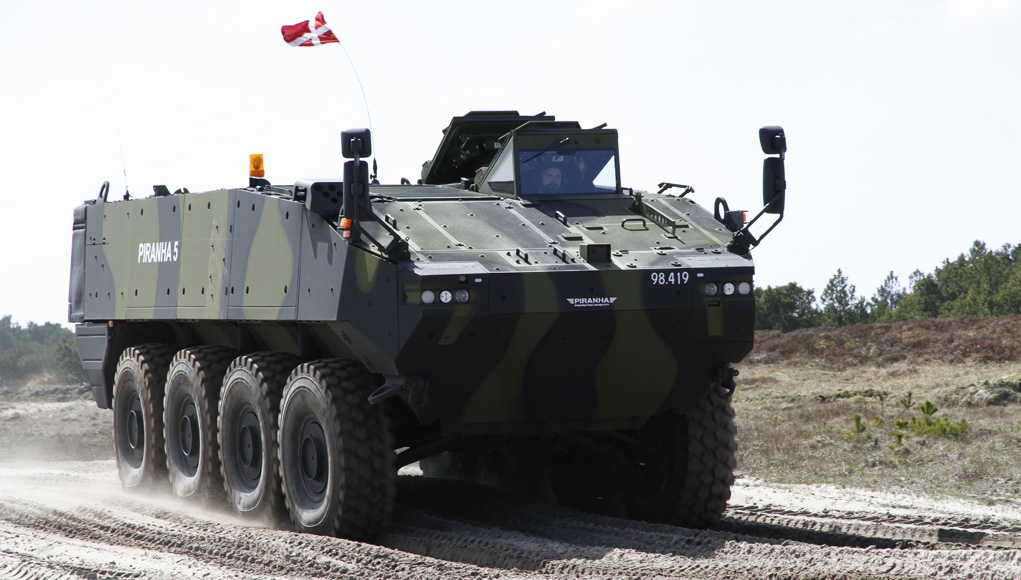
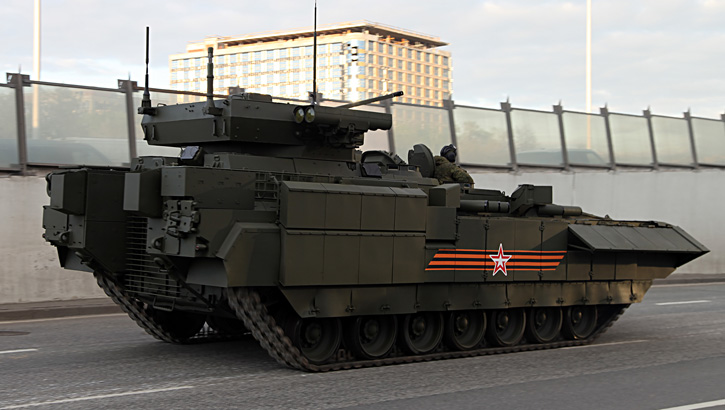
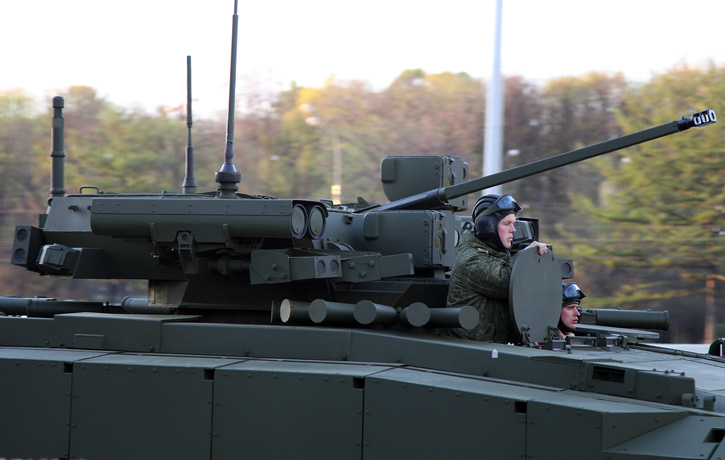
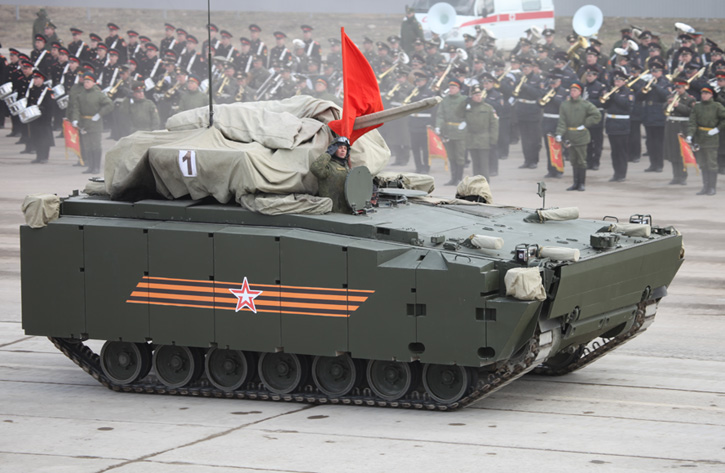
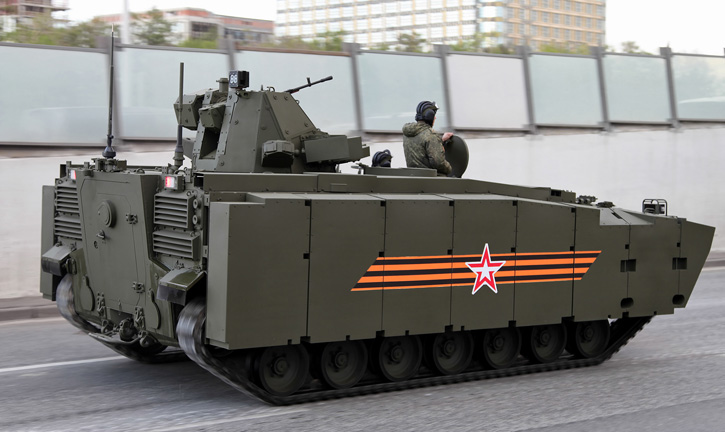
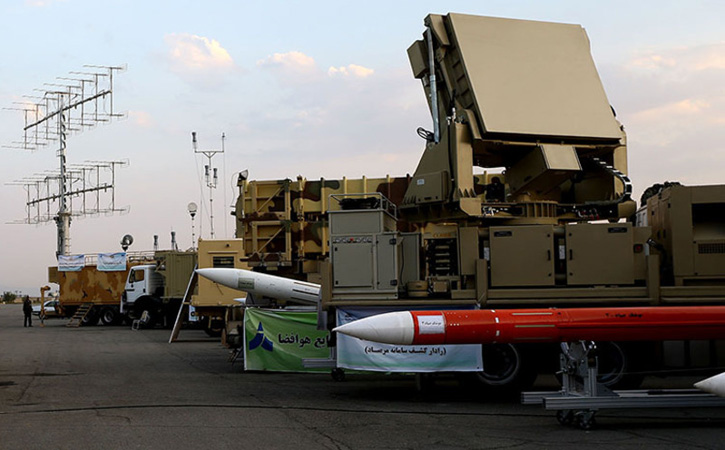
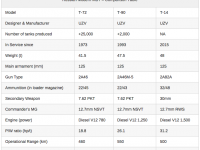
The Danish Ministry of Defense announced the selection of the Swiss Piranha 5 8×8 wheeled APC for the future armored personnel carrier of the Danish Army (Forsvaret).
Piranha 5, developed by Mowag GmbH, the Swiss subsidiary of General Dynamics Europe Land Systems (GDELS) was selected after a thorough evaluation of four candidates. In the final round the Swiss 8×8 APC has beaten the the tracked Swedish Armadillo CV90 from BAE Systems, GDELS ASCOD (recently selected for the British Scout SV program) and PMMC G5 modified M-113. Piranha 5 was one of two wheeled APCs evaluated – the other was its French rival, the 8×8 VBCI from Nexter.
The Danish M-113 replacement program was considered one of the largest procurement of armored vehicles in Europe, evaluating both wheeled and tracked variants ‘head to head’.
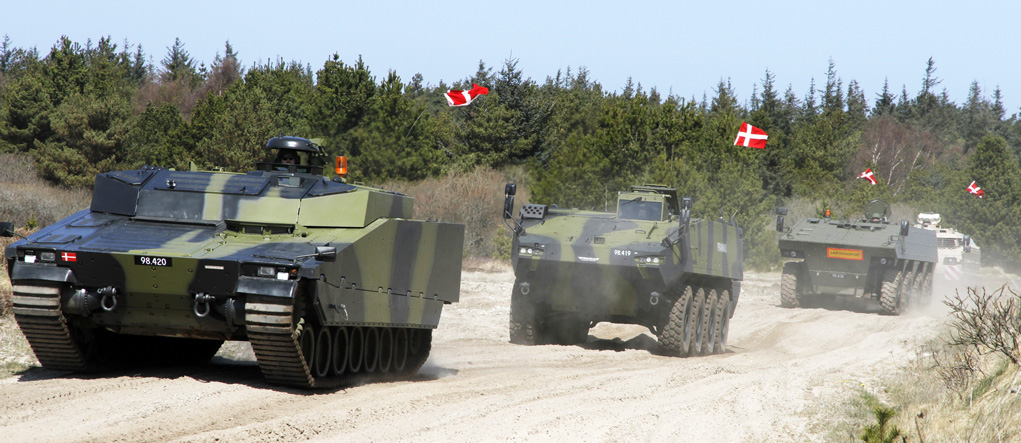


Almost all candidates considered by the Danes were new vehicles. Except VBCI, which is in service with the French Army, the Piranha 5, Armadillo and G5 represent new designs. The ‘Protected Mission Module Carrier’ (PMMC) G5 is considered a ‘modified M113’ remanufactured into the G5, based on the design proposed by the German company FFG. However, all three represent model improvements of vehicles currently operational with the Danish Army (CV9035, Piranha IIIC and M-113). The M-113 replacement program was launched in 2011 with a procurement options for 206, 360 or 450 vehicles, in an armored personnel carrier, command vehicle, ambulance, mortar carrier, engineering and technical support variants. The Danish contract requires the supplier to bind to support the fleet over a period of 15 years.
Denmark is planning to order at least 206 vehicles, but according to Danish Defense Minister Nicolai Wammen, the exact number is yet to be determined. Analysts forecast the total number could increase to 450. “With Piranha 5 we have found the armored personnel carrier that can best solve our defense tasks in the future” Wammen said.
The defense department will cancel a planned tender for a new artillery system, thus clearing the necessary funding for the new APCs. Denmark is exploring options to rent or borrow artillery systems from another country to enable its military to retain proficiency operating modern artillery systems. Denmark is operating a battalion of M-109A3 self-propelled howitzers. Potential bidders for that program where Nexter of France, Samsung Techwin from South Korea and Israeli Elbit Systems Soltam.
Full version available for subscribers
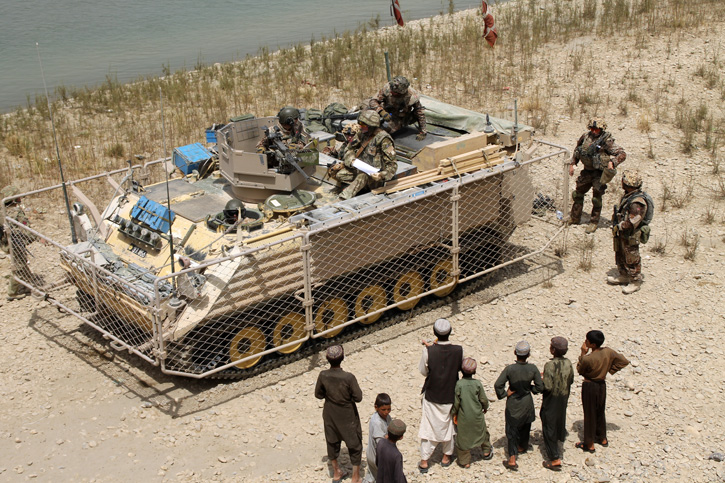

As the Danish government require significant offset buying for such significant military acquisitions, GDELS said it has already signed Industry Cooperation agreements with 40 Danish companies of all sizes and has already defined projects in excess of €0.5 billion (3,7 billion kroner) covering all of the technology areas defined in the Danish Government’s Defence Industry strategy.