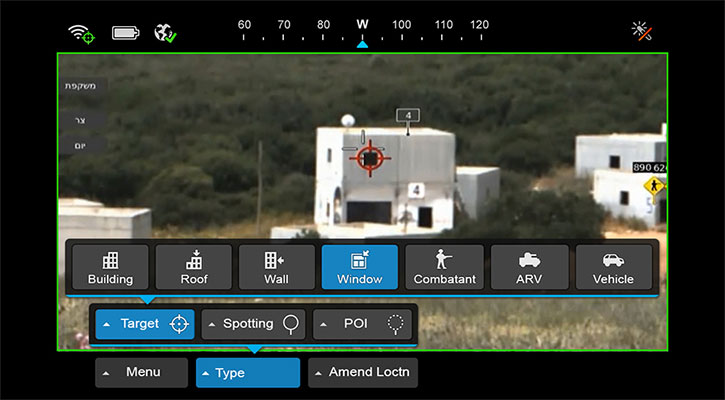
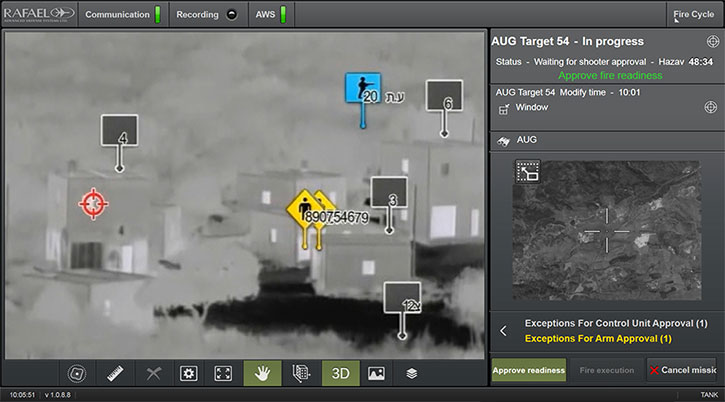
 OPAL is comprised of a range of different hardware Line Replaceable Units (LRU) configures and optimized for each application, platform or end-user. This solution delivers an advanced application middleware with optimized applications and, where needed, advanced networking and connectivity services. OPAL features high processing and graphic capabilities, and deliver essential battlefield services to the participating members, enabling all users to share a common operating picture in real-time and to communicate in the same language.
OPAL is comprised of a range of different hardware Line Replaceable Units (LRU) configures and optimized for each application, platform or end-user. This solution delivers an advanced application middleware with optimized applications and, where needed, advanced networking and connectivity services. OPAL features high processing and graphic capabilities, and deliver essential battlefield services to the participating members, enabling all users to share a common operating picture in real-time and to communicate in the same language.