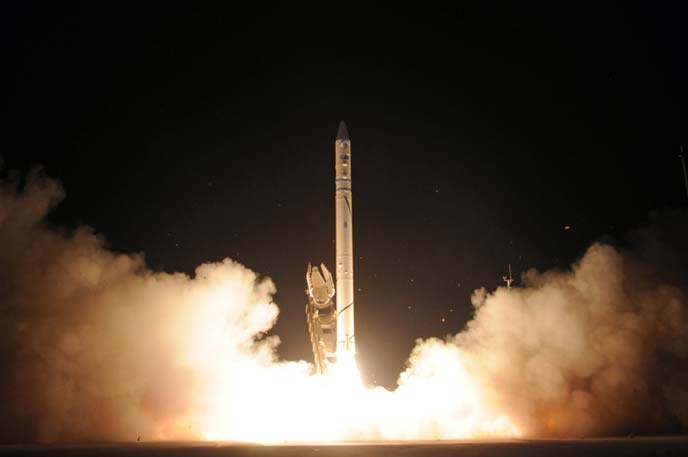
The Israeli spy satellite Ofeq 9 was launched yesterday, (June 22nd 2010) from the Palmachim Air Force Base on Israel’s Mediterranean coast. The new satellite is the sixth satellite in the Ofeq (Horizon in Hebrew) family of satellites, which began with the launch of the Ofeq 3 in 1995.
Ofeq 9 uses the OpSat 2000 bus employed with the Ofeq 5 and Ofeq 7 satellites. It carries a new High-resolution camera payload developed by Elbit Systems EL-OP. The payload is believed to be the latest version of the ‘Neptune’ camera, developed by ELOP. Positioned at an altitude of 600 kilometers, Neptune’s sensors record images panchromatic resolution 0.7 meter or less.
The Neptune space camera is based on the experience ELOP gathered from previous civilian and surveillance satellites currently on mission such as the Mercury remote-sensing camera employed with EROS-A Satellite. The original Neptune provided images with 2m resolution from an orbit of 500 km altitude. An improved payload is the Neptune, employed with EROS B satellite, which provides images with 70 cm resolution orbiting in the same altitude. ELOP also developed the Uranus-MSC multi-spectral payload providing panchromatic image resolution of 1 m’ and multi-spectral (color) images at a resolution of 4 m’ from an altitude of 680 km. ELOP also develops a multi-spectral camera for the French Space Agency, for the Venus program, a payload capable of providing 12 spectral channels. The next generation camera, to be integrated in the next Ofeq and EROS satellite is the ‘Jupiter’, a multi-spectral camera capable of delivering image panchromatic resolution of 0.5 meter and multi-spectral camera with resolution of 2 meters from an altitude of 600 km.

OptSat 2000 is 3-axis-stabilized platform designed to carry satellites weighing 250-350 Kg. Ofeq series satellite are built for the Israel Ministry of Defense by IAI MBT Missile and Space, a division of Israel Aerospace Industries. The main payload of the Ofeq is a high resolution space camera developed and built by ELOP. Other subsystems in the satellite include the navigation and attitude control subsystems provided by IAI Tamam, propulsion systems provided by Rafael, the datalink and data recording subsystem provided by Tadiran Spectralink.
Ofeq 9 weighs 294Kg and measures 2.3m in length, its diameter (with the 3.6 meter long panels in the stowed position) is 1.2 m. The satellite stores 30 liters of hydrazine fuel, necessary for station keeping through its lifespan. Pointing the camera is achieved by reaction wheels, effectively stabilizing and controlling the satellite attitude in orbit without the use of liquid fuel. The satellite can also be positioned offering optimal exposure for the solar arrays, producing 400 Watts of electrical power in average, sustaining the satellite through its orbit.
The OFEK 9 Satellite was launched with IAI’s Shavit satellite launcher. This 30 ton, 20 m high launcher is believed to be a derivative of Israel’s Jericho II ballistic missile. Two years ago Israel tested a new version of the Jericho, which could be the platform for the new and improved satellite launcher developed by IAI for future missions. Shavit is intended for launching and placing satellites in low orbits, ranging from 200 – 500 Km above earth. This three-stage launcher uses two stages of solid rocket motors made by IMI and a third, upper stage provided by Rafael.



Where is Ofek 8?

The Ofeq 9 satellite is the sixth Israeli satellite currently orbiting in space. It joined two military surveillance satellites still in orbit (Ofeq 5 and 7) and two commercial satellites (EROS A and B) all are still operational, as well as the TECSAR radar imaging satellite launched in 2008. The new satellite will upgrade Israel’s intelligence gathering and monitor sensitive areas like the Iranian nuclear sites and facilities. It will eventually replace Ofeq 5 as it reaches the end of its useful life.
The first operational Ofeq reconnaissance satellite was launched in 1995. The launch of Ofeq 4 failed in 1998, as the launcher’s second stage failed. At the time Israel launched a parallel, commercial satellite program where Ofeq class satellites launched by Start-1 Russian satellite launchers. Eros A satellite was launched in the year 2000 and Eros B, launched in 2006 both use a polar orbit, offering the Israeli government and other governmental users a ‘no risk’ turnkey service, augmenting the military program.
Two years after the Eros A launch the Ofeq program resumed with the launch of Ofeq 5 in 2002, but the program experienced another setback in 2004, as Ofeq 6 failed to enter orbit. This failure caused a major blow to the Israeli space program, which, with the MOD and Prime Minister Office recommending its shutdown. Barely escaping termination, the Israeli recce satellite program was given another chance and, in 2007 Ofeq 7 was successfully placed in orbit by the Shavit launcher, demonstrating remarkable improvement in performance.
The fate of Ofeq 8 is yet unknown. Officially, the Israel MOD skipped a number, to accept the TECSAR satellite as Israel’s eight’s satellite in space. However, Israeli officials endorsed the Ofeq 9 platform to share the OPSAT 3000, which is similar to the bus used for the TECSAR. This platform is heavier than the OPSAT 2000, which fits the Israeli launcher. Therefore, Israel opted to launch the TECSAR on an Indian PSLV-C10 vehicle. In January 2010 press reports indicated the imminent launch of the Ofeq 8, but these reports failed to materialize. Few months later, press reports in India indicated an Israeli satellite was hastily removed from the Indian GSLV-D3 satellite launcher, days before the planned launch. Eventually, on April 16, the launcher failed to carry an Indian communications satellite into orbit. Two months later, Israel launched the Ofeq 9 satellite mysteriously skipping Eros 8 with no apparent reason.
Ofeq 9 was inserted into orbit by the IAI’s Shavit II satellite launcher. The booster and second stage of the Shavit are produced by IMI and the upper stage propulsion system, inserting the satellite into orbit, is provided by Rafael. This launcher has been in use since 1988, when the first Ofeq satellite was launched. To date Israel has built six operational Ofeq satellites. Ofek 3, 5 and 7 were successfully deployed on missions of up to 10 years. Two Ofeq satellites were lost – Ofeq 4 due to a launcher failure in 1994 and, ten years later, Ofeq 6 failed due to an upper stage failure in 2004. The whereabouts of Ofeq 8 are still unknown. This satellite was reportedly scheduled to be launched earlier this year, probably on an Indian satellite launcher, but except of a launch failure reported in April, of an Indian SPLV launcher, but that launched did not carry any foreign payload. Other reports claim Ofeq 8 is technically the TECSAR launched last year.