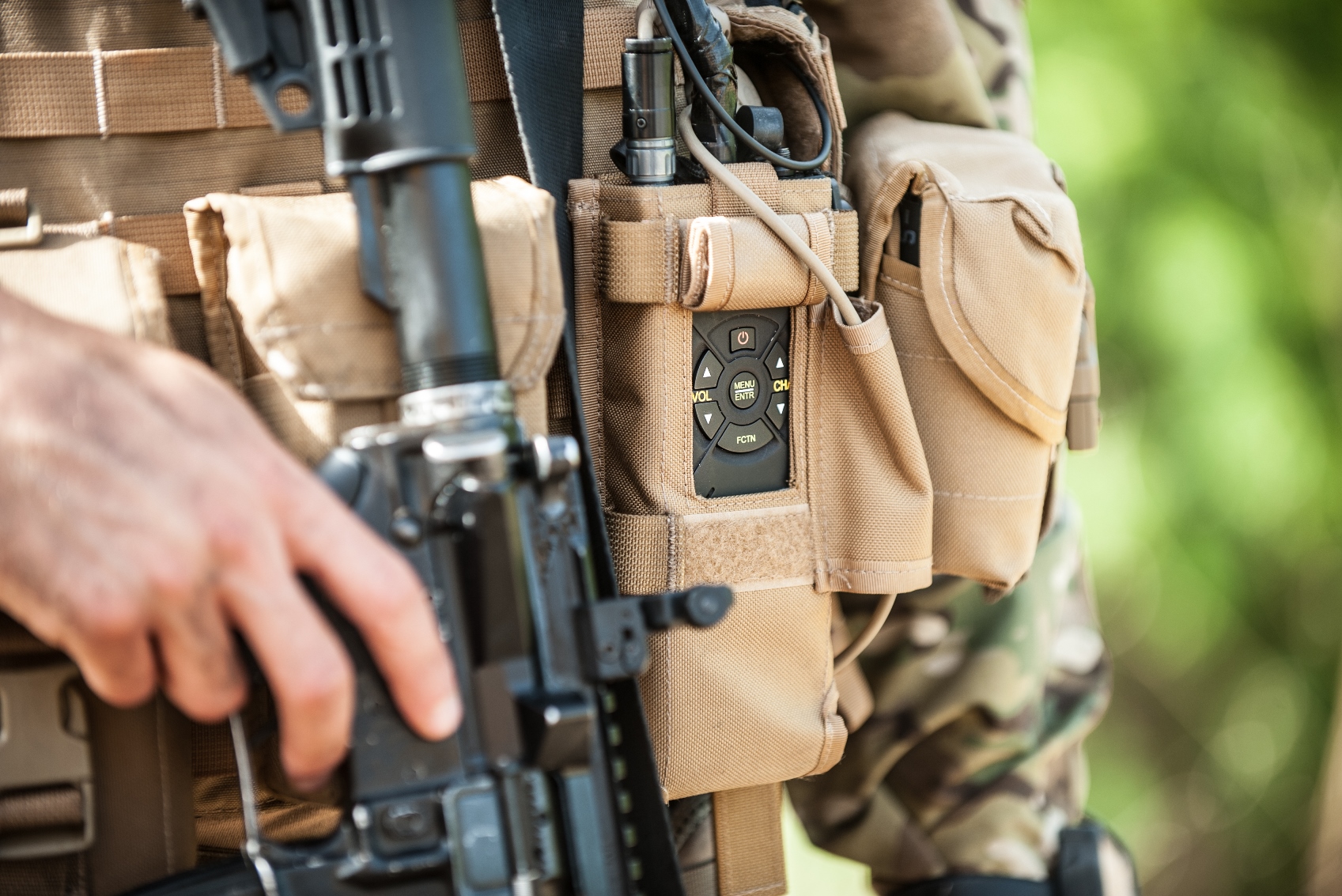
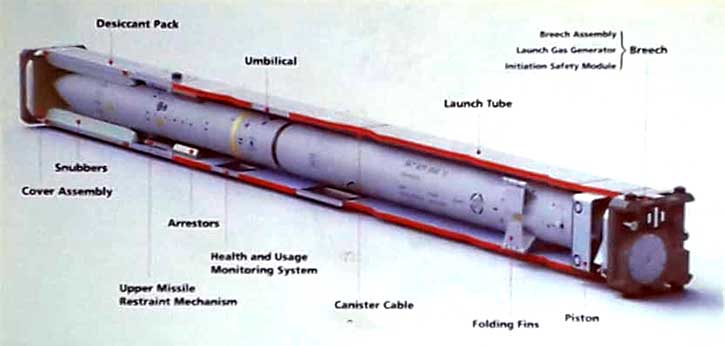
The German Federal Ministry of Defense (MOD) has selected Elbit Systems’ German subsidiary to equip its infantry units with the PNR1000 advanced soldier radio, part of Elbit Systems’ E-Lynx family of Software Defined Radios (SDR). The PNR1000, the smallest member of the family, will be delivered in handheld and vehicular configurations. These soldier radios will be used at the platoon and company levels and will be installed onboard various combat vehicles including the SPz PUMA.
The order requires an extensive transfer of technology from Elbit Systems to its German-based subsidiary, facilitating local development and manufacturing of the radios supplied to the German military, along with further extensions and capabilities. Development and production will be done in the company’s research & development (R&D) and manufacturing facilities in Ulm, Germany, which will also serve as the support and R&D center for Germany.
The E-LynX soldier radios facilitate advanced networked combat solutions in both open fields and in urban areas. This radio system provides forces with the capability to use several voice groups in a single channel, enabling flexible operation of multiple units and networks along with fast data services. With an integral Blue Force Tracking (BFT) capability, for effective, agile operations. While the soldier radio is designed for short-range operation, the E-Lynx also supports advanced networking waveform with unique concurrent flooding techniques that extend the range over a multi-hop network, improve network agility and robustness while dramatically reducing network latency.
German Army to Get Software Defined Radios for the Infantry
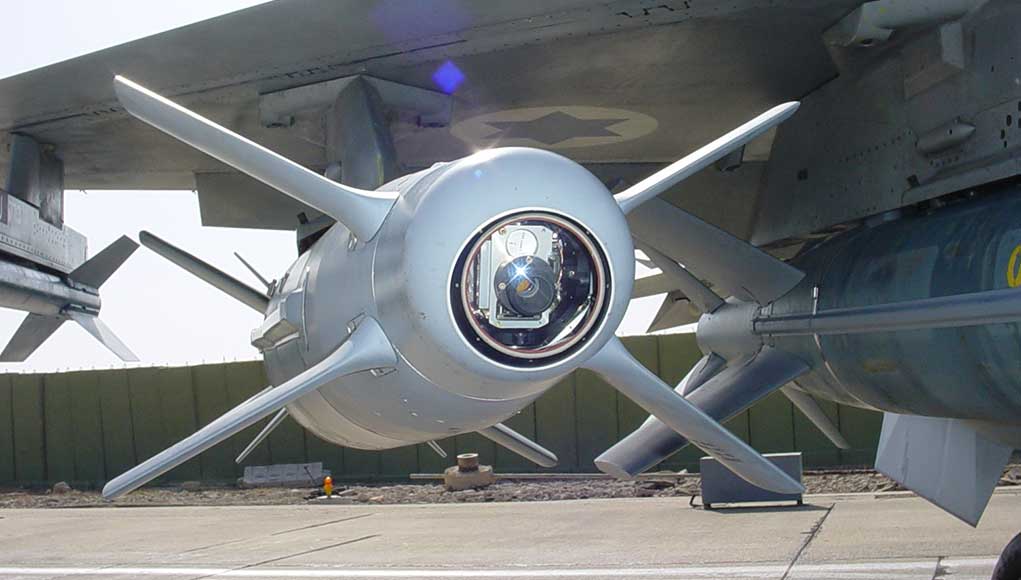
Lockheed Martin adds SPICE to its Weapons
Lockheed Martin and RAFAEL have signed a cooperation agreement to jointly develop, manufacture, market and support RAFAEL’s Smart, Precise Impact and Cost-Effective (SPICE) missile guidance kits to Lockheed Martin’s platforms. RAFAEL already subcontracts about 80 percent of SPICE subassemblies to US manufacturers in eight states. The agreement will enable Israel to buy SPICE kits from the USA, using US military support funds. The agreement follows a market assessment evaluation done by the two partners in the past year.
“Access to GPS is becoming increasingly limited in contested environments,” said Mr. Yuval Miller, executive vice president, and general manager of Rafael’s Air & C4ISR Division. “SPICE provides a solution to this challenge. Finalizing this exclusive agreement sets the scene for our two companies to provide unmatched mid-range guided air-to-surface weapon systems to enhance mission flexibility and success.
SPICE kits are compatible with Lockheed Martin F-16, and, following full integration, will also equip Israel’s Air and Space Forces F-35A. Once concluded, the SPICE will also be available to other F-35 operators. SPICE has also been integrated with the Saab Gripen E, and has already been selected to equip the new Brazilian Gripen NG fighters. RAFAEL also develops the SPICE 250 unitary guided munitions. The bigger SPICEs are designed as guidance kits added to standard bombs. The current agreement does not mention the SPICE 250.
SPICE is a family of stand-off, autonomous, air-to-surface weapon systems, capable of destroying targets with pinpoint accuracy and at high attack volumes in a GPS-denied environment. Combat-proven and in service with the Israeli Air Force and several international customers, SPICE employs a state-of-the-art electro-optical seeker with unique scene-matching algorithms, navigation guidance and homing techniques to achieve operational missions in adverse weather without GPS. The MOU covers the SPICE 1000 (453 kilogram / 1,000 pound weight class) and SPICE 2000 (907 kilogram / 2,000 pound weight class) precision-guided missile kit variants. The SPICE extends the aircraft strike range to 100 km, thus enabling attack from standoff range.
The cooperation agreement follows the partnership RAFAEL and Lockheed Martin established for the international marketing of The POPEYE EO guided missile back in the 1990s. Known as HAVE NAP (AGM-142) POPEYE was fielded by B-52 of the US Strategic Air Command, as well as F-4, and F-111 of the Australian, South Korean, Turkish and Indian Air Forces.
“SPICE is a leading air-to-surface weapon system offering U.S. and international air forces operating Lockheed Martin’s platforms, as well as strategic bomber aircraft, an important complement to their existing operational capabilities,” Miller added. “SPICE’s unique features greatly enhance the U.S.’ ability to operate in contested environments.”
“SPICE offers the U.S. Department of Defense and many allies a capability that no other weapon currently in inventory provides,” said John Varley, vice president of Close Combat Systems at Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control. “By applying our expertise in aircraft integration, mission planning, and tailkit design, along with our experience in affordable, streamlined production, we will adapt SPICE to meet U.S. standards so bomber and fighter aircraft can benefit from the added mission flexibility that SPICE offers.” Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor providing the AGM-158 family of Joint Attack Air to Surface Missile (JASSM) cruise missiles, and the Paveway family of laser-homing weapon guidance kits, widely used by airforces worldwide. SPICE adds an alternative guidance technique, strike autonomy, and independence of GPS, extending the air forces’ operational flexibility in planning and performing strike missions with modern combat aircraft.

GMLRS, HIMARS to Get New Rocket Pods
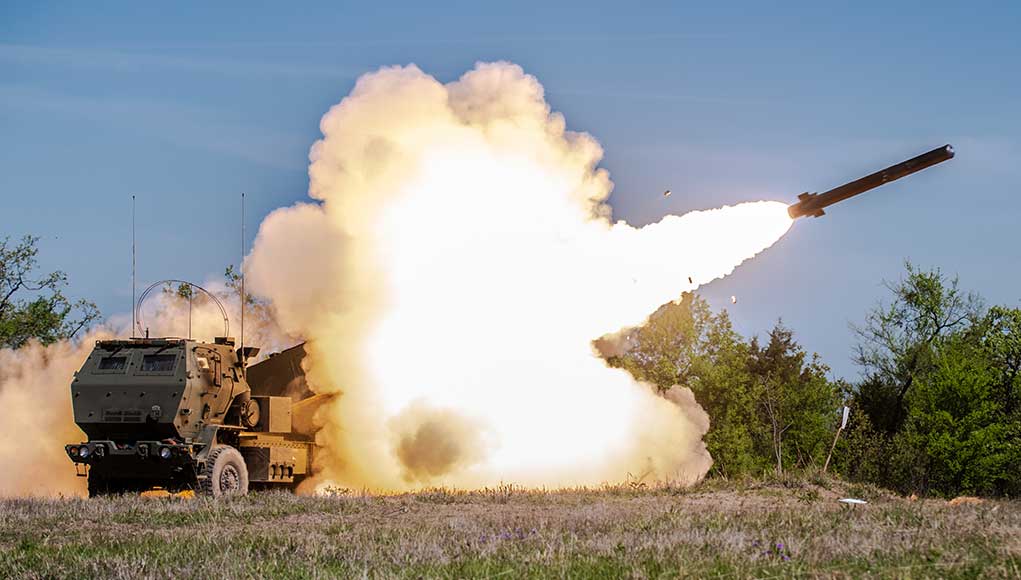
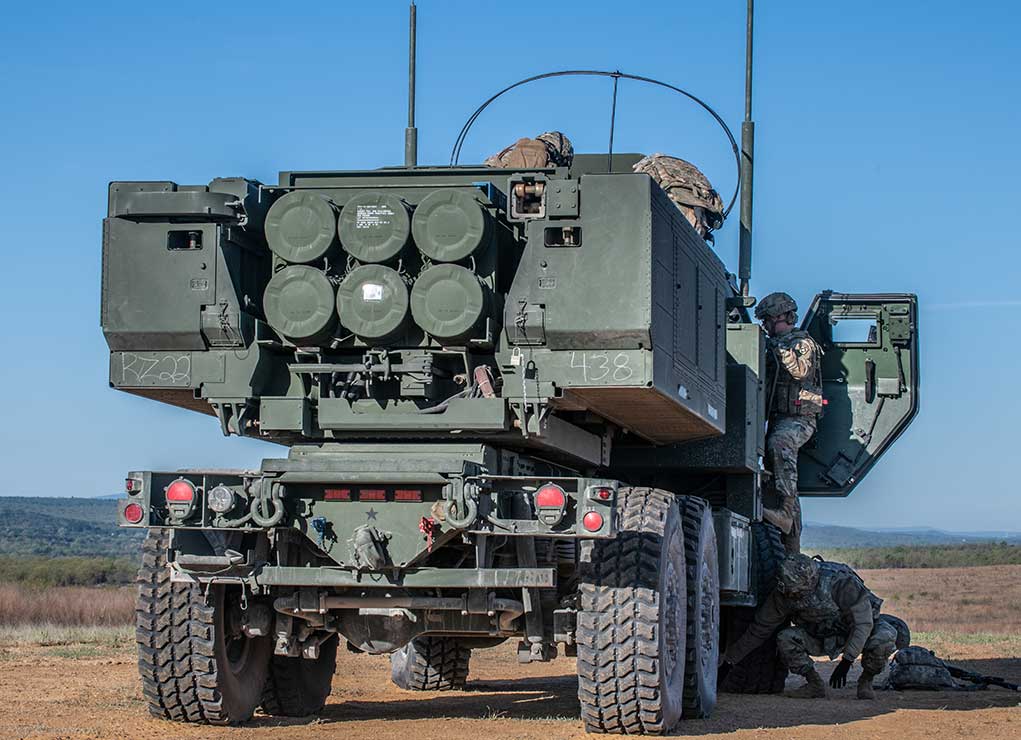


Lockheed Martin is working on a new, modular pod for Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System (GMLRS) rockets, enabling loading of individual rocket tubes as they are expended, whereas the original GMLRS pods are discarded after use. The new pods will replace the depleting inventory of M26 rocket pods that were designed for salvo firing, and support the increased production of GMLRS rounds.
The pod will be able to fire the GMLRS Unitary and Alternative Warhead variants, as well as the developmental Extended-Range GMLRS rockets and future rounds. The new pods will replace the depleting inventory of M26 rocket pods and support the increased production of GMLRS rounds. The new pods will be compatible with both the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and MLRS M270 family of launchers. The US Army awarded the company $10.5 million for the development. Ground testing will begin this fall, with a planned flight test before the end of the calendar year. The first deliveries of the new modular pod are anticipated in the fall of 2021.

US Army Contracts Dynetics to Build a Mobile, High Energy Laser Weapon
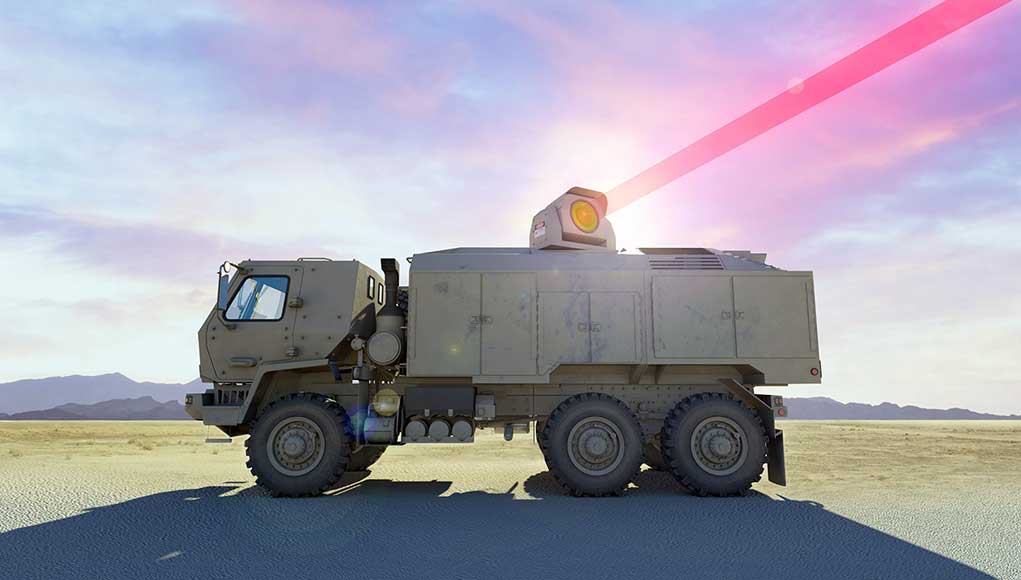

Dynetics, along with its partners, Lockheed Martin, Rolls Royce and MZA Associates have been awarded a $130 million contract to build and test a 100-kilowatt class laser weapon system under the High Energy Laser Tactical Vehicle Demonstrator (HEL TVD) program managed by the U.S. Army Space and Missile Defense Command/Army Forces Strategic Command’s (USASMDC/ARSTRAT). Team Dynetics has beaten five competitors, among them Raytheon that competed in the final phase.
As the prime contractor, Dynetics will be responsible for final assembly and integration and testing of the system. Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT), as the laser weapon system integrator, will provide the laser weapon subsystem, optimizing the performance of the laser module, power and cooling systems, and operator interfaces. Rolls-Royce LibertyWorks will design the integrated power and thermal management system to successfully meet the HEL TVD requirements. The design builds upon the successful internally funded programs that have demonstrated the technology and capability in this power class. The system will provide a high level of electrical power and thermal management required in a compact, power dense package with the responsiveness required for directed energy applications.
Earlier in 2019 Team Dynetics successfully completed a Preliminary Design Review (PDR), assuring the Army the test program is valid and low-risk from the technical aspect. The team will now move to the critical design review (CDR) as soon as possible. The CDR phase will finalize the design prior to system fabrication, documenting how laser science has matured into an achievable warfighter reality. Long-lead material orders will commence during this time. Subsequently, the team will build and integrate the laser weapon system onto an Army family of medium tactical vehicle (FMTV) platform and conduct field testing at White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico per SMDC’s program plan. According to the preliminary plan, testing will be performed in FY 2022.
The HEL TVD award was the final announcement for the SMDC Design, Development, Demonstration and Integration, or D31, Domain 1 for space, high altitude and missile defense capabilities. Dynetics was named an awardee in 2017, along with six other competitors, and advanced after completing the system requirements review in 2018.
Harris Night Vision Acquisition – a Big Deal for Elbit Systems

Elbit Systems of America, a subsidiary of Elbit Systems and the Harris Corporation have agreed to move forward with the acquisition of Harris’ Night Vision business for $350 million. The acquisition of Harris’ night vision business opens a huge market for Elbit Systems, both domestic and international. Over 50 years Harris and its predecessors Exelis and ITT have established their night vision systems as the market leader. But with the planned merger between Harris and L3 Technologies, Inc., the night vision systems business becomes redundant under the combined portfolio.
Expected to be completed by mid-year the planned merger between Harris and L3 creates a defense electronics giant worth $33.5 billion, to be ranked sixth in the US market, after Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Raytheon, Northrop Grumman, and General Dynamics. Harris and L3 are both major suppliers of night systems to the US military and Government. One of the two competing lines had to go. With annual revenues around $150-160 million, and solid profit margins, Harris’ night vision portfolio is smaller than L3’s.
Continued operation support of both activities was a concern for the Justice Department’s, considering the merger approval. For Elbit Systems this was a great opportunity, elevating its position as a major supplier in the US market and opening a new marketing channel for its large product portfolio of complementary and innovative products. “In January 2019, we announced that as part of the L3 merger regulatory process we had proactively started exploring the sale of our Night Vision business,” said William M. Brown, chairman, president, and chief executive officer. “With the signing of the agreement to divest the Night Vision business and yesterday’s approval by shareholders of the L3 Harris merger, we have achieved two significant milestones towards completing the transformational merger in mid-calendar 2019.”
Harris has led the night vision industry for over 50 years. According to Harris, the company produced more night vision devices than all competitors combined. Harris Night Vision activity is a remnant of several acquisitions. The first, was in 2011, as Exelis was a spinoff from ITT Corporation, becoming an independent defense company, and in 2015, as Exelis was acquired by Harris.
Among the latest innovations Harris offers are AN/PSQ-20A enhanced night vision goggles, i-Aware Fusion lines, combining third generation night vision, thermal vision and integrated live video display on an advanced headset. Harris is the leading supplier of aviators night vision systems (ANVIS), used by the military. In 2018 the company’s light intensification tubes and ANVIS assembly (AN/AVS-9) was certified by the Federal Aviation Authority (FAA) for civilian use for night flying with fixed and rotary wing aircraft. Elbit Systems’ portfolio provides many complimentary activities, including thermal imaging, weapon sights, soldier systems, day and night helmet mounted aviator displays and pilot sights for combat helicopters. “The market position and technological strength of Harris Night Vision make this acquisition significant to our long-term growth strategy, with a particular focus on the U.S.” Bezhalel (Butzi) Machlis, Elbit Systems President & CEO commented.
Soft Launch Delivers a Hard Fist

Following first deployments at sea on Type 23 frigates, MBDA’s Sea Ceptor matures to become highly effective and efficient all-weather air defense weapon system. Designed for efficient deployment on land and at sea, Sea Ceptor offers unique advantages for operations of small surface vessels. Relying on active-RF guided CAMM missile, the system uses different radars and command and control systems provide short and medium air defense covering an area of 500 square miles.
Selected for use on next-generation Type 26 frigates, Sea Ceptor has also been installed on existing Type 23 frigates, replacing the Sea Wolf missile system. CAMM relies on existing capabilities from MBDA’s portfolio, such as datalink C3 and propulsion from the Advanced Short-Range Air-Air Missile (ASRAAM), along with command and control from the Sea Viper, used on six Royal Navy Type 45 destroyers.
Variants of Sea Ceptor have been ordered by three nations – UK, New Zealand, and Chile. The Royal Navy (Type 23 upgrades and new Type 26 frigates), Chilean Navy (for Type 23 frigates) and Royal New Zealand Navy (ANZAC frigate system upgrade). To date, Sea Ceptor systems have been deployed on two Royal Navy frigates, HMS Argyll in 2017 and HMS Westminster in 2018. Two systems are also deployed on Royal New Zealand Navy vessels, HMNZS Te-Kaha and Te-Mana. Brazil has also selected the weapon for its new Tamandare class corvettes. Spain, Finland, and India are also potential customers for the system.
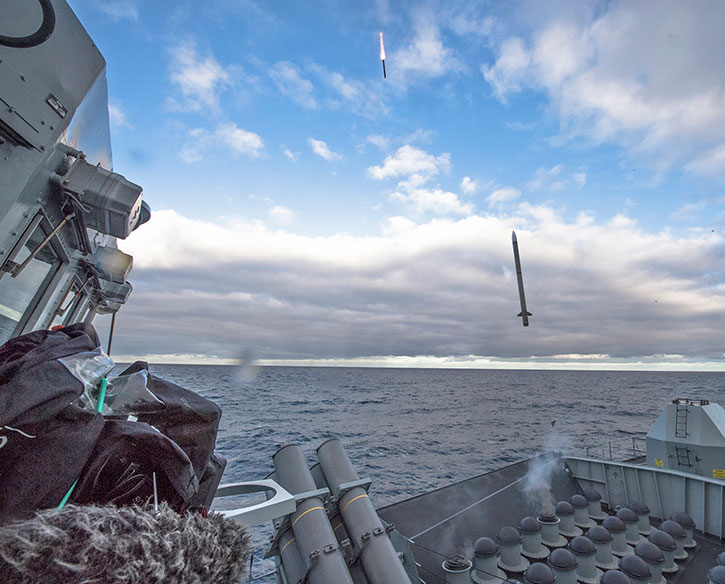

Sea Ceptor can also be retrofitted on a range of platforms, beginning at 50m offshore patrol vessels (OPV) and corvettes, frigates, and destroyers. On larger vessels, CAMM missiles can also integrate with standard VL-41 vertical launch system (VLS), with each cell containing four CAMM canisters. MBDA has worked with Lockheed Martin to develop a lightweight version of the MK41 launcher for CAMM. Using an active RF seeker for targeting, CAMM does not rely on target illumination by the launching platform and can therefore simultaneously engage multiple targets. Target data can be uploaded to the missile in flight, as the missile maintains continuous two-way data link with the launcher immediately after launch.
A key capability of CAMM is the use of a soft launch mechanism that imposes minimal loads on the launchers and structure. This concept minimizes smoke and flash effects that may obstruct sensors and systems on board. It also enables the simultaneous firing of multiple missiles against different targets. The missile performance derives from optimal use of onboard propellant. Its powerful rocket motor sustains the missile kinematics at twice the range of the Sea Wolf it replaces, using alternative propulsion for ejection and platform separation. The engine is ignited high above the vessel, after being injected to the air by compressed air. Using separate propulsion for the vertical launch phase. The soft launch reduces the launch stress on the platform and eliminates the need for managing hot gas efflux on-board.
The land-based variant is ‘Land Ceptor’, designed as the interceptor element of modern Ground Based Air Defense (GBAD). The launch customer for Land Ceptor was the British Army, acquiring 14 systems for the ‘Sky Sabre’ (GBAD) capability. The system integrates three main elements from four nations: MBDA’s Land Ceptor missile system (UK), Saab Giraffe AMB radar (Sweden), and Rafael’s modular, integrated C4I air and missile defense system (MICAD – Israel). All elements will be mobilized using HX77 heavy utility trucks supplied from Germany. Replacing the Rapier SHORAD missile Land Ceptor will have a range of +25 km, three times the Rapier’s range, broadening the former weapon’s target set to more challenging threats, including guided weapons and cruise missiles.
An extended range variant, CAMM-ER is in development at MBDA Italia. The new missile offers an extended range (+40 km) is expected to assume the Italian Army Short Range Air Defense (SHORAD) mission as it replaces the ASPIDE system, expected to be phased of service by 2021. The CAMM-ER system integrates Italian radars and command and control systems. The missile uses a new propulsion augmentation system developed by Avio. The missile is expected to begin firing trials this year.

ISDEF Announces a Live Demo Day
On its 10th edition, Israel’s premiere defense, homeland security, and cyber exhibition — ISDEF Expo, will celebrate the largest, most extensive event in its history. With 300 exhibitors and 15,000 visitors expected to visit, ISDEF 2019 will take place at the new recently constructed Pavilion #2, the largest at Tel-Aviv’s International Convention Center. The exhibition will open its doors on June 4th and continue until June 6th, 2019.
Preceding the exhibition in Tel-Aviv, ISDEF has organized a true one-of-a-kind live fire and dynamic demonstration day held on Monday, June 3rd at the ‘Adam’ military training facility located thirty minutes drive from the convention center in Tel Aviv. Named after the legendary General Yektiuel Adam (1927-1982) The facility is home to Israel’s IDF counter-terrorism and sniper school. The Adam facility features extensive live firing ranges and unique realistic training areas offering an excellent setting for the live demonstrations and hands-on evaluation of firearms and weapon systems. The range and live demonstration day offers a unique and practical opportunity for both domestic and foreign manufacturers of firearms, ammunition, accessories, target acquisition and observation equipment to demonstrate their products to official delegations participating in the event.
ISDEF’s range day** will offer select official delegations to try out the weapons on short, medium and long-distance firing ranges, during day and night time firing, at the same facilities Israel’s special forces and snipers use for training. Other demonstrations expected here include smart sights, thermal and night vision systems, signature reduction management systems, ballistic protection solutions, remotely controlled systems, tactical and armored vehicles, maintenance equipment, barriers, carry cases, tactical textiles, training aids, CBRNE equipment and more.
ISDEF Expo 2019
When: June 4th-6th, 2019.
Where: Pavilion #2 International ConfereCenterExhibition center, Tel-Aviv, Israel
Those interested in attending ISDEF 2019 are requested to register online on ISDEF’s official website.
** Please note that the ‘Live demonstration & range day’ is not open to the general public, participation is for relevant official government and industry delegations.
Russian Push for Drone Export
The Russian drone manufacturer is aggressively marketing the Orion E, a Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) unmanned aerial system (UAS). The current export-oriented variant was launched in 2017. Seeking new customers at the LAAD 2019 exhibition in Brazil and LIMA 2019 in Malaysia, the developer, Kronshtadt Group is making the first steps entering a busy and competitive drone market.
Unlike comparable Chinese and US drones, Orion E is not positioned as a strike-recce platform as it is not offered in weaponized configuration and is currently limited to the surveillance and reconnaissance role. However, Orion-E offers a 24-hour mission endurance with its basic configuration, a score other competitors have worked hard to achieve. A complete Orion unmanned aerial system comprises four to six UAVs, a ground control station, automated take-off and landing systems, and communications elements.
At a maximum takeoff weight of one ton, it carries a payload weight of 60 kg, on 24-hour missions and a cruising speed of 200 km/h. On shorter missions, Orion-E can carry up to 200 kg of payloads. Typical sensors carried on the drone include ground mapping and DF, maritime surveillance and electro-optical imagery surveillance capabilities. At its operational ceiling of 25,000 ft, Orion E is remotely controlled, from a distance of 250 km, via line of sight datalink. This range can be extended to 300 km, using a radio repeater on another drone.
Roughly equivalent to early generation MALEs such as the Chinese Wing Loong, Israeli Heron I and American Predator, Orion E is offered in an unarmed configuration, similar to the Predator XP and Heron I. Unlike the US and Israelis, Chinese and Turkish drone manufacturers offer weaponized platforms and have sold such systems to customers in the Middle East, Africa and central Asia. Chinese sources have claimed over a hundred Wing Loong series drones have been delivered for export. These drones have dropped more than 3,000 weapons, many of them in combat missions, scoring an average hit rate of 90 percent. Kronshtadt has also evaluated the use of small diameter weapons on its drone. Both 50 and 100 kg guided missiles are being evaluated, with a loadout of four and two weapons per drone.
Addressing the demand for more mission endurance, speed and payload drone manufacturers are fielding heavier, more capable drones to assume more missions. Israeli, US, and Chinese drone manufacturers are now offering the Heron TP, Hermes 900, Predator B, CH-5, and Wing Loong II platforms, all equipped to carry long missions at extended ranges. By 2021 Kronshtadt is expected to join this group with a more advanced version – Orion-2 that will have a maximum takeoff weight of five tons, and be able to carry heavier payloads, fly faster (350 km/h) and at higher altitude (38,000 ft). The new drone is expected to carry a satellite communications data link, extending its operational range to thousands of kilometers.
Enhancing Combat Vehicles with Thermal Vision
Modern Armored Fighting Vehicles (AFV) are designed to provide the firepower and protection to overmatch adversaries, whether it is enemy tanks, anti-armor or other kinetic and non-kinetic weapons, from land, subsurface or the aerial threats.
Protected behind heavy armor, crewmembers need effective vision systems to obtain situational awareness and perceive their surroundings at close quarters. Since their creation AFVs relied on optical gear such as periscopes and telescopes. Today, when AFVs are required to fight in the day, night and under adverse weather and limited visibility conditions, human vision is not enough. Electro-optical systems, particularly thermal vision equipment is fielded with new platforms and as part of modernization and upgrades for existing AFVs, preparing them to fight and win in the modern battlefield.
Upgrading entire fleets of AFVs is costly and complex but is essential to prevent the weapon systems obsolesce. Most combat vehicles delivered since the 1960s already have optronic systems of some type. Many are still in service and undergo periodical modernization to maintain combat effectiveness. While new optronic systems and fire controls are often too costly for aging platforms, armies may consider upgrading the optronic systems themselves, to enhance AFV performance within a limited budget.
Such upgrades were developed by Israel’s Thermal Imaging System (TIS) provider Opgal. Among these systems are upgrade kits for commander and gunner sights and new situational awareness systems for the driver and crew.
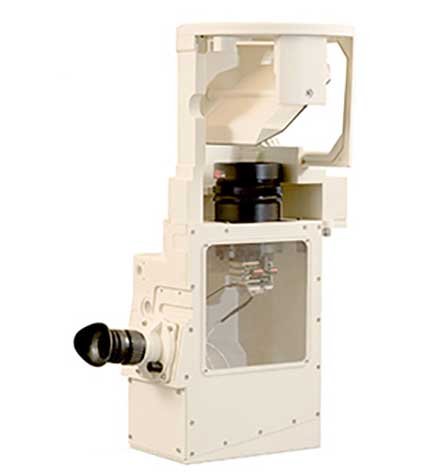

The Gunner Sight Upgrade Kit enables increased visual range for target identification and acquisition. Based on the Opgal’s EyeR Core AD it enables the gunner a clear view of the target under limited visibility conditions that would be impossible to engage with optical or night vision devices or thermal vision systems of early generations. Comprising an uncooled high sensitivity core that fits right into the existing thermal channel housing, Opgal’s field-tested Gunner Sight Upgrade Kit is designed as a drop-in replacement of I2 and 2nd generation thermal imaging channels, with applications for a range of tanks and armored vehicles of western and eastern origin.

The Commander Sight Upgrade Kit gives armored vehicles crews the ability to reconnoiter, identify and tag targets at greater distances as well as at close range, under limited visibility conditions. As Opgal’s optronic upgrade kits it fits as a replacement for InfraRed (IR) and Image Intensification (I2) channels and comes with a new AMOLED 800×600 eyepiece. Built around the Opgal’s Arbel thermal camera the system maintains both wide and narrow field of view.
The systems are ruggedized to IP65 with optional IP66 to withstand the harshest weather and environmental conditions, vibrations and shock such systems are exposed to when operating in the combat vehicles.

Opgal has developed a suite of thermal imaging systems designed specifically for the new and modernized armored vehicles.

Opgal’s combat-proven TIS suite comprises Situational Awareness (SA) systems, Local Situational Awareness (LSA) and Driver Vision Enhancer (DVE) products and retrofits developed and produced in Israel as ITAR/EAR free equipment. In response to the growing need for clear thermal vision at an affordable cost. Integrated with armored vehicles, Opgal’s suite replaces outdated image intensifiers that are limited to night operations and suffer from blinding effect, particularly in urban scenes. The new thermal imaging systems enhance crew effectiveness and survivability, by operating continuously in day or night, enabling with vision through obscurants such as smoke, dust, and haze.
Tavor SM is a rugged, compact and versatile camera that can be mounted on both manned and unmanned vehicles. Comprising a dual channel (day color/thermal) camera that can be used in ground or naval applications, Tavor SA can be paired with various displays as part of the vehicle’s vision system.
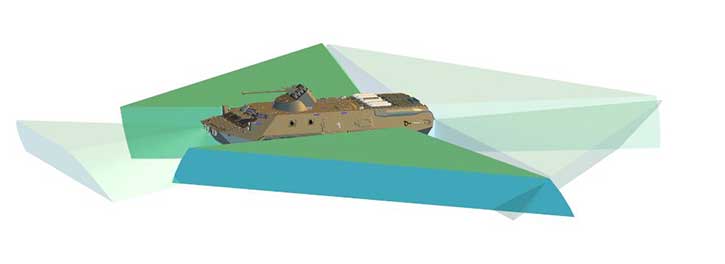
Tavor SA kit utilizes four or six ruggedized day/night cameras providing the crew with panoramic video surveillance at low latency video connectivity over an Ethernet link. The video feed from the cameras cover up to 360 degrees and is displayed in real-time in several matrix configurations inside the vehicle, on the crewmember’s display screens.
The DVE is a complete system comprised of a thermal imaging camera, a high-resolution LCD display that fits the available space at the driver’s position, and an adaptor fitting the system to the vehicle. Providing enhanced driver vision under all visibility conditions the DVE kit improves the vehicle’s combat mobility, effectiveness, and survivability in all combat conditions.
Advanced optronic systems are essential to enhance armored vehicles’ combat effectiveness. Thermal sights, panoramic vision, and enhanced driver vision capabilities are some of the elements available for new and upgraded fighting vehicles keeping them ready and potent combat systems.
Source: Opgal
First Flight of the Valkyrie – a Step Closer to Manned-Unmanned Flying Formations
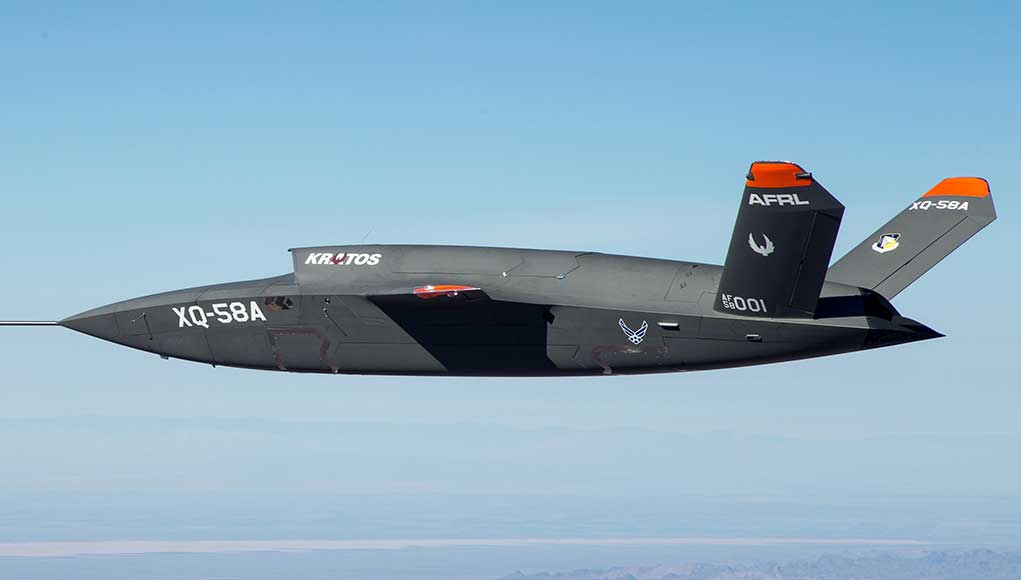

The US Air Force’s latest unmanned aircraft system (UAS), XQ-58A Valkyrie demonstrator completed its inaugural flight March 5, 2019, at Yuma Proving Grounds, Arizona. The Valkyrie is a long-range, high subsonic unmanned air vehicle designed to operate autonomously or in cooperation with manned aircraft as part of the Air Forces’ ‘Loyal Wingman’ concept. The Air Force Research Laboratory partnered with Kratos Unmanned Aerial Systems to develop the XQ-58A. According to the designer, the 30 ft (9 meters) long Valkyrie has a range of more than 3,000 nautical miles (5,556 km)
Based on Kratos’ low-cost target aircraft design philosophy, Valkyrie is part of the Air Force Research Laboratory’s Low-Cost Attritable Aircraft Technology (LCAAT) portfolio, which has the objective to break the escalating cost trajectory of tactically relevant aircraft. The objectives of the LCAAT initiative include designing and building UAS faster by developing better design tools, and maturing and leveraging commercial manufacturing processes to reduce build time and cost. It took Kratos and the Air Force little over 2.5 years to develop Valkyrie, from contract award to the first flight. “XQ-58A is the first example of a class of UAV that is defined by low procurement and operating costs while providing game-changing combat capability,” said Doug Szczublewski, AFRL’s XQ-58A Program Manager. According to the Air force, by teaming unmanned assets like the Valkyrie with an F-35 or an F-22, each manned platform can cover more space at a lower cost point.
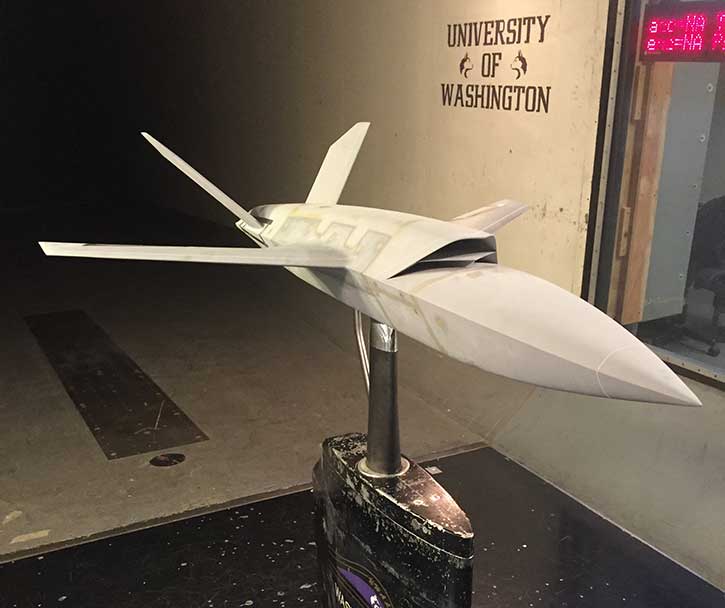

Unlike the UTAP-22 Mako that was used in flight tests with 3 and 4 GEN fighters the design features on Valkyrie are likely to reduce radar and thermal signature, better preparing it for operations with stealth aircraft. Among those features are the trapezoidal profile, canted tails, low-profile dorsal air intake and engine exhaust, serrated access panels, and weapons bay doors.
Developed for runway independence, the aircraft was launched and behaved as expected on its first flight that lasted 76 minutes. The XQ-58A has a total of five planned test flights in two phases with objectives that include evaluating system functionality, aerodynamic performance, and launch and recovery systems.
Previous experimentations were done with UTAP-22 Mako, another platform developed by Kratos. A derivative of Kratos’ BQM-167 aerial target drone, the platform provides a highly maneuverable unmanned aircraft, capable of carrying and operating weapons and advanced sensor systems. It demonstrated the capability to operate in synch with manned formations. It has flown in multiple large-scale military exercises and has been cleared for export.
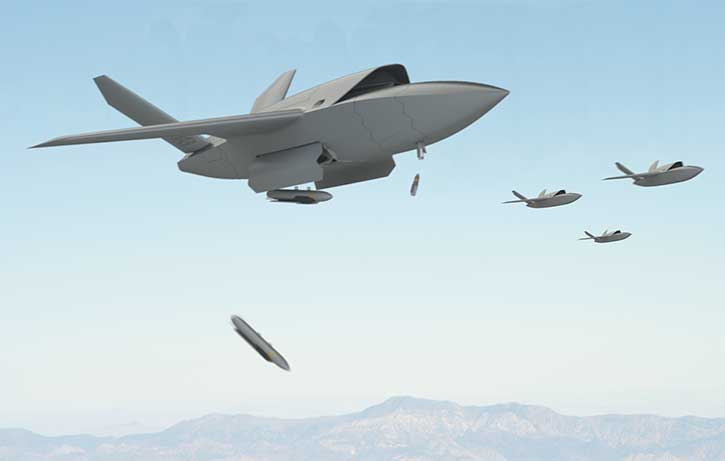

A Locally Developed ‘Loyal Wingman’ to Fly in Australia by 2020
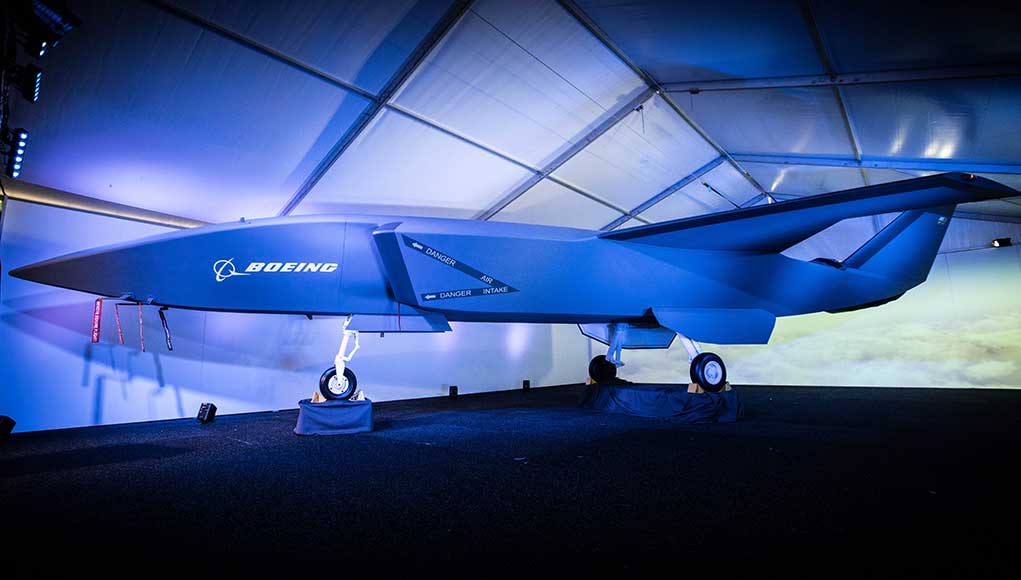

Boeing has introduced its newest unmanned platform, the Boeing Airpower Teaming System. The aircraft will complement and extend airborne missions through smart teaming with existing military aircraft. Designed and built by Boeing Australia, the project is the company’s largest investment in a new unmanned aircraft program outside the United States.
Boeing unveiled today a full-scale model of the new aircraft at the Australian International Airshow. The Australian Minister for Defence, Hon Christopher Pyne MP. that uncovered the aircraft, said the research and development activity, “The partnership will produce a concept demonstrator of a low cost unmanned ‘Loyal Wingman’ aircraft, capable of operating in concert with Air Force’s fifth-generation air combat capability,” Minister Pyne said. Boeing plans to invest over $60 million in the project, along with the Australian government that invests up to $40 million. The first flight is planned for 2020.
An operational platform based on this prototype will be able to operate alongside manned aircraft such as the RAAF F-35A, E-7, EA-18G, F/A-18E/F, and P-8 Poseidon aircraft, each evolved and came along linear development paths. Under the modernization plan called ‘Plan Jericho,’ the RAAF considers elevating itself to a ‘Fifth Generation Air Force’, enhancing today’s platforms through advanced man-unmanned teaming, to augment the human capabilities in a future combat mission. ‘Our concept of edge processing will allow us to fully develop the capabilities of each of those linear paths, to intercept and fuse into the future,’ RAAF Air Vice-Marshal Gavin Turnbull told The Strategist in an interview published today. ‘They can do highly advanced and highly effective processing on each of those platforms while communicating with each other about the information they’re gathering. And then, from the edge of that battlespace, we transmit back knowledge—not reams and reams of something that needs to be processed by lots of humans or computers.’
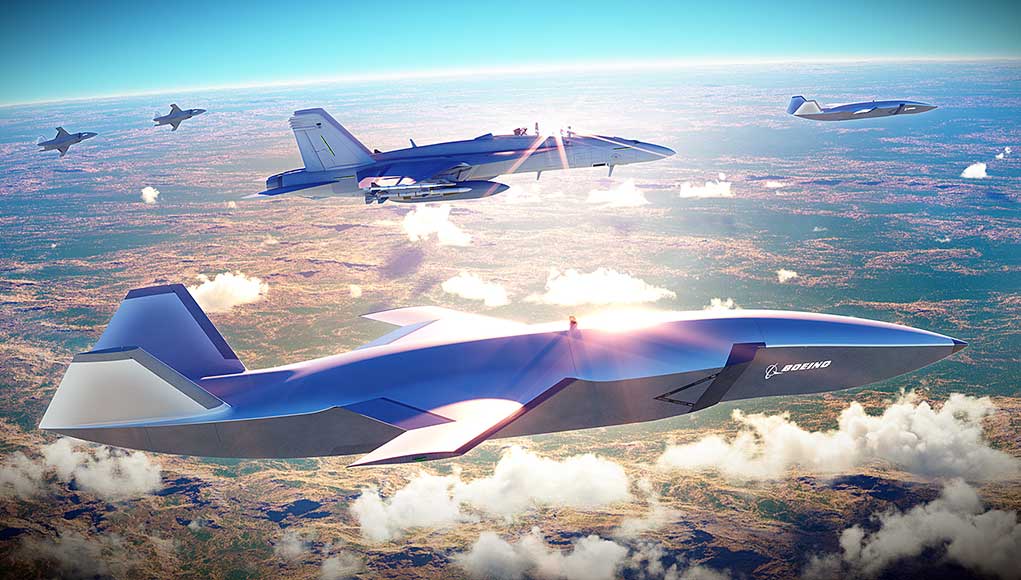

Plan Jericho will exploit advanced technological solutions such as manned-unmanned teaming, artificial intelligence and machine learning to make up for the RAAF relatively small conventional force.
The Air Force’s augmented intelligence approach combines the freedom and agility of the human with the power of machines creating a ‘human edge in the information age.’ Augmented intelligence is the central concept in shifting the RAAF from one that uses people to operate machines and cooperate with other people, to a force in which people and machines operate together.
According to RAAF documents Plan Jericho exploits autonomous processing to infuse machine processing power throughout the force to enhance decision-making quality and tempo, and advanced sensors to detect and track challenging targets in difficult environments. It will employ a ‘combat cloud’ to optimize decision and action tempo, by integrating the fifth-generation force and enabling resources from across the force to be distributed and applied as a unified whole. Finally, it harnesses human-machine augmentation to optimize individual and collective human and human-machine performance within a proactively developed ethical, moral, and legal framework.
‘We’re understanding that the force mix we’ll have in the future will overwhelm us with the amount of information that we can produce, and we need to get much smarter about how we deal with that.’ According to Turnbull, a future force will evolve based on requirements, but the human will always be there somewhere. ‘The air campaign in Iraq and Syria has demonstrated that human judgment is still crucial in terms of issues such as when to bomb and when not to bomb,’ Turnbull says, adding that the key is to put the humans in a place where they have the maximum effect while facing minimal risk. ‘So into the future, you have to give consideration to what the force mix looks like between manned and unmanned combat entities. And there will always be a synergy in mixing them in some way.’

The Boeing Airpower Teaming System will provide fighter-like performance in a small unmanned platform measure 11.7 m’ (38 feet) long platform, capable of flying missions beyond 2,000 nautical miles. The aircraft will have a modular design allowing ‘snap-in’ payloads and rapid reconfiguration capability. Sensor packages onboard to support intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance missions and electronic warfare. It will use artificial intelligence to fly independently or in support of manned aircraft while maintaining a safe distance between other aircraft. The aircraft will have a level of autonomy to meet specific mission phases. Otherwise, it will be controlled via ground station, or from other aircraft.
The aircraft is developed and built in Australia where it will benefit from the vast, empty desert ranges and available airspace for experimentation. It is intended for domestic use and export, that will be easier outside the US complex foreign military sales system.
“This aircraft is a historic endeavor for Boeing. Not only is it developed outside the United States, but it is also designed so that our global customers can integrate local content to meet their country-specific requirements,” said Marc Allen, president, Boeing International. “The Boeing Airpower Teaming System will provide a disruptive advantage for allied forces’ manned/unmanned missions,” added Kristin Robertson, vice president, and general manager of Boeing Autonomous Systems. “With its ability to reconfigure quickly and perform different types of missions in tandem with other aircraft, our newest addition to Boeing’s portfolio will truly be a force multiplier as it protects and projects air power.”
According to Hon Steven Ciobo Minister for Defence Industry, Boeing will seek to team with large, medium and small Australian businesses and partner with research organizations, including universities and the Defence Science and Technology Group.
























