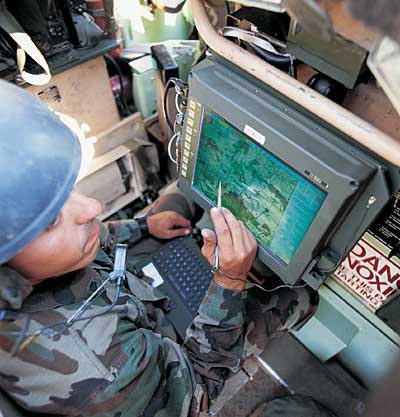
UK’s Land Digitization Program is an central enabler for the British Army’s Network Enabled Capability (NEC) initiative. The £1.9 billion Bowman program comprises a new family of radios, computers and C3 applications, which will establish the communications and computing infrastructure for existing and future forces. Bowman digital radios are replacing the aging Clansman range of analog radios, in service since the 1970s. As a data-capable radio. Bowman systems will support communications between headquarters, replacing part of the Ptarmigan trunk system currently in service.
The new radios provide tactical, secure voice communications, and data messaging and are embedded with GPS receivers to provide location information for “Blue Force Tracking” systems.
Bowman systems entered service in 2004 and are expected to remain in service at least through 2026. Some 46,500 radios and 26,000 computers will be procured under the multiyear program, fitted to 20,000 military vehicles, 156 ships and 276 aircraft.
The VHF elements are based on the ITT’s SINCGARS technology developed for the US military. Bowman is also integrating the Harris HF radios Both systems are embedded with UK specific encryption technology. Both VHF and HF radios are supporting secured voice and data communications. VHF sets use fixed or frequency hopping regimes, while HF supports advanced Automatic Link Establishment (ALE) and Free Channel Search (FCS). DRS Tactical Systems is providing four variants of its Scorpion notebook computers for the Bowman program, including vehicle mounted and dismountable terminals. AEA Battery Systems is supplying rechargeable li-ion batteries and chargers for the dismountable and man-portable sets.
Bowman networks will automatically establish a “tactical Internet” network to support IP based communications over HF, VHF and High Capacity Radio networks. ALl communications devices will be able to communicate over Local Area Sub System (LAS), connecting individual vehicles fitted with the Vehicle Internal Distribution System (VIDS) set to receipt of radio nets from designated, similarly equipped vehicles.
 The first increment of the current digitization program started in 2002. Designated DS1, it was fielded at Brigade headquarters level, in support the Battle group HQ and HQ Allied Rapid Reaction Corps. The current system encompass a battlefield management system generating situational awareness information locally and between HQs. Another feature is the personnel tracking application, aggregating information gathered from personnel role radios allocated to all mounted and dismounted combat elements operating under the battle group command. This application is being used as the OPLOC tracking system in Kosovo, Afghanistan and Iraq. DS1 is scheduled to transition to full Bowman configuration by 2006. In April 2005, 12 Mechanized Brigade deployed to Iraq with a core Bowman capability alongside some existing capability. Another milestone for the program was in July 2005 as the systems were fielded with the Scots Dragoon Guards battle group, taking part in Exercise Medicine Man at the British Army Training Unit Suffield (BATUS).
The first increment of the current digitization program started in 2002. Designated DS1, it was fielded at Brigade headquarters level, in support the Battle group HQ and HQ Allied Rapid Reaction Corps. The current system encompass a battlefield management system generating situational awareness information locally and between HQs. Another feature is the personnel tracking application, aggregating information gathered from personnel role radios allocated to all mounted and dismounted combat elements operating under the battle group command. This application is being used as the OPLOC tracking system in Kosovo, Afghanistan and Iraq. DS1 is scheduled to transition to full Bowman configuration by 2006. In April 2005, 12 Mechanized Brigade deployed to Iraq with a core Bowman capability alongside some existing capability. Another milestone for the program was in July 2005 as the systems were fielded with the Scots Dragoon Guards battle group, taking part in Exercise Medicine Man at the British Army Training Unit Suffield (BATUS).
Apart from the various radios, the program will integrate new C4 application systems, such as the Common Battlefield Applications Toolset (ComBAT), and Platform Battlefield Information Systems Application (P-BISA), collectively known as CIP. Personal Role Radio (PRR) will also integrate with the Bowman program in its future course. One such application is the integration of Bowman with vetronics under the Challenger 2 main battle tank Digitization program.
The initial CBM(L) capability will be introduced with Bowman to provide a core battle management system. It will enable the battlefield information systems being developed for armored fighting vehicles, artillery fire control, ground based air defense, to exploit Bowman’s data messaging capability concurrently, and insure effective interoperability issues with our allies.
The Royal Netherlands Navy is buying Bowman systems worth of EUR94 million from General Dynamics UK for the Royal Dutch Marines, under the Dutch Integrated Marines Communications and Information System (NIMCIS). This is the first export contract for the Bowman C4I system. The systems are expected to be installed on tactical vehicles such as the BAE Systems Land Systems Hägglunds BvS 10 armored all-terrain tracked vehicles recently ordered for the forces.