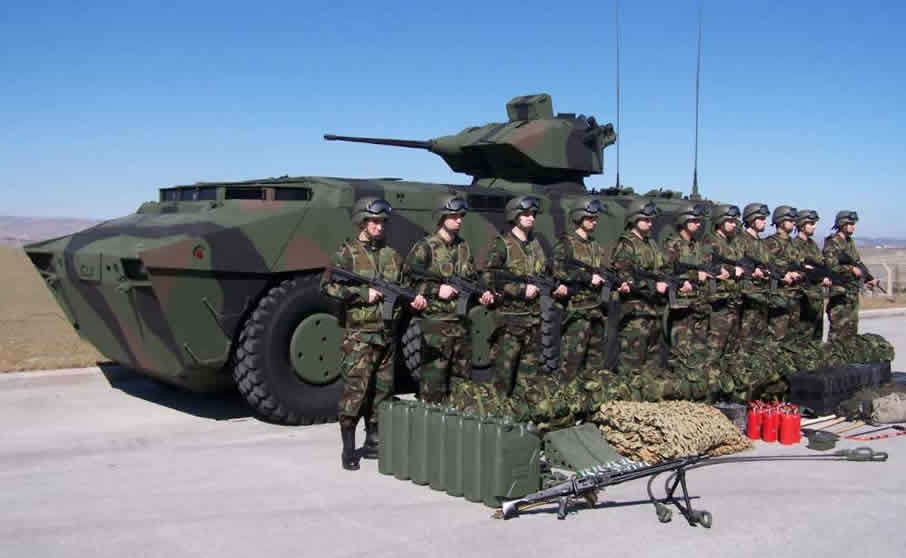
The Malaysian procurement of 257 wheeled armored vehicles from the Turkey has moved a step forward with the signature of ‘letter of offer and acceptance’ by DRB-Hicom Defence Technologies (Deftech) for the design, development and manufacture of the vehicles. Deftech will be FNSS’ local partner, manufacturing and supporting the $559 million program in Malaysia. FNSS is a joint venture between BAE Systems, Inc., and Turkey’s Nurol Holding. Four months earlier Deftech received the letter of award from the Malaysian government, for the design, development, manufacturing, commission, supply and delivery of these vehicles.
The government award covers seven years of deliveries and is valued at RM 7.55 billion (about $2.51 billion). How this cost is compared with the $559 million Deftech has committed to pay FNSS, and why Deftech will get four times that amount has yet to be explained. Certainly, 80% mark-up is a bit too high by any standard. At a cost of $2 million apiece, including development of 12 versions, the AV8 looks highly competitive, but at nearly $10 million per unit it becomes extremely expensive by any standards (read more). The justification of spending much of the money on infrastructure development in Malaysia cannot justify the cost either. Development costs that could be separated from the production contract could justify the difference, but the ‘letter of offer acceptance’ covers the development in the $599 package.
The AV-8 vehicle selected by the Malaysian military is based on the FNSS-designed PARS 8×8 multi-purpose, multi-mission, wheeled armored vehicle. The contract includes technology transfer arrangements to Deftech and logistics support for the Malaysian army, positioning the vehicle and its 12 variants to become Malaysia’s first indigenous family of 8×8 armored wheeled vehicles.
Deftech already operates a vehicle production line at the Malaysian city of Pekan in Pahang State where FNSS designed ACV-300 (M-113 derivatives) are assembled. According to Nail Kurt, chief executive of FNSS, the new project builds on the successful industrial partnership with Deftech, producing 259 Adnan Armored Combat Vehicles and eight 120mm ACV Mortar Carriers for the Malaysian Army under a contract signed in 2000. Deftech is scheduled complete the delivery of the last 48 Adnan ACVs order underway since 2008.
“This effort will not only benefit the Malaysian army but will also further develop the indigenous capability in Malaysia,” John Kelly, vice president of exports and international business for BAE Systems’ Land and Armaments sector, said. “BAE Systems, Inc., actively looks to support FNSS in its ambition to market its land vehicle expertise globally.” FNSS is currently offering the PARS 8×8 to other potential customers in the region, including Indonesia. The UAE has also been interested in the vehicle for several years.