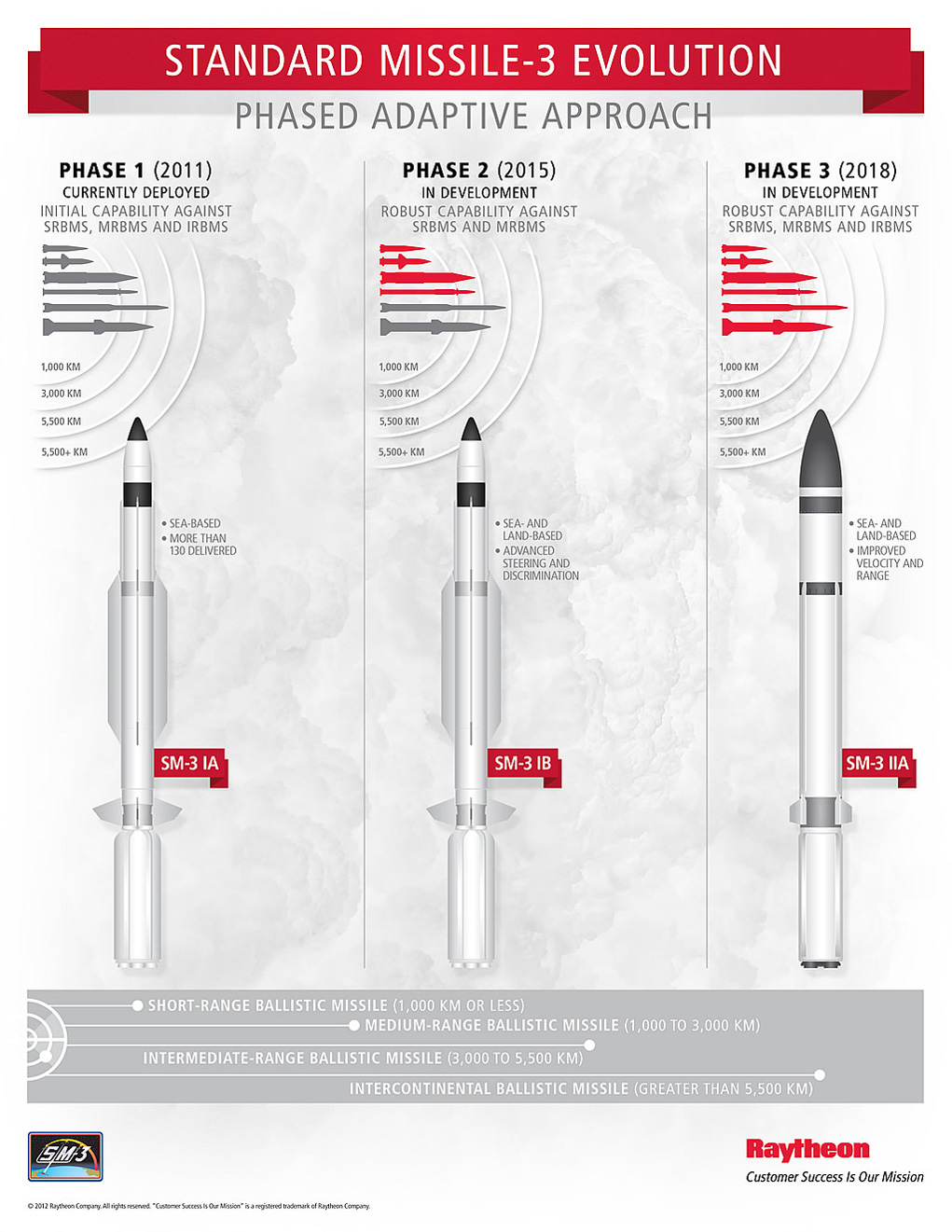
Subscribe to see past eventsFor Events taking place before April 2016 – Click Here
Travelling abroad? Try our Travel Partner Agoda – attractive deals – recommended hotels
 FIDAE 2016 31 March – 3 April 2016, Santiago, Chile
FIDAE 2016 31 March – 3 April 2016, Santiago, Chile
 Marine South, 6-7 April 2016, MCB Camp Lejeune, NC, USA
Marine South, 6-7 April 2016, MCB Camp Lejeune, NC, USA
 Border Security Expo – 13-14 April 2016, San Antonio, TX, USA
Border Security Expo – 13-14 April 2016, San Antonio, TX, USA
 SPIE DSS (Defense, Security & Sensing) 17-21 April 2016, Baltimore MD, USA
SPIE DSS (Defense, Security & Sensing) 17-21 April 2016, Baltimore MD, USA
 DSA 2016 – April 18-21 2016, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
DSA 2016 – April 18-21 2016, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
 Counter Terror expo 2016 19-20 April, 2016 Olympia, London
Counter Terror expo 2016 19-20 April, 2016 Olympia, London
 Marrakech Aero Expo & Air Show 27-30 April, 2016 Menara Airport, Marrakech, Morocco
Marrakech Aero Expo & Air Show 27-30 April, 2016 Menara Airport, Marrakech, Morocco
 QUAD-A, 27-30 April 2016, Atlanta, GA
QUAD-A, 27-30 April 2016, Atlanta, GA
 XPONENTIAL (AUVSI) 2-5 May 2016, Ernest N. Morial Convention Center New Orleans, MS, USA
XPONENTIAL (AUVSI) 2-5 May 2016, Ernest N. Morial Convention Center New Orleans, MS, USA
 SOFEX 2016 May 9-12, 2016, Amman, Jordan
SOFEX 2016 May 9-12, 2016, Amman, Jordan
 IDEB 10-12 May 2016, Bratislava, Slovakia
IDEB 10-12 May 2016, Bratislava, Slovakia
 Sea-Air-Space (Navy League) 16-18 May, 2016 Gaylord National Convention Center, National Harbor, MD. USA
Sea-Air-Space (Navy League) 16-18 May, 2016 Gaylord National Convention Center, National Harbor, MD. USA
 4th International Fires Conference 17-18 May 2016, Beit Hatothan – Zikhron Ya’akov, Israel.
4th International Fires Conference 17-18 May 2016, Beit Hatothan – Zikhron Ya’akov, Israel.
 The two-day event is organized by the Israeli Artillery Association in cooperation with the IDF Ground Forces HQ and the Artillery Corps. The conference will discuss lessons learned from recent conflicts and future developments related to artillery and fires. It will focus on a range of themes including, missiles, rocket artillery and precision fires, air/ground coordination, deployment of static and precision networked fires, cyber aspects of modern weapons and more.
The two-day event is organized by the Israeli Artillery Association in cooperation with the IDF Ground Forces HQ and the Artillery Corps. The conference will discuss lessons learned from recent conflicts and future developments related to artillery and fires. It will focus on a range of themes including, missiles, rocket artillery and precision fires, air/ground coordination, deployment of static and precision networked fires, cyber aspects of modern weapons and more.
 Future Armoured Vehicles Eastern Europe (AUVSI) 17-18 May 2016, Prague, Czech Republic.
Future Armoured Vehicles Eastern Europe (AUVSI) 17-18 May 2016, Prague, Czech Republic.
 The Future Armoured vehicles event returns to Prague, featuring the development plans and armoured vehicle focus of Eastern Europe, with speakers from the military and MODs of Czech Republic, Slovakia, Estonia, Poland, Austria, Spain, Netherlands, as well as industry briefings covering the latest technologies.
The Future Armoured vehicles event returns to Prague, featuring the development plans and armoured vehicle focus of Eastern Europe, with speakers from the military and MODs of Czech Republic, Slovakia, Estonia, Poland, Austria, Spain, Netherlands, as well as industry briefings covering the latest technologies.
 Rapid 2016 – Printing, Scanning, Additive manufacturing 17-19 May, Orange County Convention Center, Orlando, FL. USA
Rapid 2016 – Printing, Scanning, Additive manufacturing 17-19 May, Orange County Convention Center, Orlando, FL. USA
 ITEC 2016 (Defense, Training & Simulation expo) 17-19 May 2016, ExCel, London, UK
ITEC 2016 (Defense, Training & Simulation expo) 17-19 May 2016, ExCel, London, UK

 Helicopter Technology Eastern Europe 2016 19-20 May 2016, Budapest, Hungary
Helicopter Technology Eastern Europe 2016 19-20 May 2016, Budapest, Hungary
Helicopter Technology Eastern Europe 2016 returns for a second successful year, this time to Budapest, Hungary on the 19th and 20th May 2016. Last year’s inaugural event was recognized for excellence by many leading defence forces in both central and Eastern Europe and hosted more senior heads of Air Force and Helicopter Commands than any other event in Europe. As Central and Eastern Europe continue to be a key focus for defence equipment upgrades, the rotary fleet remains a key asset in both domestic and international military operations and therefore a focused conference is essential to ensure continued advancement of capability, equipment and joint interoperability.
 HeliRussia 19-21 May 2016 – Crocus Expo, Moscow, Russia
HeliRussia 19-21 May 2016 – Crocus Expo, Moscow, Russia
 Asia Pacific China Police 20-23 May 2016, CNCC – Beijing, China.
Asia Pacific China Police 20-23 May 2016, CNCC – Beijing, China.
 Future Artillery 2016 23-25 May 2016, Radisson Blu Portman Hotel, London, UK
Future Artillery 2016 23-25 May 2016, Radisson Blu Portman Hotel, London, UK
 Humanitarian Airlift and Disaster Response Asia-Pacific 23-24 May 2016, Singapore
Humanitarian Airlift and Disaster Response Asia-Pacific 23-24 May 2016, Singapore
 SMi’s Humanitarian Airlift and Disaster Response Asia-Pacific conference will provide updates on capabilities and requirements from national militaries for humanitarian operations, detailing how civil-military cooperation is enhancing the NGO response to regional humanitarian disasters. Furthermore, the two-day programme will also address what is being done to overcome the key challenges of humanitarian logistics and what role innovative technologies have to play in enhancing the disaster response. These topics will be addressed by military speakers, civil-military coordinators, regional logistic experts and disaster response organisations, therefore bringing together all key regional stakeholders for disaster response exercises.
SMi’s Humanitarian Airlift and Disaster Response Asia-Pacific conference will provide updates on capabilities and requirements from national militaries for humanitarian operations, detailing how civil-military cooperation is enhancing the NGO response to regional humanitarian disasters. Furthermore, the two-day programme will also address what is being done to overcome the key challenges of humanitarian logistics and what role innovative technologies have to play in enhancing the disaster response. These topics will be addressed by military speakers, civil-military coordinators, regional logistic experts and disaster response organisations, therefore bringing together all key regional stakeholders for disaster response exercises.
 Security Israel 2016 24-25 May 2016, TLV Convention Center, Tel Aviv, Israel.
Security Israel 2016 24-25 May 2016, TLV Convention Center, Tel Aviv, Israel.
 Naval Combat Systems 2016 24-25 May 2016, London Marriott Hotel Kensington, London, UK
Naval Combat Systems 2016 24-25 May 2016, London Marriott Hotel Kensington, London, UK
 CANSEC 2016 Canada’s Global Defence & Security Trade Show 25-26 May 2016, El Centre, Ottawa, Canada
CANSEC 2016 Canada’s Global Defence & Security Trade Show 25-26 May 2016, El Centre, Ottawa, Canada
 Hemus 2016 international exhibition for defence, anti-terror and security 25-28 May 2016, Plovdiv, Bulgaria
Hemus 2016 international exhibition for defence, anti-terror and security 25-28 May 2016, Plovdiv, Bulgaria
 KADEX 25-28 May, 2016 Astana, Kazakhstan
KADEX 25-28 May, 2016 Astana, Kazakhstan
 MilSatCom Asia Pacific 26-27 May, 2016 Singapore
MilSatCom Asia Pacific 26-27 May, 2016 Singapore
 This edition of the MilSatCom Asia-Pacific conference will provide national updates on space and MilSatCom programmes and how the development of these programmes is satisfying current critical regional requirements.
This edition of the MilSatCom Asia-Pacific conference will provide national updates on space and MilSatCom programmes and how the development of these programmes is satisfying current critical regional requirements.
 C4ISR Summit 2016 31 May – 1 June 2016, Armed Forces Officers Club & Hotel, Abu Dhabi, UAE
C4ISR Summit 2016 31 May – 1 June 2016, Armed Forces Officers Club & Hotel, Abu Dhabi, UAE
 ILA 2016 31 May – 5 June 2016, Berlin, Germany
ILA 2016 31 May – 5 June 2016, Berlin, Germany

 7th annual International Port Security Conference 1-2 June 2016, London, UK
7th annual International Port Security Conference 1-2 June 2016, London, UK
The conference aims to bring together key decision makers in the industry to discuss modern methods of port security and provide effective learning experiences for all delegates through the carefully selected expert speaker line up.
Interacting with delegates from across the globe and hearing from industry leading experts will ensure delegates are up-to-date with high priority information that enables you to best secure your seaports, civilians and means of trade. Topics to be discussed include terrorism, cyber security, resolving external threats, optimisation of technological systems, regulatory systems and change and case studies featuring some of the busiest ports from across the world. Our diverse range of topics will allow delegates to learn best practices for port security and understand further how other ports are resolving core challenges.
 UDT Global Undersea Defence technology 1-3 June 2016 Oslo, Norway
UDT Global Undersea Defence technology 1-3 June 2016 Oslo, Norway
 Aerospace & Defense Meetings – 6-9 June 2016, Seville Conference Palace, Seville, Spain
Aerospace & Defense Meetings – 6-9 June 2016, Seville Conference Palace, Seville, Spain
 Arctic Patrol & Reconnaissance 2016 7-9 June 2016, Park Inn by Radisson Copenhagen Airport, Denmark
Arctic Patrol & Reconnaissance 2016 7-9 June 2016, Park Inn by Radisson Copenhagen Airport, Denmark
 GPEC 2016 – International Police & Special Equipment Expo – 7-9 June, 2016 Leipzig, Germany
GPEC 2016 – International Police & Special Equipment Expo – 7-9 June, 2016 Leipzig, Germany
 Offshore Partol Vessels Technology 8 – 9 June, London UK.
Offshore Partol Vessels Technology 8 – 9 June, London UK.
 This inaugural OPV Technology event will focus on the new potential for OPVs within this proliferation in combat and combat support technology capabilities. The event will discuss how individual nations are working to enhance the capabilities of their coastal fleets and highlight the prospect for future cooperation and interoperability.
This inaugural OPV Technology event will focus on the new potential for OPVs within this proliferation in combat and combat support technology capabilities. The event will discuss how individual nations are working to enhance the capabilities of their coastal fleets and highlight the prospect for future cooperation and interoperability.
 Maritime Security & Coastal Surveillance Philippines – 9-10 June 2016 – Manila, Philippines
Maritime Security & Coastal Surveillance Philippines – 9-10 June 2016 – Manila, Philippines
 Fast Jet Pilot Training Eastern Europe 9 – 10 June, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic
Fast Jet Pilot Training Eastern Europe 9 – 10 June, 2016 Prague, Czech Republic
 This two-day event provides a platform to discuss the implementation of new technologies such as simulated flight training and new advanced trainer aircraft into current pilot training systems for improved interoperability amongst regional partners, as well as conversion to more modern fighter jets in the wake of higher operational demands. These topics are of special importance to countries with smaller air forces, seeking to improve interoperability and maximise the effectiveness of small fleets of jet fighters. Prague is particularly suitable for this conference as the Czech Air Force has already announced it is actively seeking to establish an international training centre for regional pilots to meet that very demand with support from NATO by 2018.
This two-day event provides a platform to discuss the implementation of new technologies such as simulated flight training and new advanced trainer aircraft into current pilot training systems for improved interoperability amongst regional partners, as well as conversion to more modern fighter jets in the wake of higher operational demands. These topics are of special importance to countries with smaller air forces, seeking to improve interoperability and maximise the effectiveness of small fleets of jet fighters. Prague is particularly suitable for this conference as the Czech Air Force has already announced it is actively seeking to establish an international training centre for regional pilots to meet that very demand with support from NATO by 2018.
 Eurosatory 2016 June 13-17, 2016, Paris Nord, France
Eurosatory 2016 June 13-17, 2016, Paris Nord, France
 Unmanned Global Systems (UGS) 2016 June 13-17, 2016, Paris Nord, France
Unmanned Global Systems (UGS) 2016 June 13-17, 2016, Paris Nord, France
 Balt Military Expo June 20-22, Amberexpo, Gdansk, Poland
Balt Military Expo June 20-22, Amberexpo, Gdansk, Poland
 Directed Energy and Next Generation Munitions 20-22 June 2016, Hyatt Regency Fairfax, Fairfax, VA.
Directed Energy and Next Generation Munitions 20-22 June 2016, Hyatt Regency Fairfax, Fairfax, VA.
 Cyber Security & Defense 22-24 June 2016, DoubleTree by Hilton Hotel Augusta, Augusta, GA
Cyber Security & Defense 22-24 June 2016, DoubleTree by Hilton Hotel Augusta, Augusta, GA
 Security Week Israel – 24-25 June 2016 – Tel Aviv, Israel
Security Week Israel – 24-25 June 2016 – Tel Aviv, Israel
 Future Armoured Vehicles Weapons Systems 28 – 29 June, London UK.
Future Armoured Vehicles Weapons Systems 28 – 29 June, London UK.
 Drawing on the operational and strategic experience of military experts, as well as the technical expertise of those at the forefront of industry and research, SMi’s Future Armoured Vehicles Weapons Systems conference shall explore the defining factors that contribute to enhanced lethality and fire superiority for land forces. An examination of emerging technologies in these key areas, ranging from the latest weapon systems, smart munitions, fire control and target acquisition, shall be combined with operational case studies and key programme updates from commanders and military project leaders, to develop definitive requirements and solutions for enhancing lethality.
Drawing on the operational and strategic experience of military experts, as well as the technical expertise of those at the forefront of industry and research, SMi’s Future Armoured Vehicles Weapons Systems conference shall explore the defining factors that contribute to enhanced lethality and fire superiority for land forces. An examination of emerging technologies in these key areas, ranging from the latest weapon systems, smart munitions, fire control and target acquisition, shall be combined with operational case studies and key programme updates from commanders and military project leaders, to develop definitive requirements and solutions for enhancing lethality.
 Mortar Systems Technology 29 – 30 June, London UK.
Mortar Systems Technology 29 – 30 June, London UK.
 This inaugural Mortar Systems Technology conference shall tackle cutting-edge mortar technologies, highlighting precision, range, lethality and manoeuvrability of mortar systems, as well as counter Fire technologies. This event, organized by SMi, will bring together opinion leaders from across the world to discuss the matters that truly matter in the realm of Mortar Systems.
This inaugural Mortar Systems Technology conference shall tackle cutting-edge mortar technologies, highlighting precision, range, lethality and manoeuvrability of mortar systems, as well as counter Fire technologies. This event, organized by SMi, will bring together opinion leaders from across the world to discuss the matters that truly matter in the realm of Mortar Systems.
 Armored vehicles latin America – 30 June – 1 July, 2016 – Sheraton Lima Hotel & Convention Center, Lima, Peru
Armored vehicles latin America – 30 June – 1 July, 2016 – Sheraton Lima Hotel & Convention Center, Lima, Peru
Travelling abroad? Try our Travel Partner Agoda – attractive deals – recommended hotels
Want to include your event in our list?
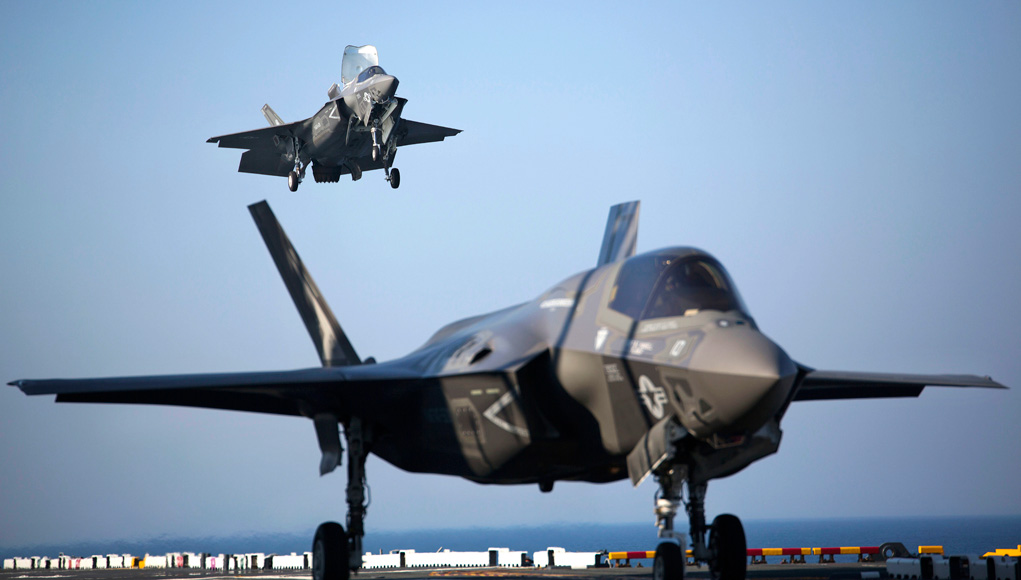
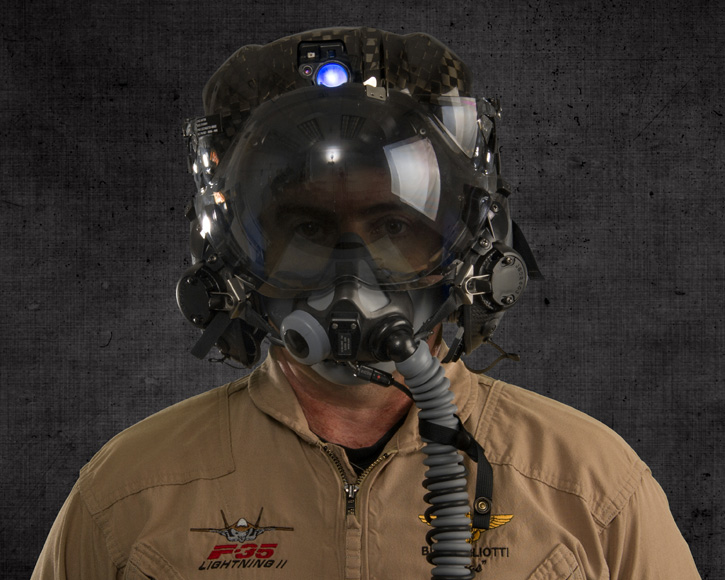
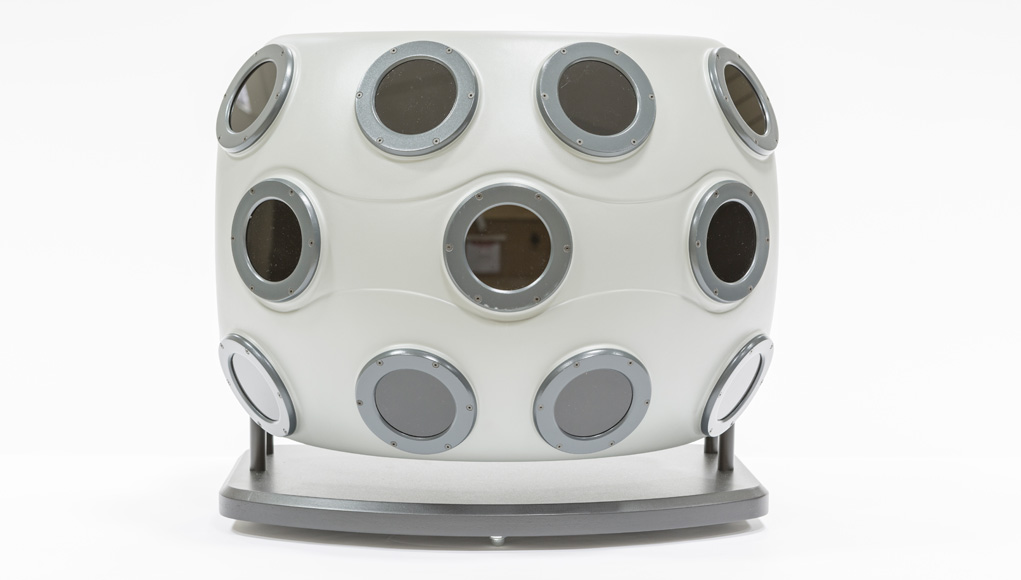













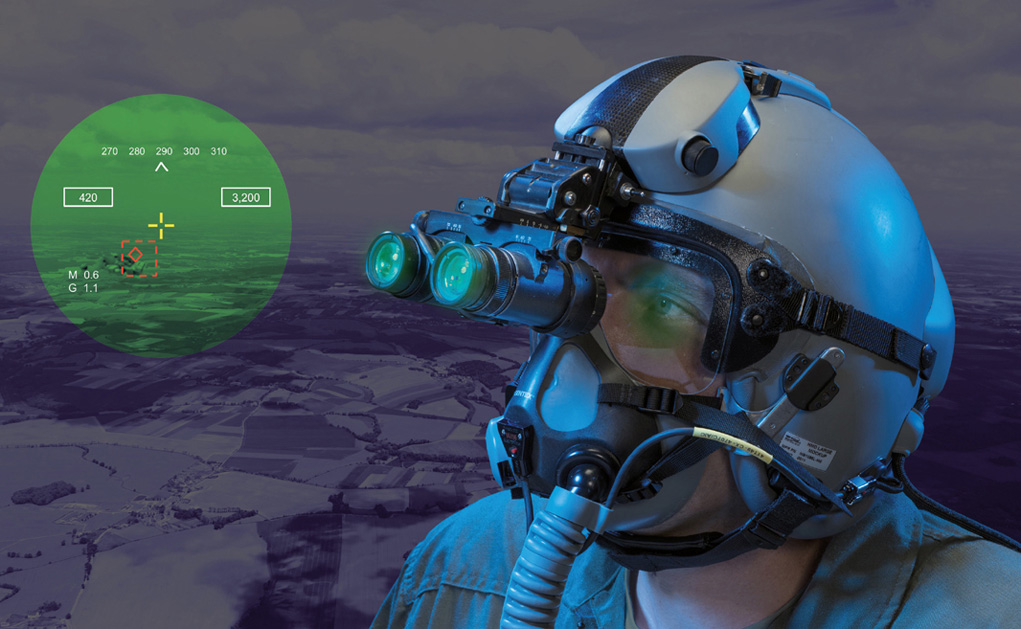
 Elbit Systems is also developing BrightNite as a primary flight sensor for helicopters, augmenting the standard Aviator Night Vision Imaging System (ANVIS) and Forward Looking Infra-Red (FLIR) used on current platforms. BriteNite enables utility helicopters to successfully perform Degraded Visual Environment (DVE) missions, including Brownout and Whiteout, in more than 90% of the nights, provides them with piloting capabilities of attack helicopters and enables a new level of operational flight.
Elbit Systems is also developing BrightNite as a primary flight sensor for helicopters, augmenting the standard Aviator Night Vision Imaging System (ANVIS) and Forward Looking Infra-Red (FLIR) used on current platforms. BriteNite enables utility helicopters to successfully perform Degraded Visual Environment (DVE) missions, including Brownout and Whiteout, in more than 90% of the nights, provides them with piloting capabilities of attack helicopters and enables a new level of operational flight.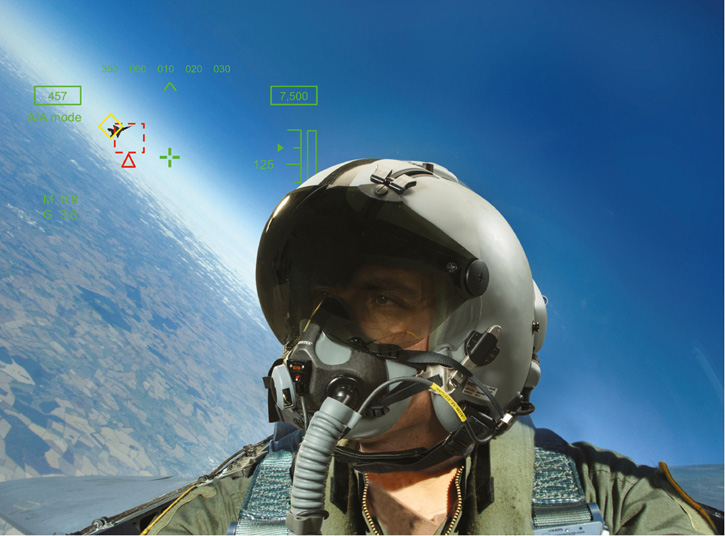 For fighter aircraft and trainers, the new Digital Joint Head Mounted Cueing System (D-JHMCS) or Elbit Systems’ Targo helmet display will provide the main SuperVision display and cueing system. The helmets will be used with lightweight and comfortable head mounted display (HMD), which offers an improved HMD Center of Gravity (CG) and balance and thus reduces neck strains. Plug and play, with minimal installation requirements and the ability to operate with the aircraft’s current tracker and Electronic Unit, DJHMCS can replace legacy JHMCS equipment with no A/C modifications required, thus reducing life-cycle costs.
For fighter aircraft and trainers, the new Digital Joint Head Mounted Cueing System (D-JHMCS) or Elbit Systems’ Targo helmet display will provide the main SuperVision display and cueing system. The helmets will be used with lightweight and comfortable head mounted display (HMD), which offers an improved HMD Center of Gravity (CG) and balance and thus reduces neck strains. Plug and play, with minimal installation requirements and the ability to operate with the aircraft’s current tracker and Electronic Unit, DJHMCS can replace legacy JHMCS equipment with no A/C modifications required, thus reducing life-cycle costs.