Command and Control : MDM provided an interesting insight into the advanced command and control systems developed for and by the USMC. The centerpiece of the C4 display was provided by General Dynamics C4 Systems, demonstrating the future Command Operations Center (COC) for the Marine Air Ground Task Force (MAGTF) Command and Control center, as well as the latest communications, information processing and distribution applications. Dismounted C2 systems and Command and Control On-the-Move (COTM) were demonstrated by a number of exhibitors. Another facet of C4ISR discussed here was image intelligence – different providers demonstrated innovative applications, including unattended ground sensors, GPS cameras operated by patrols, elevated mast-mounted payloads etc.
The Marine Combat Operations Center (COC)
Numerous COC are employed by US Marine Corps Marine Expeditionary Force (MEF) units deployed in Iraq and more systems are being delivered to support other units operating worldwide. Of 271 systems ordered, GD has already delivered 102. The COC is designed for rapid deployment, using trailers mounting a power and environmental support unit, with another trailer packing all servers, routers and other communications and networking support. Outside at the main display at the exhibition grounds at Quantico, a large tent accommodated a typical Combat Operations Center (COC) was erected. The display provided a unique insight into the Marine Corps’ current and future command and control elements comprising the Marine Air Ground Task Force (MAGTF) Command and Control center.
Networking inside the COC utilized high speed Ethernet or wireless networks, using the Secure Wireless Infrastructure System (SWIS) developed by General Dynamics (GD) Information Technology. SWIS operates Secure 802.11 wireless LAN solution to extend wireless connectivity to high security (NSA Type 1 encryption) applications, including field deployable military command and control. Further exploiting this secure wireless connectivity, GD is offering a number of military oriented computing devices supporting
internet, email, chat, phone video streaming and conferencing. Typical devices include the GoBook VR mini laptop, GoBook tablet PC and pocket PC devices.
GD C4S also demonstrated its latest digital radio switching system at the COC. The Distributed Scalable AccessNet (DSAN) a Voice over IP (VOIP) softswitch facilitating intercom support and seamless connectivity through network-connected radios. DSAN can be implemented on stand-alone access points or as an overlay on standard workstations, enabling users equipped with DSAN applications or monitors to control multiple radios transceivers, conduct phone conversations and conferences (supporting the H.323 industry standard) contacting local users on the intercom, from a single
user-interface.
 The live display also provided an insight into the company’s field deployable command and control solutions. A typical application for the COC is the Marine Air Ground Task Force Command and Control (MAGTF-C2) center. Within the MAGTF-C2 environment, information is integrated, aggregated and distributed from disparate C2 and ISR systems to users at all echelons – ranging from the command center to the individual soldier. The MAGTF-C2 concept allows for visualization of a complete air/ground picture, improving Marine planning and execution, while supporting joint forces interoperability. The system utilized General Dynamics C4Systems’ common viewer, facilitating three-dimensional air/ground views and two-dimensional collaborative environment developed for the US Army style ‘Command Post of the Future” (CPOF) system. CPOF applications will be introduced in the standard COC in upcoming months, and are expected to substatianlly improve work efficiency at the COC through collaboration and maintenance of constantly updated COP. Such applications could also be shared, to a limited extent, with command and control of combat elements on the move, considered for deployment in the upcoming months.
The live display also provided an insight into the company’s field deployable command and control solutions. A typical application for the COC is the Marine Air Ground Task Force Command and Control (MAGTF-C2) center. Within the MAGTF-C2 environment, information is integrated, aggregated and distributed from disparate C2 and ISR systems to users at all echelons – ranging from the command center to the individual soldier. The MAGTF-C2 concept allows for visualization of a complete air/ground picture, improving Marine planning and execution, while supporting joint forces interoperability. The system utilized General Dynamics C4Systems’ common viewer, facilitating three-dimensional air/ground views and two-dimensional collaborative environment developed for the US Army style ‘Command Post of the Future” (CPOF) system. CPOF applications will be introduced in the standard COC in upcoming months, and are expected to substatianlly improve work efficiency at the COC through collaboration and maintenance of constantly updated COP. Such applications could also be shared, to a limited extent, with command and control of combat elements on the move, considered for deployment in the upcoming months.
In a different display Naval Sea Systems Command (NAVSEA) and the Office of Naval Research introduced a collective display of their Joint Battlespace Viewerm (JBV) developmental effort, a 3D visualization program providing a whole-earth representation on a modern PC. Users can view any spot on the Globe, with image resolution of up to 10 cm. These images can be integrated with 3D models and layered information. The present demonstration included live video from UAV embedded in real-time onto satellite imagery. JBV is already used by the First Marine expeditionary Force (I MEF) in Iraq.
SelectFocus Tools
In another display associated with the future combat operations center, GD C4Systems outlined the benefits of advanced image processing applications for Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) support, using the company’s SelectFocus applications. These include the SelectFocus Mosaic video mosaicking application, creating a ‘panoramic’ image in near-real-time from pre-stored or live video sequence. Through processing, SelectFocus compensates for camera translation, rotation and illumination variations generating a coherent image. The system’s output is translated into standard image format, hence dramatically reducing the amount of data (or bandwidth used).
A different application, called SelecFocus Image conducts smart compression of high resolution images, facilitating image distribution over ultra-low-bandwidth communications channels (suitable for basic Iridium channels bandwidth of 2.4 kbps). This application uses a modified JPEG 2000 image coder compressing images with multiple Regions of Interest (ROI). These sections are defined by the analyst and preserved with optimal detail and resolution throughout the compression process. To ease collaboration between analysts the system integrates IP-based transmit and receive functionality for one-touch image transmission and text messaging to any
networked user. SelectFocus applications are being considered for integration in the COC environment by 2008.
Other command and control elements were highlighted by Northrop Grumman. The
company is offering Windows-based applications designed for standard PCs, enabling users at different echelons to create and share a Common Operating Picture (COP) across multiple workstations, in stationary, moving and dismounted combat environments and among multiple agencies. The company developed the Command and Control PC (C2PC) platform enabling USMC users to create and share tactical information and integrate it with information accessed through COP from the Global Command and Control System (GCCS) server. A subset of the system is implemented on Windows Mobile, the Command and Control Compact Edition (C2CE). This Personal Digital Assistant (PDA)- based device enables mobile users to share and edit the COP, while supporting local functionality such as reporting users position, location, navigation and situational awareness.
Lockheed Martin is developing a fleet of mobile operations centers called C2AMMO, focused on enabling C2OTM for a variety of missions and users, including military, federal and commercial applications. The vehicle can support commanders at all echelons, facilitating network access, sharing a broad common operating picture, or used as a self-sustained network node, support local operations and small units, for example, a platoon leader’s command vehicle supporting dismounted troops with local communications, cross-unit collaboration and access to higher echelon network.
The system is integrated in a Hummer H1 testbed, integrating computing, tactical radio,
wireless data (including 802.11 wi-fi, 802.16 WiMAX and secured 802.11 WLAN) and satellite communications systems. The vehicle carries low-profile on-the-move SATCOM terminals operating in the Ku and L band. The commander’s workstation consists of a detachable tablet PC, which automatically synchronizes with the network when dismounted to ensure operational continuity. Testing and evaluation of C2AMMO systems began in 2006, and in 2007 the system already participated in several joint-forces exercises including Joint Fires, and the Air Assault Expeditionary Force exercise
planned for fall 2007. Different C2 On-The-Move application integrated in a HMMWV was demonstrated at MDM 07 by DRS.
 500SE-M GPS Enabled Tactical Camera
500SE-M GPS Enabled Tactical Camera
In June 2007 Defense Update covered the USMC use of compact digital cameras on patrols to collect and support generating HUMINT and IMINT intelligence through routine patrols. At MDM 07 Geo Tactical Solutions introduced a GPS embedded camera offering many details making reconnaissance and intelligence collection and report preparation a simple and intuitive process. Offering a complete geo-tactical solution, the 500SE-M GPS camera comes in dust, drop and a waterproof impact resistant package with a large 2.5″ screen showing the images taken with superimposed grid position. This information is recorded and stored with every picture taken. After the mission, images are downloaded and processed on a laptop. The report wizard coming with the package, tracks all images plotting the mission’s trail, from GPS track-log ‘breadcrumb’. Each image automatically provides a hyperlink viewed on Google Earth or the military equivalent FalconView. The selected images are imprinted with relevant metadata and embedded into reports.
comes in dust, drop and a waterproof impact resistant package with a large 2.5″ screen showing the images taken with superimposed grid position. This information is recorded and stored with every picture taken. After the mission, images are downloaded and processed on a laptop. The report wizard coming with the package, tracks all images plotting the mission’s trail, from GPS track-log ‘breadcrumb’. Each image automatically provides a hyperlink viewed on Google Earth or the military equivalent FalconView. The selected images are imprinted with relevant metadata and embedded into reports.
Other topics covered in this review:
 Among the aviation programs promoted at the 2007 Modern Day Marine expo were the new CH-53K Sikorsky, and FireScout Vertical Takeoff and Landing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (VT-UAV) from Northrop Grumman, which was presented for the first time as a weaponized platform, loaded with a quad launcher carrying Viper Strike weapons. Models of Sikorsky’s future helicopter versions based on the X2 coaxial rotor propulsion system included a VT-UAV, an attack helicopter which could become a future successor for the AH-1W Cobra and an assault helicopter platform, a potential successor to the UH-60 helicopter.
Among the aviation programs promoted at the 2007 Modern Day Marine expo were the new CH-53K Sikorsky, and FireScout Vertical Takeoff and Landing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (VT-UAV) from Northrop Grumman, which was presented for the first time as a weaponized platform, loaded with a quad launcher carrying Viper Strike weapons. Models of Sikorsky’s future helicopter versions based on the X2 coaxial rotor propulsion system included a VT-UAV, an attack helicopter which could become a future successor for the AH-1W Cobra and an assault helicopter platform, a potential successor to the UH-60 helicopter. 
 A new concept from Boeing highlighted a future pulsejet powered hevy lift VTOL platform, capable of carrying medium armored vehicles weighing up to 30 tons. Advanced PulseJet Vertical Lifters Boeing is studying a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft that could lift heavy payloads of up to 30 tons, utilizing innovative ‘advanced pulsejet’ propulsion. While basic pulsejet is well understood (it was implemented in the 1940s with the V-1 flying bombs) Boeing patented this concept for vertical takeoff and lending applications, combining separate axial and vertical propulsion sources. The vertical propulsion source includes pulsejet engines located in separate augmentor bays fitted with having apertured walls to equalize pulsejet thrust. Embedded within the aircraft structure, multiple PulseJet engines ‘banks’ will be used to control the aircraft attitude, ascent and pitch and support the structural loads. By using separate axial and vertical thrust sources and pulsejet engines for vertical thrust, aircraft speed, payload and operating range are improved while a loss of one or more lift engines is mitigated by the remaining engines offering redundant and resilient VTOL capability over any terrain. According to Boeing, typical operating distance of such aircraft could be in the 500 – 1,500 nm range, cruising at a speed of 300 – 450 mph. Boeing considers various platforms utilizing the novel VTOL propulsion, including manned aircraft lifting payloads of 20 – 30 tons, and small manned or unmanned platforms, lifting payloads of 1,500 – 10,000 lbs (0.75 – 5 tons).
A new concept from Boeing highlighted a future pulsejet powered hevy lift VTOL platform, capable of carrying medium armored vehicles weighing up to 30 tons. Advanced PulseJet Vertical Lifters Boeing is studying a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft that could lift heavy payloads of up to 30 tons, utilizing innovative ‘advanced pulsejet’ propulsion. While basic pulsejet is well understood (it was implemented in the 1940s with the V-1 flying bombs) Boeing patented this concept for vertical takeoff and lending applications, combining separate axial and vertical propulsion sources. The vertical propulsion source includes pulsejet engines located in separate augmentor bays fitted with having apertured walls to equalize pulsejet thrust. Embedded within the aircraft structure, multiple PulseJet engines ‘banks’ will be used to control the aircraft attitude, ascent and pitch and support the structural loads. By using separate axial and vertical thrust sources and pulsejet engines for vertical thrust, aircraft speed, payload and operating range are improved while a loss of one or more lift engines is mitigated by the remaining engines offering redundant and resilient VTOL capability over any terrain. According to Boeing, typical operating distance of such aircraft could be in the 500 – 1,500 nm range, cruising at a speed of 300 – 450 mph. Boeing considers various platforms utilizing the novel VTOL propulsion, including manned aircraft lifting payloads of 20 – 30 tons, and small manned or unmanned platforms, lifting payloads of 1,500 – 10,000 lbs (0.75 – 5 tons). X2 VT-UAV
X2 VT-UAV
 Boomerang III Acoustic Gunshot detector
Boomerang III Acoustic Gunshot detector MPSVS from EDO
MPSVS from EDO ODR HV from ODF Optronics
ODR HV from ODF Optronics

 VIPeR from Elbit Systems
VIPeR from Elbit Systems For example, the small RMP 50 weighs only 70 lbs (32 kg), but has a maximum payload capacity of 75 lb (34 kg). The RMP 400 has even better ratio – at a curb weight of 240 lbs (109kg) it can carry 400 lbs of payload (181 kg). These robots are designed to operate at a range of 10 – 15 miles (16-24 km) at an off-road speed of up to 18 mph (29 km/h). The RMP robot is powered by 48 NiMh batteries while the larger models use multiple Saphion lithium-ion battery packs. Both versions require battery recharging for 8 – 10 hours. Although these are well adapted to harsh field conditions, the batteries temperature tolerance limit their operational use from -10 to +50 C. This range could be expanded by using different batteries, which could be more suitable for sub-freezing conditions. (Some Saphion cells operate as low as -20C).
For example, the small RMP 50 weighs only 70 lbs (32 kg), but has a maximum payload capacity of 75 lb (34 kg). The RMP 400 has even better ratio – at a curb weight of 240 lbs (109kg) it can carry 400 lbs of payload (181 kg). These robots are designed to operate at a range of 10 – 15 miles (16-24 km) at an off-road speed of up to 18 mph (29 km/h). The RMP robot is powered by 48 NiMh batteries while the larger models use multiple Saphion lithium-ion battery packs. Both versions require battery recharging for 8 – 10 hours. Although these are well adapted to harsh field conditions, the batteries temperature tolerance limit their operational use from -10 to +50 C. This range could be expanded by using different batteries, which could be more suitable for sub-freezing conditions. (Some Saphion cells operate as low as -20C). The live display also provided an insight into the company’s field deployable command and control solutions. A typical application for the COC is the Marine Air Ground Task Force Command and Control (MAGTF-C2) center. Within the MAGTF-C2 environment, information is integrated, aggregated and distributed from disparate C2 and ISR systems to users at all echelons – ranging from the command center to the individual soldier. The MAGTF-C2 concept allows for visualization of a complete air/ground picture, improving Marine planning and execution, while supporting joint forces interoperability. The system utilized General Dynamics C4Systems’ common viewer, facilitating three-dimensional air/ground views and two-dimensional collaborative environment developed for the US Army style ‘Command Post of the Future” (CPOF) system. CPOF applications will be introduced in the standard COC in upcoming months, and are expected to substatianlly improve work efficiency at the COC through collaboration and maintenance of constantly updated COP. Such applications could also be shared, to a limited extent, with command and control of combat elements on the move, considered for deployment in the upcoming months.
The live display also provided an insight into the company’s field deployable command and control solutions. A typical application for the COC is the Marine Air Ground Task Force Command and Control (MAGTF-C2) center. Within the MAGTF-C2 environment, information is integrated, aggregated and distributed from disparate C2 and ISR systems to users at all echelons – ranging from the command center to the individual soldier. The MAGTF-C2 concept allows for visualization of a complete air/ground picture, improving Marine planning and execution, while supporting joint forces interoperability. The system utilized General Dynamics C4Systems’ common viewer, facilitating three-dimensional air/ground views and two-dimensional collaborative environment developed for the US Army style ‘Command Post of the Future” (CPOF) system. CPOF applications will be introduced in the standard COC in upcoming months, and are expected to substatianlly improve work efficiency at the COC through collaboration and maintenance of constantly updated COP. Such applications could also be shared, to a limited extent, with command and control of combat elements on the move, considered for deployment in the upcoming months. 500SE-M GPS Enabled Tactical Camera
500SE-M GPS Enabled Tactical Camera comes in dust, drop and a waterproof impact resistant package with a large 2.5″ screen showing the images taken with superimposed grid position. This information is recorded and stored with every picture taken. After the mission, images are downloaded and processed on a laptop. The report wizard coming with the package, tracks all images plotting the mission’s trail, from GPS track-log ‘breadcrumb’. Each image automatically provides a hyperlink viewed on Google Earth or the military equivalent FalconView. The selected images are imprinted with relevant metadata and embedded into reports.
comes in dust, drop and a waterproof impact resistant package with a large 2.5″ screen showing the images taken with superimposed grid position. This information is recorded and stored with every picture taken. After the mission, images are downloaded and processed on a laptop. The report wizard coming with the package, tracks all images plotting the mission’s trail, from GPS track-log ‘breadcrumb’. Each image automatically provides a hyperlink viewed on Google Earth or the military equivalent FalconView. The selected images are imprinted with relevant metadata and embedded into reports.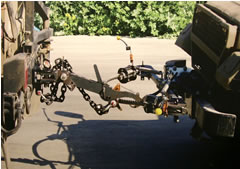
 Recovery under fire (RUF) system designed by the Israeli automotive accessories specialist Tal&Hadas enables vehicle recovery during combat operations, specifically in dense urban terrain. The RUF enables tow vehicles to recover RUF equipped disabled vehicles without manual support, thus eliminating the need for warfighters to leave the protected vehicles and expose themselves to hostile fire. The RUF kit can be mounted on a vehicle within fire minutes, without
Recovery under fire (RUF) system designed by the Israeli automotive accessories specialist Tal&Hadas enables vehicle recovery during combat operations, specifically in dense urban terrain. The RUF enables tow vehicles to recover RUF equipped disabled vehicles without manual support, thus eliminating the need for warfighters to leave the protected vehicles and expose themselves to hostile fire. The RUF kit can be mounted on a vehicle within fire minutes, without special tools. During the recovery the towing vehicle can approach the disabled vehicle at wide angles, and maneuver effectively in narrow streets. Tal&Hadas are currently offering the system for the HMMWV, Zeev (Ford 150 based armored vehicle), the David armored Defender, and armored Storm (Jeep based) light vehicles. A heavier version designed for the MRAP will be completed by December 2007.
special tools. During the recovery the towing vehicle can approach the disabled vehicle at wide angles, and maneuver effectively in narrow streets. Tal&Hadas are currently offering the system for the HMMWV, Zeev (Ford 150 based armored vehicle), the David armored Defender, and armored Storm (Jeep based) light vehicles. A heavier version designed for the MRAP will be completed by December 2007.
 Another essential accessory is the electrical door assist mechanism, designed to operate the u-armored door weighing over 400 kg (applied with FRAG 6 kit). This mechanism, introduced by BAE System’s mobility and protection systems (formerly Armor Holdings) can operate the door on level ground or up to 17 deg slope (30%), opening or closing it within five seconds. Another system that became too heavy for manual operation is the gunner protection kit. An electric traverse kit moves the turret at up to 6 rpm, under all inclinations, therefore improving the gunner’s situational awareness and response even under difficult conditions. The traverse mechanism is powered by rechargeable batteries offering independent operation regardless of the vehicle’s condition. BAE Systems also proposes an improved air conditioning and integrated cooling systems,
Another essential accessory is the electrical door assist mechanism, designed to operate the u-armored door weighing over 400 kg (applied with FRAG 6 kit). This mechanism, introduced by BAE System’s mobility and protection systems (formerly Armor Holdings) can operate the door on level ground or up to 17 deg slope (30%), opening or closing it within five seconds. Another system that became too heavy for manual operation is the gunner protection kit. An electric traverse kit moves the turret at up to 6 rpm, under all inclinations, therefore improving the gunner’s situational awareness and response even under difficult conditions. The traverse mechanism is powered by rechargeable batteries offering independent operation regardless of the vehicle’s condition. BAE Systems also proposes an improved air conditioning and integrated cooling systems,  designed to reduce the temperature in the simmering cabin to bearable 82 F (29 C) and further reduce the crew’s temperature to 60-70 F (15-21C), utilizing water circulating cooling vests.
designed to reduce the temperature in the simmering cabin to bearable 82 F (29 C) and further reduce the crew’s temperature to 60-70 F (15-21C), utilizing water circulating cooling vests.
 Several companies presented blast protected seat technologies at Modern Day Marine and AUSA 07. For example, ArmorWorks displayed two types of blast attenuating seats of the ShockRide series. The company offers individual, folding high-back troop seats as well as driver and commander’s seats with rigid base. Both types are fitted with blast attenuating straps and frame. ArmorWorks also designed bench seats offering improved protection as well as a gunner’s post mounted seat which offers four point restraint harness and flip-up mechanism, improving comfort, access and survivability.
Several companies presented blast protected seat technologies at Modern Day Marine and AUSA 07. For example, ArmorWorks displayed two types of blast attenuating seats of the ShockRide series. The company offers individual, folding high-back troop seats as well as driver and commander’s seats with rigid base. Both types are fitted with blast attenuating straps and frame. ArmorWorks also designed bench seats offering improved protection as well as a gunner’s post mounted seat which offers four point restraint harness and flip-up mechanism, improving comfort, access and survivability. BAE Systems also produces different designs for mine blast, driver/passenger and troop seats. These seats can absorb energy pulses exceeding 400 G by employing vertical, fixed load wire benders providing five inches of downward stroke. (9″ or 23 cm in the troop seats). The troop seats use hinged pan for stowage when not in use. The energy absorbing system uses four point restraint, integral headrest and shoulder cushion.
BAE Systems also produces different designs for mine blast, driver/passenger and troop seats. These seats can absorb energy pulses exceeding 400 G by employing vertical, fixed load wire benders providing five inches of downward stroke. (9″ or 23 cm in the troop seats). The troop seats use hinged pan for stowage when not in use. The energy absorbing system uses four point restraint, integral headrest and shoulder cushion. Another type of blast protected seat is produced by Plasan Sasa and installed in the
Another type of blast protected seat is produced by Plasan Sasa and installed in the 
 Another light tactical vehicle is proposed by the armored tactical vehicle (ATV) manufacturer Polaris Defense. The company offers the Ultra Light Tactical Vehicle with a 40 hp engine powered by gas or JP8 fuel. This vehicle configured to carry a crew of four seated side by side, is rated for payload capacity or towing of up to 1,500 lbs. The rear flat bed can be configured to carry specialist equipment such as combat recon, surveillance, sensors, or anti-tank missiles (Javelin), ammunition, supplies and litter racks for casualty evacuation.
Another light tactical vehicle is proposed by the armored tactical vehicle (ATV) manufacturer Polaris Defense. The company offers the Ultra Light Tactical Vehicle with a 40 hp engine powered by gas or JP8 fuel. This vehicle configured to carry a crew of four seated side by side, is rated for payload capacity or towing of up to 1,500 lbs. The rear flat bed can be configured to carry specialist equipment such as combat recon, surveillance, sensors, or anti-tank missiles (Javelin), ammunition, supplies and litter racks for casualty evacuation. Raytheon’s entry into the light strike vehicle field is also based on an off-road racing and extreme rock crawler derivative. But Raytheon decided to take innovation one step further introducing a powerful hybrid electric drive system, with the all-terrain vehicle called Hy-DRA (Hybrid Defense Recon Assault vehicle). The vehicle uses a diesel engine to power a generator, driving four in-hub motors for the four wheel drive. While moving in ‘stealth mode’ HyDRA can achieve speed up to 35 mph. Otherwise, hybrid powered (diesel and electrical) sustained speed top 125 mph. The hybrid electric drive offers good fuel efficiency of about 35 mpg. The vehicle can carry an M2 (0.50 Cal) or Mk-19 or minigun on a turret mount and an M240/249 on a swing arm. The vehicle has a curb weight of 2,400 lbs. carrying a crew of three, and a complement of weapons and supplies, HyDRA is internally transported in a CV-22 Osprey, CH/MH-53, CH/MH-47 and C-130. It is capable of towing 1.5 tons or carrying heavy loads of up to half a ton. Besides its role as primary propulsion for the vehicle, the four 40hp motors can also perform as generators, providing 30 kW of power for external use.
Raytheon’s entry into the light strike vehicle field is also based on an off-road racing and extreme rock crawler derivative. But Raytheon decided to take innovation one step further introducing a powerful hybrid electric drive system, with the all-terrain vehicle called Hy-DRA (Hybrid Defense Recon Assault vehicle). The vehicle uses a diesel engine to power a generator, driving four in-hub motors for the four wheel drive. While moving in ‘stealth mode’ HyDRA can achieve speed up to 35 mph. Otherwise, hybrid powered (diesel and electrical) sustained speed top 125 mph. The hybrid electric drive offers good fuel efficiency of about 35 mpg. The vehicle can carry an M2 (0.50 Cal) or Mk-19 or minigun on a turret mount and an M240/249 on a swing arm. The vehicle has a curb weight of 2,400 lbs. carrying a crew of three, and a complement of weapons and supplies, HyDRA is internally transported in a CV-22 Osprey, CH/MH-53, CH/MH-47 and C-130. It is capable of towing 1.5 tons or carrying heavy loads of up to half a ton. Besides its role as primary propulsion for the vehicle, the four 40hp motors can also perform as generators, providing 30 kW of power for external use.
 GDLS and AM General invested over $10 million for risk reduction development and maturation of this vehicle and its innovative In-Hub Hybrid Electric Drive system. AGMV has unique protection attributes, combining a hexagon shaped armored capsule for mine protection while optimizing also for side blast deflection and small-arms protection. At a gross vehicle weight of 14,000 – 16,000 lbs with integral A kit armor, protecting against small arms, mines, IEDs and blast, the new vehicle can carry payloads of up to 5,000 lbs and be air transportable in C-130, CH-53 and CH-47.
GDLS and AM General invested over $10 million for risk reduction development and maturation of this vehicle and its innovative In-Hub Hybrid Electric Drive system. AGMV has unique protection attributes, combining a hexagon shaped armored capsule for mine protection while optimizing also for side blast deflection and small-arms protection. At a gross vehicle weight of 14,000 – 16,000 lbs with integral A kit armor, protecting against small arms, mines, IEDs and blast, the new vehicle can carry payloads of up to 5,000 lbs and be air transportable in C-130, CH-53 and CH-47.
 Light Utility Hybrid (LUV) from MillenWorks
Light Utility Hybrid (LUV) from MillenWorks



 UT-25-30mm Unmanned Turret Weapon Station
UT-25-30mm Unmanned Turret Weapon Station ILWS (ORCWS 7.62)
ILWS (ORCWS 7.62) Small Caliber UltraLight (SCUL)
Small Caliber UltraLight (SCUL)

 situational awareness and mission capability. The increased visibility and lightweight design minimizes eye and neck strain, common problems for pilots managing the demands of longer missions and increasingly complex rules of engagement. Additionally, the decreased size and weight of the display allows the pilot complete freedom of movement within the cockpit.
situational awareness and mission capability. The increased visibility and lightweight design minimizes eye and neck strain, common problems for pilots managing the demands of longer missions and increasingly complex rules of engagement. Additionally, the decreased size and weight of the display allows the pilot complete freedom of movement within the cockpit.
 A160T
A160T 18 consecutive hours with a 300-pound payload. At AUSA Boeing displayed a model of an armed version of the A160T, loaded with an EO payload and eight Hellfire type missiles. The vehicle has a length of 35 feet and a 36-foot rotor diameter.
18 consecutive hours with a 300-pound payload. At AUSA Boeing displayed a model of an armed version of the A160T, loaded with an EO payload and eight Hellfire type missiles. The vehicle has a length of 35 feet and a 36-foot rotor diameter. nd improved braking. An EOD MAARS will be equipped with a new manipulator arm having a nominal 100 lb lift capability. The arm can quickly replace the turret mounted M240B weapon, literally transforming from a remote weapons platform to an Improvised Explosive Device (IED).
nd improved braking. An EOD MAARS will be equipped with a new manipulator arm having a nominal 100 lb lift capability. The arm can quickly replace the turret mounted M240B weapon, literally transforming from a remote weapons platform to an Improvised Explosive Device (IED).











